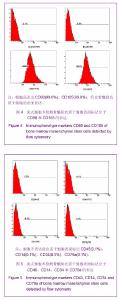
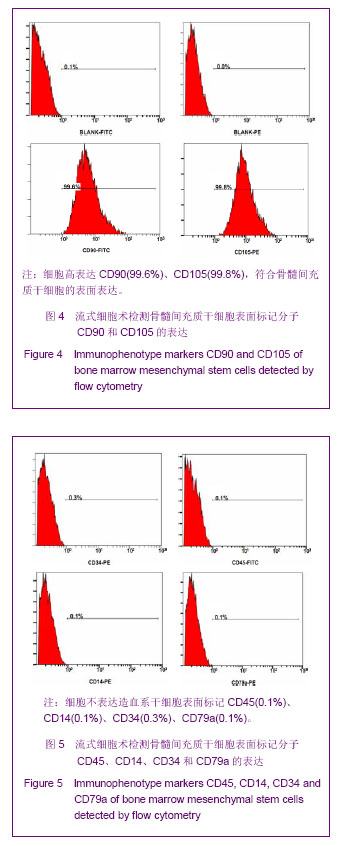
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (49): 8512-8519.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.49.008
Previous Articles Next Articles
Salidroside and cholestatic serum induce differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocytes
Du Chao, Jiang Ming-de, Zeng Wei-zheng, Gao Yong
- Department of Gastroenterology, General Hospital of Chengdu Military Command, Chengdu 610083, Sichuan Province, China
-
Revised:2013-09-02Online:2013-12-03Published:2013-12-03 -
Contact:Jiang Ming-de, Master, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Gastroenterology, General Hospital of Chengdu Military Command, Chengdu 610083, Sichuan Province, China jiangmd88@yahoo.com.cn -
About author:Du Chao★, Master, Attending physician, Department of Gastroenterology, General Hospital of Chengdu Military Command, Chengdu 610083, Sichuan Province, China 176147067@qq.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Du Chao, Jiang Ming-de, Zeng Wei-zheng, Gao Yong. Salidroside and cholestatic serum induce differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocytes[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(49): 8512-8519.
share this article

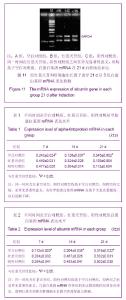
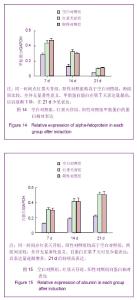
2.3 大鼠淤胆血清测定 淤胆型大鼠模型建立8 d后测定血清总胆红素浓度为(46.0±10.9) µmol/L,其5%培养基体系中胆红素浓度为(2.00±0.21) µmol/L。 2.4 RT-PCR法检测诱导后各组甲胎蛋白、白蛋白基因mRNA表达 诱导培养7 d后空白对照组、红景天苷组、阳性对照组均可见甲胎蛋白、白蛋白基因mRNA阳性表达。各组凝胶电泳图灰度值半定量分析结果显示,同一时间点红景天苷组、阳性对照组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),均高于空白对照组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。其中各组甲胎蛋白基因mRNA在第7天表达量最高,以后逐渐下降,在21 d几乎未见表达,见图6-8;而白蛋白基因mRNA在第7天可见少量表达,后表达量逐渐增多,21 d后持续高表达,见图9-11。半定量分析结果见表1,2。"

| [1] Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.[2] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 1999, 284(5411):143-147. [3] Spees JL, Gregory CA, Singh H, et al. Internalized antigens must be removed to prepare hypoimmunogenic mesenchymal stem cells for cell and gene therapy. Mol Ther. 2004;9(5): 747-756. [4] Sarah S, Tamara V, Peggy P, et al. Sequential Exposure to Cytokines Reflecting Embryogenesis: The Key for in vitro Differentiation of Adult Bone Marrow Stem Cells into Functional Hepatocyte-like Cells. Toxicological Science. 2006;94(2):330-341.[5] Dong XJ, Zhang H, Pan RL, et al. Identification of cytokines involved in hepatic differentiation of mBM-MSCs under liver- injury conditions.World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16(26):3267-3278.[6] Huang YH, Shi MN, Zheng WD, et al. Therapeutic effect of interleukin-10 on CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12(9):1386-1391.[7] Weng HL, Wang BE, Jia JD, et al. Effect of interferon-γ on hepatic fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B virus infection:a randomized controlled study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;3(8):819-828.[8] Petersen BE, Bowen WC, Patrene KD, et al. Bone marrow as a potential source of hepatic oval cells. Science. 1999; 284 (5417):1168-1170. [9] Am Esch JS 2nd, Knoefel WT, Klein M, et al. Portal application of autologous CD133+ bone marrow cells to the liver: a novel concept to support hepatic regeneration. Stem Cells. 2005;23(4):463-470.[10] Feng Z, Li C, Jiao S,et al.In vitro differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocytes. Hepatogastroenterology. 2011;58(112):2081-2086.[11] 吴晓玲,曾维政,蒋明德,等.红景天甙对肝纤维化大鼠肝组织ROCK表达的影响[J].世界华人消化杂志,2009,8:765-769.[12] 张华,戴立里,曾维政,等.红景天甙对大鼠肝组织TGF-β1/Smads 信号通路的作用[J].重庆医科大学学报,2011, 36(6):699-703.[13] 杨斌,曾维政,蒋明德,等.红景天甙对乙醛刺激的大鼠肝星状细胞中Wnt 信号通路的影响及其意义探讨[J].重庆医科大学学报, 2010,35(11):1630-1633.[14] 荣黎,戴立里,曾维政,等.红景天甙对拟高原缺氧大鼠肝损伤的保护作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(31): 5813- 5817.[15] Ouyang JF, Lou J, Yan C, et al. In-vitro promoted differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells towards hepatocytes induced by salidroside. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2010;62(4):530-538.[16] 邹毅清,蔡志扬,李小宝,等.红景天苷预处理对大鼠全脑缺血再灌注后炎症反应的影响[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2011,22(3): 253-255.[17] 高琨,胡美琴,祁洪刚,等.红景天苷对大鼠肾脏缺血再灌注损伤的预防保护时限[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2012,38(4):687-691.[18] 黄晓颖,樊荣,蔡学定,等.腺苷A2a受体在红景天苷调节大鼠低氧性肺动脉高压中的作用[J].中国病理生理杂志,2012,28(12): 2135-2140.[19] Colter DC,Class R, Digirolamo CM,et al.Rapid expansion of recycling stem cells in cultures of plastic-adherent cells from human bone marrow.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97(7): 3213-3218.[20] Tonraeau T,Lagneaux L,Edjeneffe M,et al.Isolation of BMSCs by plastic adhesion or negative selection:phenotype,proliferation kinetics and differentiation potential. Cytotherapy. 2004;6(4):372-379.[21] Gindraux F,Selmani Z,Obert L,et al.Human and rodent bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells that express primitive stem cell markers can be directily enriched by using the CD49a molecule.Cell Tissue Res.2007;327(3):471-483.[22] Lee BK, Choi SJ, Mack D, et al. Isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from the mandibular marrow aspirates. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2011c;112(6): e86-93. [23] Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.[24] Dong XJ, Zhang H, Pan RL, et al. Identification of cytokines involved in hepatic differentiation of mBM-MSCs under liver-injury conditions.World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16(26): 3267-3278.[25] Hu JJ, Sun C, Lan L, et al. Therapeutic effect of transplanting β2m-/Thy1+ bone marrow-derived hepatocyte stem cells transduced with lentiviral-mediated HGF gene into CCl4-injured rats. J Gene Med. 2010;12(3):244-254.[26] 哈小琴,董芳,吕同德.肝细胞生长因子基因对骨髓间充质干细胞的修饰及活性观察[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2010,24(5): 613-617.[27] Forte G, Minieri M, Cossa P, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor effects on mesenchymal cells: Proliferation, migration, and differentiation. Stem Cells. 2006;24(1):23-33.[28] Schwartz RE, Reyes M, Koodie L, et al. Multipotent adult progenitor cells from bone marrow differentiate into functional hepatocyte-like cells. J Clin Invest. 2002;109(10):1291-1302.[29] Avital I,Inderbitzin D,Aoki T,et al.Isolation, characterization, and transplantation of bone marrow-derived hepatocyte stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;288(1):156-164.[30] 钟晓琳,万居易,王忠琼,等.淤胆血清及肝细胞生长因子体外诱导BMSCs向肝细胞分化[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2010,24(3): 344-349. |
| [1] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(在线): 3-. |
| [2] | Chen Qiang, Zhuo Hongwu, Xia Tian, Ye Zhewei . Toxic effects of different-concentration isoniazid on newborn rat osteoblasts in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1162-1167. |
| [3] | Chen Jinsong, Wang Zhonghan, Chang Fei, Liu He. Tissue engineering methods for repair of articular cartilage defect under special conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1272-1279. |
| [4] | Liu Chundong, Shen Xiaoqing, Zhang Yanli, Zhang Xiaogen, Wu Buling. Effects of strontium-modified titanium surfaces on adhesion, migration and proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and expression of bone formation-related genes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1009-1015. |
| [5] | Lin Ming, Pan Jinyong, Zhang Huirong. Knockout of NIPBL gene down-regulates the abilities of proliferation and osteogenic differentiation in mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1002-1008. |
| [6] | Zhang Wen, Lei Kun, Gao Lei, Li Kuanxin. Neuronal differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via lentivirus-mediated bone morphogenetic protein 7 transfection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 985-990. |
| [7] | Wu Zhifeng, Luo Min. Biomechanical analysis of chemical acellular nerve allograft combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for repairing sciatic nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 991-995. |
| [8] | Huang Yongming, Huang Qiming, Liu Yanjie, Wang Jun, Cao Zhenwu, Tian Zhenjiang, Chen Bojian, Mai Xiujun, Feng Enhui. Proliferation and apoptosis of chondrocytes co-cultured with TDP43 lentivirus transfected-human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1016-1022. |
| [9] | Qin Xinyu, Zhang Yan, Zhang Ningkun, Gao Lianru, Cheng Tao, Wang Ze, Tong Shanshan, Chen Yu. Elabela promotes differentiation of Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells into cardiomyocyte-like cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1046-1051. |
| [10] | Liu Mengting, Rao Wei, Han Bing, Xiao Cuihong, Wu Dongcheng. Immunomodulatory characteristics of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1063-1068. |
| [11] |
Cen Yanhui, Xia Meng, Jia Wei, Luo Weisheng, Lin Jiang, Chen Songlin, Chen Wei, Liu Peng, Li Mingxing, Li Jingyun, Li Manli, Ai Dingding, Jiang Yunxia.
Baicalein inhibits the biological behavior of hepatocellular
carcinoma stem cells by downregulation of Decoy receptor 3 expression |
| [12] | Zhang Peigen, Heng Xiaolai, Xie Di, Wang Jin, Ma Jinglin, Kang Xuewen. Electrical stimulation combined with neurotrophin 3 promotes proliferation and differentiation of endogenous neural stem cells after spinal cord injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1076-1082. |
| [13] | Huang Cheng, Liu Yuanbing, Dai Yongping, Wang Liangliang, Cui Yihua, Yang Jiandong. Transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor gene for spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1037-1045. |
| [14] | Han Bo, Yang Zhe, Li Jing, Zhang Mingchang . Regulation of limbal stem cells via Wnt signaling in the treatment of limbal stem cell deficiency [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1057-1062. |
| [15] | Li Jia, Tang Ying, Zhu Qi, Zhang Yanping, Zhou Peigang, Gu Yongchun. Transplantation of human stem cells from the apical papilla for treating dextran sulfate sodium-induced experimental colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1069-1075. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||