Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (12): 2458-2465.doi: 10.12307/2025.381
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bioinformatics analysis and functional verification of hsa-miR-3202 in osteoarthritic chondrocytes
Zhang Jiaqi, Liu Yanhong, Liang Huiting, Zhou Jingjing, Wang Yawen, Xu Jingyu, Li Yushuang, Lei Lijian, Hu Xiaoqin
- Department of Epidemiology, School of Public Health, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2024-03-30Accepted:2024-06-03Online:2025-04-28Published:2024-09-09 -
Contact:Hu Xiaoqin, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Epidemiology, School of Public Health, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Zhang Jiaqi, Master candidate, Department of Epidemiology, School of Public Health, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81803326 (to HXQ); Shanxi Huajin Orthopaedic Public Welfare Foundation, Nos. 20211120 (to LHT) and 20221116 (to ZJJ); Shanxi Applied Basic Research Program, No. 201801D221265 (to HXQ); Teaching Reform Innovation Program for Higher Education Institutions in Shanxi Province, No. J20220372 (to HXQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Jiaqi, Liu Yanhong, Liang Huiting, Zhou Jingjing, Wang Yawen, Xu Jingyu, Li Yushuang, Lei Lijian, Hu Xiaoqin. Bioinformatics analysis and functional verification of hsa-miR-3202 in osteoarthritic chondrocytes[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(12): 2458-2465.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
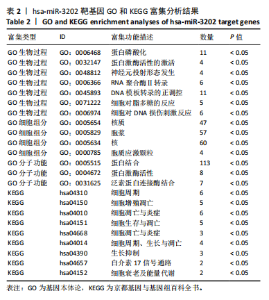
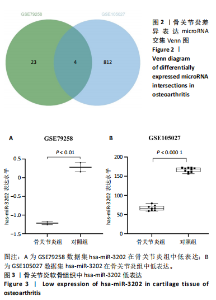
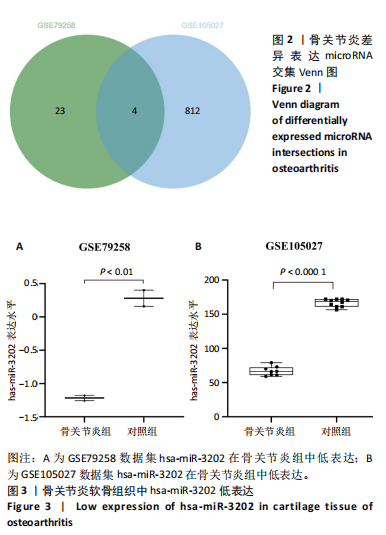
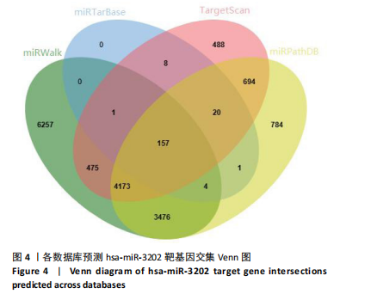
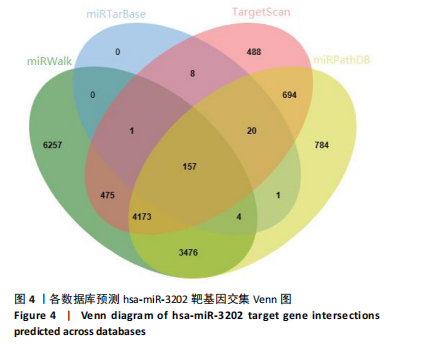
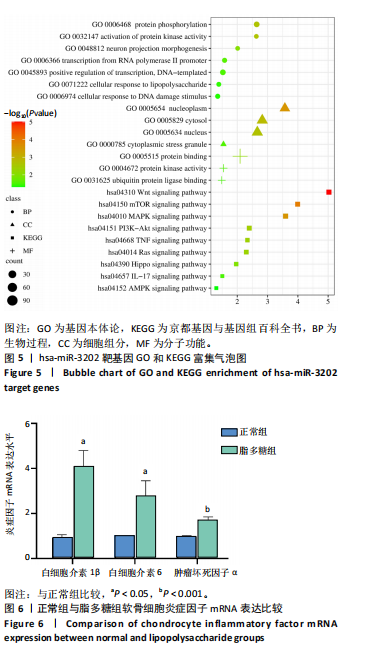
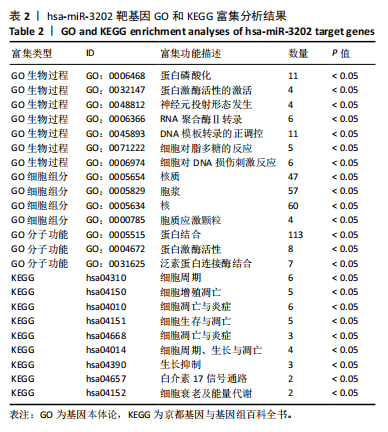
2.1 骨关节炎差异表达microRNA GSE79258和GSE105027 microRNA微阵列数据集共分析了18个骨关节炎软骨组织和14个正常软骨组织,分别对2个数据集进行标准化并做差异分析,得到差异表达microRNA共888个,其中低表达的共有843个,见图1。对两数据集差异表达microRNA做交集,得到4个共同低表达的microRNA,分别是hsa-miR-4306、hsa-miR-3202、hsa-miR-483-5p、hsa-miR-1275,见图2,3。基于国内外研究现状,尚无有关hsa-miR-3202与骨关节炎相关性的研究,此次研究进一步探索了hsa-miR-3202对骨关节炎软骨细胞功能的影响。 2.2 hsa-miR-3202靶基因预测 使用在线数据库预测hsa-miR-3202的靶基因,miRWalk、miRTarBase、TargetScan、miRPathDB数据库分别预测到14 544,191,6 016,9 310个靶基因,对各数据库预测结果作交集,获得靶基因共157个(图4)。 2.3 hsa-miR-3202靶基因GO和KEGG富集分析结果 运用DAVID数据库对hsa-miR-3202靶基因进行GO功能富集分析;运用KOBAS-i数据库对hsa-miR-3202靶基因进行KEGG通路富集分析,见图5。GO功能富集结果显示,hsa-miR-3202靶基因主要集中在细胞核、细胞质、染色质等细胞组分上,且在蛋白质磷酸化、转录调控、细胞内信号转导、蛋白激酶活性激活等生物过程中集中,在分子功能上主要参与蛋白结合、DNA结合、RNA结合等。KEGG通路富集发现,hsa-miR-3202的靶基因多参与细胞生存、凋亡和炎症相关通路,如丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPK)信号通路、哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mTOR)信号通路、磷脂酰肌醇三激酶-蛋白激酶B(PI3K-Akt)信号通路、肿瘤坏死因子信号通路等(表2)。"
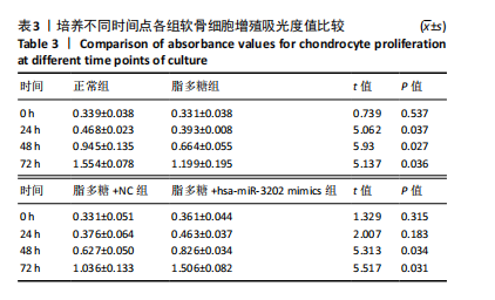
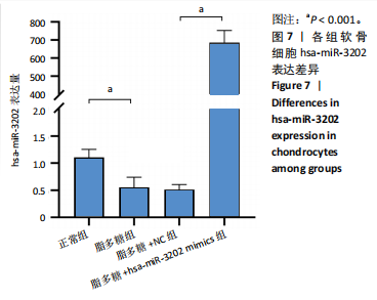
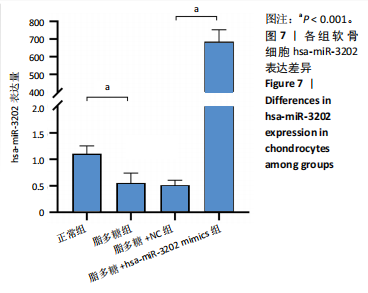
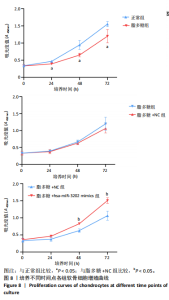
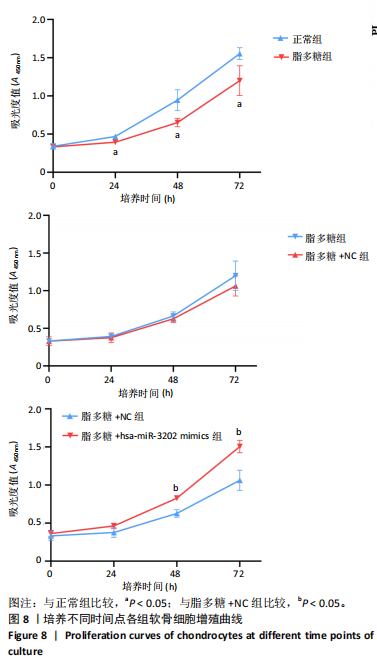
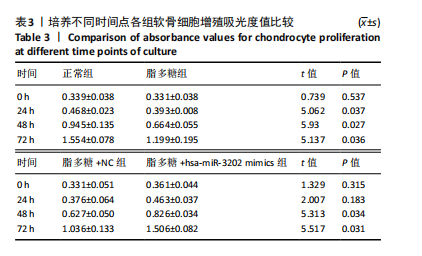
2.4 体外细胞实验验证结果 2.4.1 各组软骨细胞炎症因子mRNA和hsa-miR-3202表达比较 与正常组比较,脂多糖组软骨细胞中白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α mRNA表达升高(t=6.312,P=0.024;t=4.156,P=0.014;t=8.811,P < 0.001),见图6,提示骨关节炎模型造模成功。 各组软骨细胞中hsa-miR-3202表达见图7。与正常组比较,脂多糖组软骨细胞中hsa-miR-3202表达降低(t=6.141,P < 0.001),证明hsa-miR-3202在骨关节炎软骨细胞中低表达;脂多糖组与脂多糖+NC组hsa-miR-3202表达比较差异无显著性意义(t=0.388,P=0.708);与脂多糖+NC组相比,脂多糖+hsa-miR-3202 mimics组 hsa-miR-3202表达升高(t=2.250,P < 0.001),提示实验成功过表达软骨细胞hsa-miR-3202。 2.4.2 各组软骨细胞增殖活力比较 各组软骨细胞增殖活力见图8。与正常组比较,脂多糖组培养24-72 h的软骨细胞增殖活力降低(t=5.062,P=0.037;t=5.93,P=0.027;t=5.137,P=0.036);脂多糖组与脂多糖+NC组培养24-72 h的软骨细胞增殖活力比较差异无显著性意义(t=0.452,P=0.675;t=0.859,P=0.439;t=1.004,P=0.372);与脂多糖+NC组比较,脂多糖+hsa-miR-3202 mimics组培养48,72 h的软骨细胞增殖活力升高(t=5.313,P=0.034;t=5.517,P=0.031),提示hsa-miR-3202过表达可促进软骨细胞增殖,在一定程度上修复炎症状态下软骨细胞的增殖能力,见表3。"

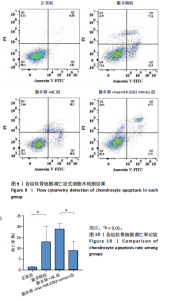
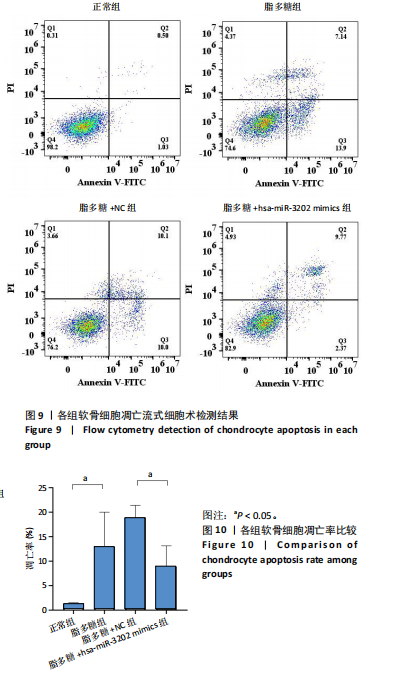
2.4.3 各组软骨细胞凋亡率比较 各组软骨细胞凋亡流式细胞术检测结果,见图9。正常组、脂多糖组、脂多糖+ NC组、脂多糖+hsa-miR-3202 mimics组软骨细胞凋亡率分别为(1.22±0.28)%,(12.92±7.09)%,(18.91±2.49)%,(8.94±4.20)%,见图10。脂多糖组软骨细胞凋亡率高于正常组(t=43.766,P=0.020),与脂多糖+NC组比较差异无显著性意义(t=1.181,P=0.303);脂多糖+hsa-miR-3202 mimics组软骨细胞凋亡率低于脂多糖+NC组(t=3.540,P=0.024)。结果表明炎症状态下软骨细胞凋亡率增加,而hsa-miR-3202过表达可抑制骨关节炎软骨细胞凋亡。"

| [1] LIU S, PAN Y, LI T, et al. The Role of Regulated Programmed Cell Death in Osteoarthritis: From Pathogenesis to Therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(6):5364. [2] 王欢,孙贺,张耀南,等.中国40岁以上人群原发性膝骨关节炎各间室患病状况调查[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2019,12(7): 528-532. [3] SALIMINEJAD K, KHORRAM KHORSHID HR, SOLEYMANI FARD S, et al. An overview of microRNAs: Biology, functions, therapeutics, and analysis methods. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(5):5451-5465. [4] DIENER C, KELLER A, MEESE E. Emerging concepts of miRNA therapeutics: from cells to clinic. Trends Genet. 2022;38(6): 613-626. [5] KOPAŃSKA M, SZALA D, CZECH J, et al. MiRNA expression in the cartilage of patients with osteoarthritis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017; 12(1):51. [6] XU B, LI YY, MA J, et al. Roles of microRNA and signaling pathway in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2016;17(3):200-208. [7] ALI SA, PEFFERS MJ, ORMSETH MJ, et al. The non-coding RNA interactome in joint health and disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021; 17(11):692-705. [8] ZHANG H, ZHENG W, LI D, et al. miR-146a-5p Promotes Chondrocyte Apoptosis and Inhibits Autophagy of Osteoarthritis by Targeting NUMB. Cartilage. 2021;13(2_suppl):1467S-1477S. [9] SWINGLER TE, NIU L, SMITH P, et al. The function of microRNAs in cartilage and osteoarthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2019;37 Suppl 120(5):40-47. [10] JIN L, MA J, CHEN Z, et al. Osteoarthritis related epigenetic variations in miRNA expression and DNA methylation. BMC Med Genomics. 2023;16(1):163. [11 DUAN L, LIANG Y, MA B, et al. Epigenetic regulation in chondrocyte phenotype maintenance for cell-based cartilage repair. Am J Transl Res. 2015;7(11):2127-2140. [12] XU H, XU B. BMSC-Derived Exosomes Ameliorate Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting Pyroptosis of Cartilage via Delivering miR-326 Targeting HDAC3 and STAT1//NF-κB p65 to Chondrocytes. Mediators Inflamm. 2021;2021:9972805. [13] HUANG X, XIE H, XUE G, et al. MiR-3202 - Promoted H5V Cell Apoptosis by Directly Targeting Fas Apoptotic Inhibitory Molecule 2 (FAIM2) in High Glucose Condition. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:975-983. [14] SHEN W, LIU J, FAN M, et al. MiR-3202 protects smokers from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease through inhibiting FAIM2: An in vivo and in vitro study. Exp Cell Res. 2018;362(2):370-377. [15] SOLIMAN HAN, TOSO EA, DARWISH IE, et al. Antiapoptotic Protein FAIM2 is targeted by miR-3202, and DUX4 via TRIM21, leading to cell death and defective myogenesis. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(4):405. [16] AN S, HU H, LI Y, et al. Pyroptosis Plays a Role in Osteoarthritis. Aging Dis. 2020;11(5):1146-1157. [17] XIA L, GONG N. Identification and verification of ferroptosis-related genes in the synovial tissue of osteoarthritis using bioinformatics analysis. Front Mol Biosci. 2022;9:992044. [18] CHENG P, GONG S, GUO C, et al. Exploration of effective biomarkers and infiltrating Immune cells in Osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics analysis. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2023;51(1):242-254. [19] EKIMLER S, SAHIN K. Computational Methods for MicroRNA Target Prediction. Genes (Basel). 2014;5(3):671-683. [20] BU D, LUO H, HUO P, et al. KOBAS-i: intelligent prioritization and exploratory visualization of biological functions for gene enrichment analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49(W1):W317-w325. [21] SHU Y, LONG J, GUO W, et al. MicroRNA-195-5p inhibitor prevents the development of osteoarthritis by targeting REGγ. Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(6):4561-4568. [22] LUO X, WANG J, WEI X, et al. Knockdown of lncRNA MFI2-AS1 inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced osteoarthritis progression by miR-130a-3p/TCF4. Life Sci. 2020;240:117019. [23] 陈天,李博野,于渤洋,等.人参皂苷Rg_1, Rb_1对脂多糖体外诱导肠上皮屏障损伤的保护作用[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2022,28(7): 64-72. [24] DUENSING TD, WATSON SR. Assessment of Apoptosis (Programmed Cell Death) by Flow Cytometry. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2018;2018(1).doi: 10.1101/pdb.prot093807. [25] RILEY JS, BOCK FJ. Voices from beyond the grave: The impact of apoptosis on the microenvironment. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2022;1869(11):119341. [26] AN S, HU H, LI Y, et al. Pyroptosis Plays a Role in Osteoarthritis. Aging Dis. 2020;11(5):1146-1157. [27] 赵奎,潘润桑,蓝奉军,等.骨关节炎中自噬与凋亡相互作用的分子机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(18):2912-2917. [28] DUAN R, XIE H, LIU ZZ. The Role of Autophagy in Osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:608388. [29] LIN Z, DENG Z, LIU J, et al. Chloride Channel and Inflammation-Mediated Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis. J Inflamm Res. 2022;15:953-964. [30] TIAN F, WANG J, ZHANG Z, et al. miR-107 modulates chondrocyte proliferation, apoptosis, and extracellular matrix synthesis by targeting PTEN. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019;12(2):488-497. [31] Qian J, Fu P, Li S, et al. miR-107 affects cartilage matrix degradation in the pathogenesis of knee osteoarthritis by regulating caspase-1. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):40. [32] ZHANG Y, XU S, HUANG E, et al. MicroRNA-130a regulates chondrocyte proliferation and alleviates osteoarthritis through PTEN/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(6):3699-3708. [33] ZHOU Y, ZHAO Z, YAN L, et al. MiR-485-3p promotes proliferation of osteoarthritis chondrocytes and inhibits apoptosis via Notch2 and the NF-κB pathway. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2021;43(3):370-379. [34] GAO L, WANG X, XIONG J, et al. Circular RNA from phosphodiesterase 4D can attenuate chondrocyte apoptosis and matrix degradation under OA milieu induced by IL-1β via circPDE4D/miR-4306/SOX9 Cascade. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2022;44(5):682-692. [35] PENG H, YU Y, GU H, et al. MicroRNA-483-5p inhibits osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by targeting the RPL31-mediated RAS/MEK/ERK signaling pathway. Cell Signal. 2022;93:110298. [36] ZOU Z, DAI R, DENG N, et al. Exosomal miR-1275 Secreted by Prostate Cancer Cells Modulates Osteoblast Proliferation and Activity by Targeting the SIRT2/RUNX2 Cascade. Cell Transplant. 2021;30: 9636897211052977. [37] LEI S, CAO W, ZENG Z, et al. JUND/linc00976 promotes cholangiocarcinoma progression and metastasis, inhibits ferroptosis by regulating the miR-3202/GPX4 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(11):967. [38] VOSS AK, STRASSER A. The essentials of developmental apoptosis. F1000Res. 2020;9:F1000 Faculty Rev-148. [39] LAN CN, CAI WJ, SHI J, et al. MAPK inhibitors protect against early‑stage osteoarthritis by activating autophagy. Mol Med Rep. 2021;24(6):829. [40] LI Z, HUANG Z, ZHANG H, et al. Moderate-intensity exercise alleviates pyroptosis by promoting autophagy in osteoarthritis via the P2X7/AMPK/mTOR axis. Cell Death Discov. 2021;7(1):346. [41] SUN K, LUO J, GUO J, et al. The PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in osteoarthritis: a narrative review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(4): 400-409. [42] 李田洋,郑曙光.PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路在骨关节炎中的作用[J].中国现代医学杂志,2021,31(20):58-63. [43] CHEN Y, YANG H, WANG Z, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes mesenchymal stem cell transplantation-based articular cartilage regeneration via inhibiting the TNF signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):93. [44] LIAN WS, KO JY, WU RW, et al. MicroRNA-128a represses chondrocyte autophagy and exacerbates knee osteoarthritis by disrupting Atg12. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(9):919. [45] LIU Y, SHAH KM, LUO J. Strategies for Articular Cartilage Repair and Regeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:770655. |
| [1] | Ma Chi, Wang Ning, Chen Yong, Wei Zhihan, Liu Fengji, Piao Chengzhe. Application of 3D-printing patient-specific instruments combined with customized locking plate in opening wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1863-1869. |
| [2] | Yu Shuai, Liu Jiawei, Zhu Bin, Pan Tan, Li Xinglong, Sun Guangfeng, Yu Haiyang, Ding Ya, Wang Hongliang. Hot issues and application prospects of small molecule drugs in treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [3] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [4] | Sun Yundi, Cheng Lulu, Wan Haili, Chang Ying, Xiong Wenjuan, Xia Yuan. Effect of neuromuscular exercise for knee osteoarthritis pain and function: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1945-1952. |
| [5] | Deng Keqi, Li Guangdi, Goswami Ashutosh, Liu Xingyu, He Xiaoyong. Screening and validation of Hub genes for iron overload in osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1972-1980. |
| [6] | Yin Lu, Jiang Chuanfeng, Chen Junjie, Yi Ming, Wang Zihe, Shi Houyin, Wang Guoyou, Shen Huarui. Effect of Complanatoside A on the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [7] | Wang Peiguang, Zhang Xiaowen, Mai Meisi, Li Luqian, Huang Hao. Generalized equation estimation of the therapeutic effect of floating needle therapy combined with acupoint embedding on different stages of human knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1565-1571. |
| [8] | Liu Lin, Liu Shixuan, Lu Xinyue, Wang Kan. Metabolomic analysis of urine in a rat model of chronic myofascial trigger points [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1585-1592. |
| [9] | Li Kaiying, Wei Xiaoge, Song Fei, Yang Nan, Zhao Zhenning, Wang Yan, Mu Jing, Ma Huisheng. Mechanism of Lijin manipulation regulating scar formation in skeletal muscle injury repair in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1600-1608. |
| [10] | Wang Qiuyue, Jin Pan, Pu Rui . Exercise intervention and the role of pyroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [11] | Zhao Jiacheng, Ren Shiqi, Zhu Qin, Liu Jiajia, Zhu Xiang, Yang Yang. Bioinformatics analysis of potential biomarkers for primary osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1741-1750. |
| [12] | Chen Yueping, Chen Feng, Peng Qinglin, Chen Huiyi, Dong Panfeng . Based on UHPLC-QE-MS, network pharmacology, and molecular dynamics simulation to explore the mechanism of Panax notoginseng in treating osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1751-1760. |
| [13] | Chi Wenxin, Zhang Cunxin, Gao Kai, Lyu Chaoliang, Zhang Kefeng. Mechanism by which nobiletin inhibits inflammatory response of BV2 microglia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1321-1327. |
| [14] | Yang Zhihang, Sun Zuyan, Huang Wenliang, Wan Yu, Chen Shida, Deng Jiang. Nerve growth factor promotes chondrogenic differentiation and inhibits hypertrophic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [15] | Hu Taotao, Liu Bing, Chen Cheng, Yin Zongyin, Kan Daohong, Ni Jie, Ye Lingxiao, Zheng Xiangbing, Yan Min, Zou Yong. Human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing neuregulin-1 promote skin wound healing in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1343-1349. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||