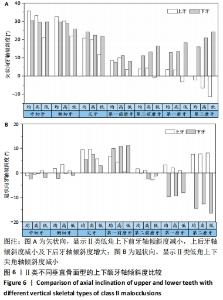
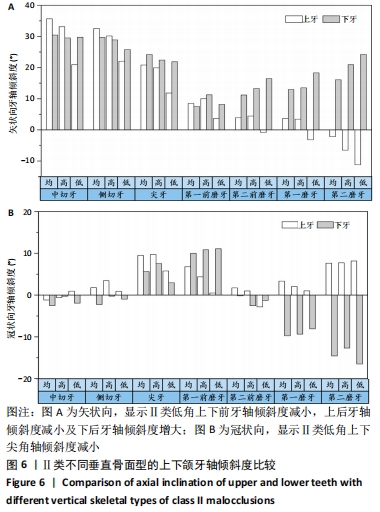
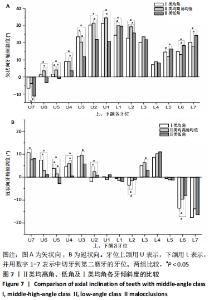
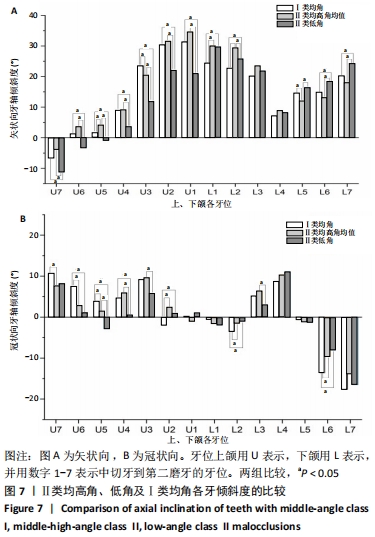
[1] 丁琪, 贾莹, 刘娟, 等. 高角骨性Ⅲ类错牙合牙齿倾斜位置特征[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2019,37(4):371-376.
[2] 邹冰爽, 曾祥龙, 曾应魁. 安氏II~1错牙合颅面类型的研究[J]. 中华口腔正畸学杂志,1998,5(2):13-16.
[3] VADEN JL, WILLIAMS RA, GOFORTH RL. Class II correction: Extraction or nonextraction? Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2018;154(6):860-876.
[4] FRANZOTTI SANT’ANNA E, CARNEIRO DA CUNHA A, PALUDO BRUNETTO D, et al. Camouflage of a high-angle skeletal Class II open-bite malocclusion in an adult after mini-implant failure during treatment. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2017;151(3):583-597.
[5] 蔡森鑫, 伍丹妮, 常琳, 等. 福建地区安氏Ⅱ类1分类骨性错牙合患者切牙及磨牙高度和倾斜度研究[J]. 中华口腔正畸学杂志,2016, 23(4):193-197.
[6] 赵勇, 张燎, 张强, 等.安氏Ⅱ~1类错牙合畸形不同垂直骨面型磨牙倾斜度的研究[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2017,31(4):206-209.
[7] 雷巧玲, 周力, 雷蕾, 等. 传统全景片和锥形束CT重建全景片测量牙轴近远中倾斜度的对比研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2014,32(4): 331-335.
[8] 刘娟. 骨性Ⅲ类错牙合体分段长轴倾斜方向的一致性评价[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2016,34(2):165-170.
[9] SOLOW B. The dentoalveolar compensatory mechanism: background and clinical implications. Br J Orthod. 1980;7(3):145-161.
[10] BUSCHANG PH , GANDINI LG . Mandibular skeletal growth and modelling between 10 and 15 years of age. Eur J Orthod. 2002;24(1): 69-79.
[11] 樊佳兵, 张军梅. 成年女性不同垂直骨面型下颌骨形态的测量分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(8):1177-1183.
[12] MACARI AT, HANNA AE. Comparisons of soft tissue chin thickness in adult patients with various mandibular divergence patterns. Angle Orthod. 2013;84(4):708-714.
[13] SAYIN MO, TÜRKKAHRAMAN H. Cephalometric evaluation of nongrowing females with skeletal and dental Class II, division 1 malocclusion Angle Orthod. 2005;75(4):656-660.
[14] ALHAMMADI MS. Dentoalveolar compensation in different anterioposterior and vertical skeletal malocclusions. J Clin Exp Dent. 2019;11(8):e745-e753.
[15] CHUNG CH, WONG WW. Craniofacial growth in untreated skeletal Class II subjects: A longitudinal study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2002;122(6):619-626.
[16] 吴浩,周力,周蕾, 等.青少年正常牙合及安氏II类1分类错牙合不同生长型的颌骨旋转类型[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2010,28(1):48-51,56.
[17] 曹安怡, 焦岚, 曹芳,等. 安氏II类错牙合患者Spee 曲线深度与牙颌面形态间的关系[J]. 口腔疾病防治,2017,25(6):385-388.
[18] 刘之奥, 徐卫华, 郑之峻. 基于CBCT的后段牙合平面和下颌骨形态间相关性研究[J]. 口腔医学研究,2019,35(11):1078-1083.
[19] 刘颖. 骨性II类牙弓与基骨弓协调性及牙齿代偿机制的研究[D].天津:天津医科大学,2013.
[20] GRIPPAUDO C, OLIVA B, GRECO AL, et al. Relationship between vertical facial patterns and dental arch form in class II malocclusion. Prog Orthod. 2013;7:14-43
[21] 王亮, 王林, 王珊, 等. 不同错畸形后牙横向关系的研究[J].中华口腔正畸学杂志,2020,27(2):73-77.
[22] HWANG S, CHOI YJ, JUNG S, et al. Posterior dental compensation and occlusal function in adults with different sagittal skeletal malocclusions. Korean J Orthod. 2020;50(2):98-107.
[23] BARROS SE, CHIQUETO K, JANSON G, et al. Effect of Class II camouflage treatment on anterior arch length ratio and canine relationship. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2021;159(1):e7-e16.
[24] 冯枫. 切牙的冠转矩和轴倾角对咬合关系影响的定量研究[D].青岛:青岛大学,2020.
|