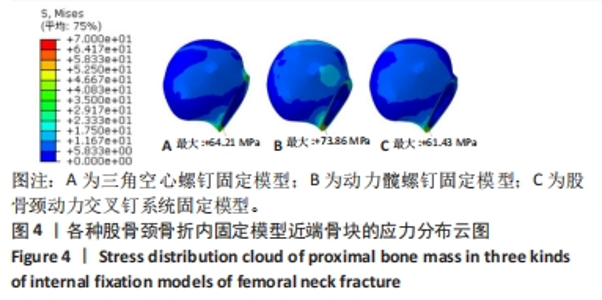
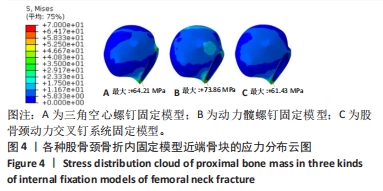
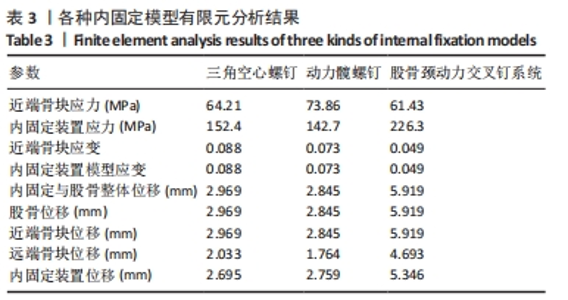
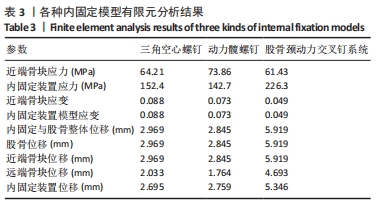
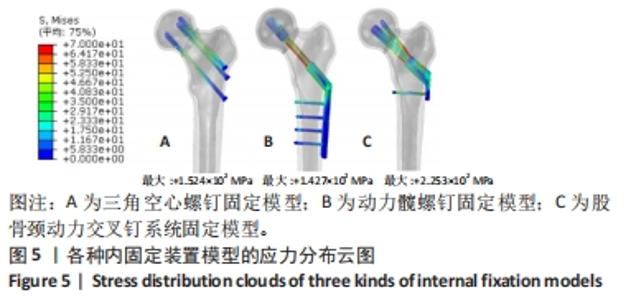
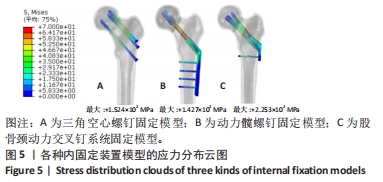
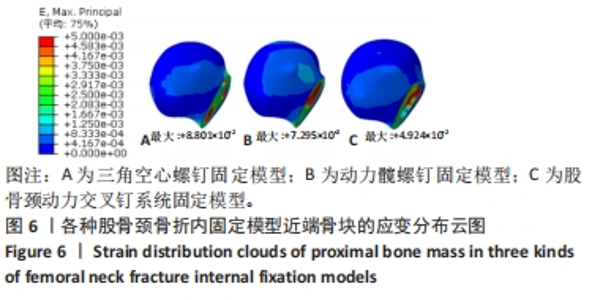
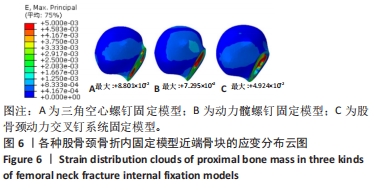
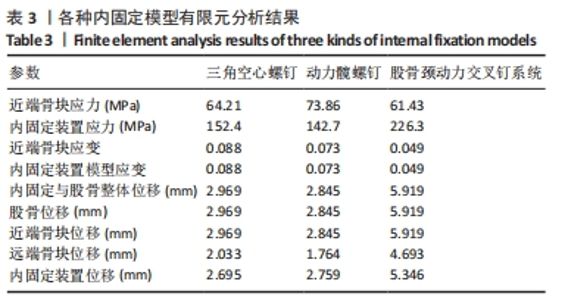
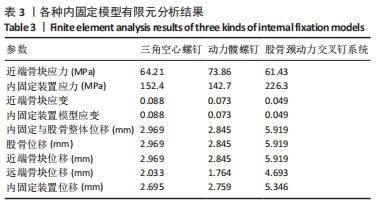
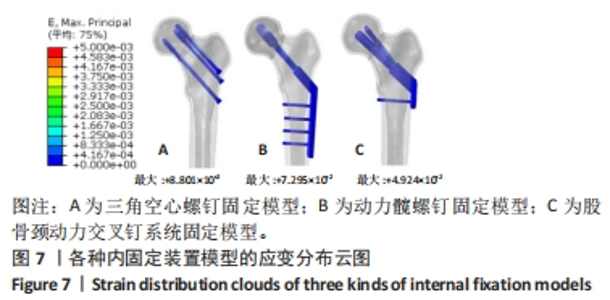
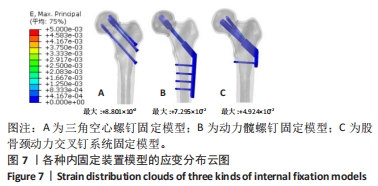
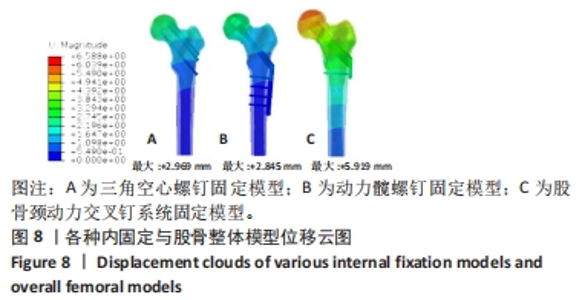
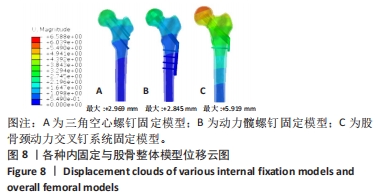
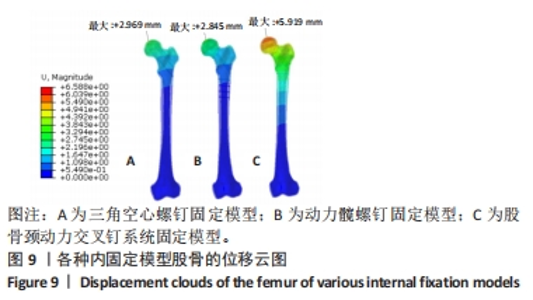
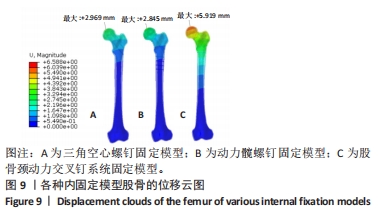
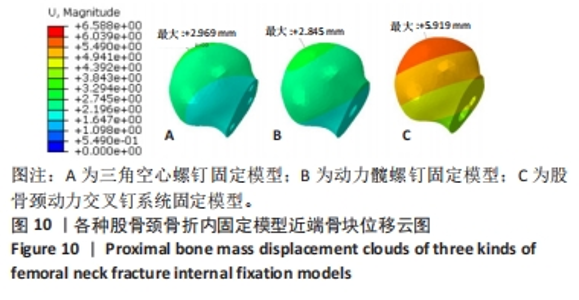
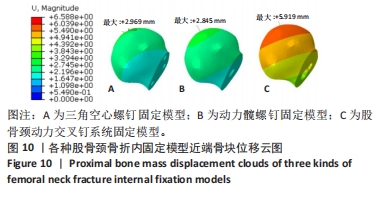
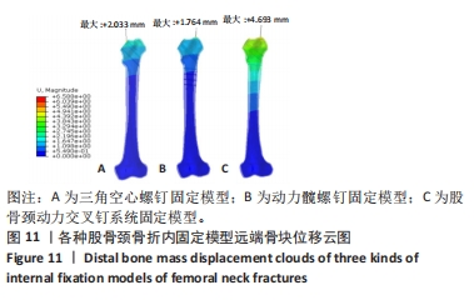
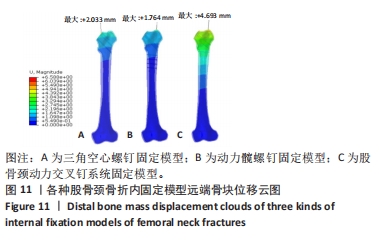
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (30): 4763-4769.doi: 10.12307/2024.645
Previous Articles Next Articles
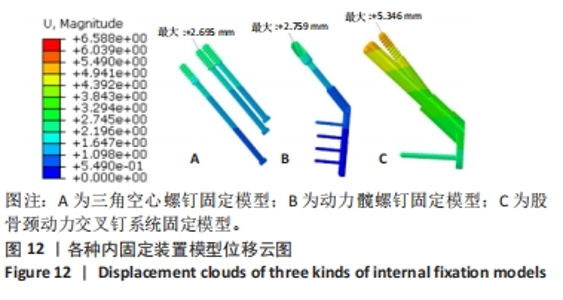
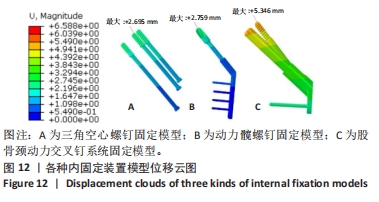
Three internal fixation devices used for finite element analysis of Pauwels type III femoral neck fractures
Qi Yuanbo1, Li Jiantao2, Liu Daohong2, 3, Tao Sheng2, 3, Wang Daofeng2, Wu Jie3
- 1Hebei North University, Zhangjiakou 075000, Hebei Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China; 3Department of Orthopedics, Eighth Medical Center of Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100091, China
-
Received:2023-06-01Accepted:2023-09-02Online:2024-10-28Published:2023-12-23 -
Contact:Liu Daohong, Associate professor, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China; Department of Orthopedics, Eighth Medical Center of Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100091, China -
About author:Qi Yuanbo, Master candidate, Hebei North University, Zhangjiakou 075000, Hebei Province, China Li Jiantao, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China -
Supported by:China National Key Research & Development Program, No. 2019YFC0840705 (to LDH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Qi Yuanbo, Li Jiantao, Liu Daohong, Tao Sheng, Wang Daofeng, Wu Jie. Three internal fixation devices used for finite element analysis of Pauwels type III femoral neck fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(30): 4763-4769.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] DENNISON E, MOHAMED MA, COOPER C. Epidemiology of Osteoporosis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2006;32(4):617-629. [2] 张英泽. 临床创伤骨科流行病学[M]. 3版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社,2018: 223-225. [3] HUANG B, WANG Y, WANG H, et al. Epidemiology and the economic burden of traumatic fractures in China: A population-based study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1104202. [4] PAUWELS F. Der Schenkelhalsbruch//PAUWELS F. Gesammelte Abhandlungen zur funktionellen Anatomie des Bewegungsapparates. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 1965:1-138. [5] SHEN M, WANG C, CHEN H, et al. An update on the Pauwels classification. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016;11(1):161. [6] COLLINGE CA, FINLAY A, RODRIGUEZ-BUITRAGO A, et al. Treatment Failure in Femoral Neck Fractures in Adults Less Than 50 Years of Age: Analysis of 492 Patients Repaired at 26 North American Trauma Centers. J Orthop Trauma. 2022;36(6): 271-279. [7] 张长青, 张英泽, 余斌, 等. 成人股骨颈骨折诊治指南[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2018,20(11):921-928. [8] Fixation using Alternative Implants for the Treatment of Hip fractures (FAITH) Investigators. Fracture fixation in the operative management of hip fractures (FAITH): an international, multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2017;389(10078):1519-1527. [9] QIU L, HUANG Y, LI G, et al. Essential role of reliable reduction quality in internal fixation of femoral neck fractures in the non-elderly patients-a propensity score matching analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):346. [10] EBERLE S, GERBER C, VON OLDENBURG G, et al. A Biomechanical Evaluation of Orthopaedic Implants for Hip Fractures by Finite Element Analysis andIn-Vitro Tests. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2010;224(10):1141-1152. [11] CHEN W, TAI C, SHIH C, et al. Selection of fixation devices in proximal femur rotational osteotomy: clinical complications and finite element analysis. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2004;19(3):255-262. [12] DAMANY DS, PARKER MJ, CHOJNOWSKI A. Complications after intracapsular hip fractures in young adults. Injury. 2005;36(1):131-141. [13] SLOBOGEAN GP, SPRAGUE SA, SCOTT T, et al. Management of young femoral neck fractures: Is there a consensus? Injury. 2015;46(3):435-440. [14] PANTELI M, RODHAM P, GIANNOUDIS PV. Biomechanical rationale for implant choices in femoral neck fracture fixation in the non-elderly. Injury. 2015;46(3): 445-452. [15] LIPORACE F, GAINES R, COLLINGE C, et al. Results of Internal Fixation of Pauwels Type-3 Vertical Femoral Neck Fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(8):1654-1659. [16] GUIMARAES J, ROCHA LR, NORONHA RT, et al. Vertical femoral neck fractures in young adults: a closed fixation strategy using a transverse cancellous lag screw. Injury. 2017;48 Suppl 4:S10-S16. [17] ZHOU L, LIN J, HUANG A, et al. Modified cannulated screw fixation in the treatment of Pauwels type Ⅲ femoral neck fractures: A biomechanical study. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2020;74:103-110. [18] JOHNSON JP, BORENSTEIN TR, WARYASZ GR, et al. Vertically Oriented Femoral Neck Fractures: A Biomechanical Comparison of 3 Fixation Constructs. J Orthop Trauma. 2017;31(7):363-368. [19] FILIPOV O. Biplane double-supported screw fixation (F-technique): a method of screw fixation at osteoporotic fractures of the femoral neck. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2011;21(7):539-543. [20] FILIPOV O, GUEORGUIEV B. Unique stability of femoral neck fractures treated with the novel biplane double-supported screw fixation method: A biomechanical cadaver study. Injury. 2015;46(2):218-226. [21] FILIPOV O, STOFFEL K, GUEORGUIEV B, et al. Femoral neck fracture osteosynthesis by the biplane double-supported screw fixation method (BDSF) reduces the risk of fixation failure: clinical outcomes in 207 patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017;137(6):779-788. [22] 严坤, 牟利民, 杨晓辉, 等. 三种空心钉构型固定Pauwels Ⅲ型股骨颈骨折的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(18):2807-2811. [23] ZHANG LL, ZHANG Y, MA X, et al. Multiple cannulated screws vs. dynamic hip screws for femoral neck fractures. Orthopade. 2017;46(11):954-962. [24] 王青, 姜达君, 贾伟涛. Pauwels三型股骨颈骨折不同内固定方式的meta分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2018,38(9):1046-1052. [25] CHA Y, SONG JU, YOO JI, et al. Improved control over implant anchorage under the use of the femoral neck system for fixation of femoral neck fractures: a technical note. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1): 621. [26] COMPANIES DS. Femoral Neck System | Trauma & Extremities| DePuy Synthes. [2023/07/12]. https://www.jnjmedtech.com/en-US/product/femoral-neck-system. [27] KARL STOFFEL CS. Femoral Neck System. [2023/07/12]. https://www.aofoundation.org/approved/approvedsolutionsfolder/2017/femoral-neck-system?searchurl=%2Fsearchresults#tab=details. [28] STOFFEL K, ZDERIC I, GRAS F, et al. Biomechanical Evaluation of the Femoral Neck System in Unstable Pauwels Ⅲ Femoral Neck Fractures: A Comparison with the Dynamic Hip Screw and Cannulated Screws. J Orthop Trauma. 2017;31(3):131-137. [29] JIANG J, CHEN J, XING F, et al. Comparison of femoral neck system versus cannulated screws for treatment of femoral neck fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):285. [30] 杨家赵, 周雪锋, 朱万博, 等. FNS与空心螺钉固定治疗青壮年股骨颈骨折的近期疗效比较[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2021,23(9):761-768. [31] 许翔宇, 周方, 田耘, 等. FNS与DHS固定治疗股骨颈骨折的早期疗效比较[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2021,23(9):754-760. [32] XIA Y, ZHANG W, HU H, et al. Biomechanical study of two alternative methods for the treatment of vertical femoral neck fractures – A finite element analysis. Comput Meth Prog Bio. 2021;211:106409. [33] TENG Y, ZHANG Y, GUO C. Finite element analysis of femoral neck system in the treatment of Pauwels type III femoral neck fracture. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(28):e29450. [34] JUNG CH, CHA Y, YOON HS, et al. Mechanical effects of surgical variations in the femoral neck system on Pauwels type III femoral neck fracture : a finite element analysis. Bone Joint Res. 2022;11(2):102-111. [35] CHA Y, SONG JU, YOO JI, et al. Improved control over implant anchorage under the use of the femoral neck system for fixation of femoral neck fractures: a technical note. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):621. [36] 范智荣, 苏海涛, 周霖, 等. 新型股骨颈内固定系统治疗不稳定性股骨颈骨折的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(15):2321-2328. [37] 杜兵, 马腾, 路遥, 等. 新型股骨颈内固定系统与3枚空心钉加内侧钢板固定青壮年Pauwels Ⅲ型股骨颈骨折的有限元分析[J]. 中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志,2021,7(6):333-338. [38] HUANG S, ZHANG Y, ZHANG X, et al. Comparison of femoral neck system and three cannulated cancellous screws in the treatment of vertical femoral neck fractures: clinical observation and finite element analysis. Biomed Eng Online. 2023;22(1):20. |
| [1] | Zhang Hao, Wang Qing, Zhang Jian, Li Guangzhou, Wang Gaoju. Comparison of posterior C2-3 fixation combined with bucking bar technique and posterior C2-3 fixation alone in treatment of unstable Hangman fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1848-1854. |
| [2] | Su Lintao, Jiang Jianfeng, Ma Jun, Huang Liangliang, Lei Changyu, Han Yaozheng, Kang Hui. Precise application of O-arm navigation system in thoracolumbar fractures with developmental pedicle stenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1855-1862. |
| [3] | Gao Zhenyang, Zeng Xiuan, Yang Qibing, Kou Xianshuai, Wang Kejing, Li Meng. Computer-simulated repositioning combined with pelvic reduction frame for treatment of anteroposterior compression-III pelvic fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1870-1875. |
| [4] | Zhou Jiajun, Ma Fei, Leng Yebo, Xu Shicai, He Baoqiang, Li Yang, Liao Yehui, Tang Qiang, Tang Chao, Wang Qing, Zhong Dejun. Assessing distribution characteristics and clinical significance of vertebral fractures in patients with osteoporosis based on whole spine MRI [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1883-1889. |
| [5] | Sun Xiaojun, Wang Huaming, Zhang Dehong, Song Xuewen, Huang Jin, Zhang Chen, Pei Shengtai. Effect of finite element method in treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1897-1904. |
| [6] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [7] | Li Liangkui, Huang Yongcan, Wang Peng, Yu Binsheng. Effect of anterior controllable anteriodisplacement and fusion on vertebrae-ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament complex and implants: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1761-1767. |
| [8] | Xu Biao, Lu Tan, Jiang Yaqiong, Yin Yujiao. Xu Biao, Lu Tan, Jiang Yaqiong, Yin Yujiao [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1768-1774. |
| [9] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [10] | Chen Xi, Tang Tao, Chen Tongbing, Li Qing, Zhang Wen. Mechanical stability of intertrochanteric fracture of femur with different internal fixation systems [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1783-1788. |
| [11] | Fu Enhong, Yang Hang, Liang Cheng, Zhang Xiaogang, Zhang Yali, Jin Zhongmin. OpenSim-based prediction of lower-limb biomechanical behavior in adolescents with plantarflexor weakness [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1789-1795. |
| [12] | Huang Haobo, Liang Xinyuan, Ye Guozhong, Xie Qingxiang, Su Boyuan. Suture tape and headless compression screws in treatment of Lisfranc injury with comminuted fractures of the first and second proximal metatarsal bones [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1803-1809. |
| [13] | Liu Yan, Wang Kai, Wu Min. Relationship between coronal angle fluctuation of ankle point and recovery of joint function after ankle fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1820-1826. |
| [14] | Lu Jieming, Li Yajing, Du Peijie, Xu Dongqing. Effects of artificial turf versus natural grass on biomechanical performance of the lower limbs in young females during jump-landing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1101-1107. |
| [15] |
Zhao Wensheng, Li Xiaolin, Peng Changhua, Deng Jia, Sheng Hao, Chen Hongwei, Zhang Chaoju, He Chuan.
Gut microbiota and osteoporotic fractures #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1296-1304.
|
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||