Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
MicroRNA-1 and microRNA-499 directly reprogram cardiac myofibroblasts into cardiomyocyte-like cells
Zhang Cheng1, Zhang Shao-zhong1, Zhang Ya-zhou2, Zhang Guo-heng1, Wang Yun-ru2, Dong Hong-yan2, Zhang Zhong-ming1
- 1Institute of Cardiovascular Disease, the Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical College, Xuzhou 221002, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Department of Biology, Neurobiological Research Center Laboratory, Xuzhou Medical College, Xuzhou 221002, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Revised:2013-08-16Online:2013-11-05Published:2013-11-05 -
Contact:Dong Hong-yan, Professor, Department of Biology, Neurobiological Research Center Laboratory, Xuzhou Medical College, Xuzhou 221002, Jiangsu Province, China dhyxzh163.@163.com Corresponding author: Zhang Zhong-ming, M.D., Professor, Institute of Cardiovascular Disease, the Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical College, Xuzhou 221002, Jiangsu Province, China zhang_zmxz@163.com -
About author:Zhang Cheng★, Master, Institute of Cardiovascular Disease, the Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical College, Xuzhou 221002, Jiangsu Province, China zhangcheng19851204@163.com -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31071307*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Cheng1, Zhang Shao-zhong, Zhang Ya-zhou, Zhang Guo-heng, Wang Yun-ru, Dong Hong-yan, Zhang Zhong-ming. MicroRNA-1 and microRNA-499 directly reprogram cardiac myofibroblasts into cardiomyocyte-like cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.45.016.
share this article
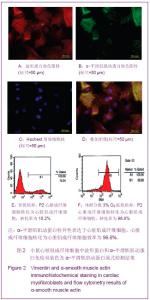
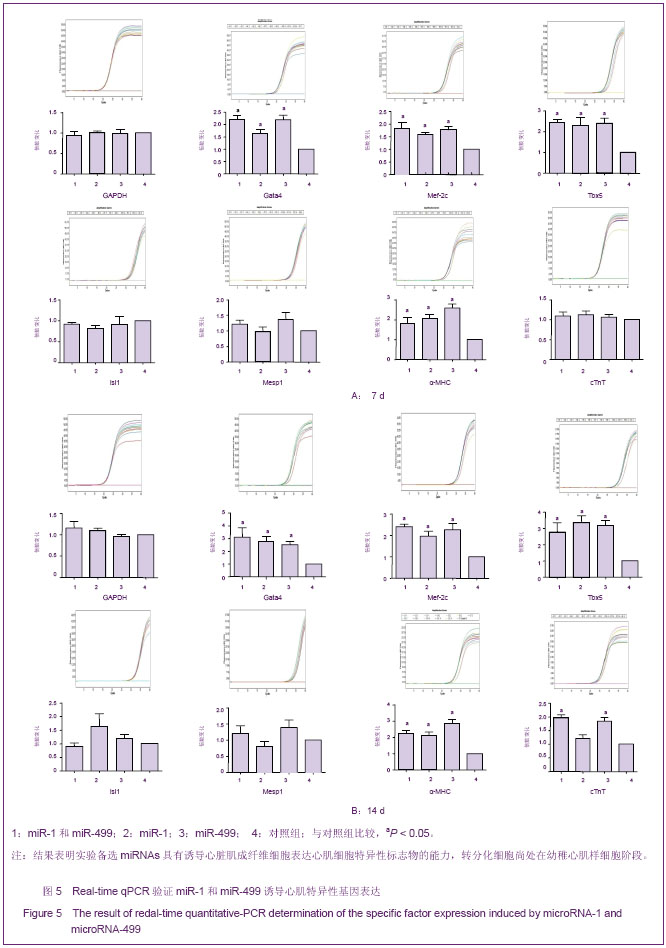
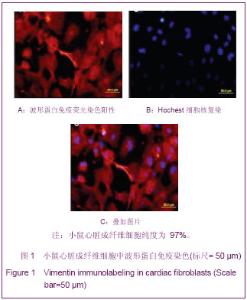
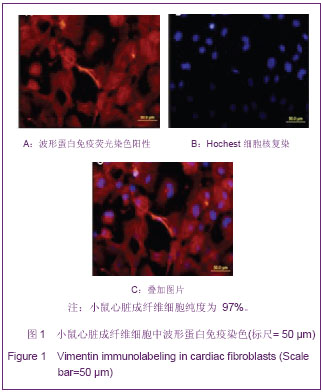
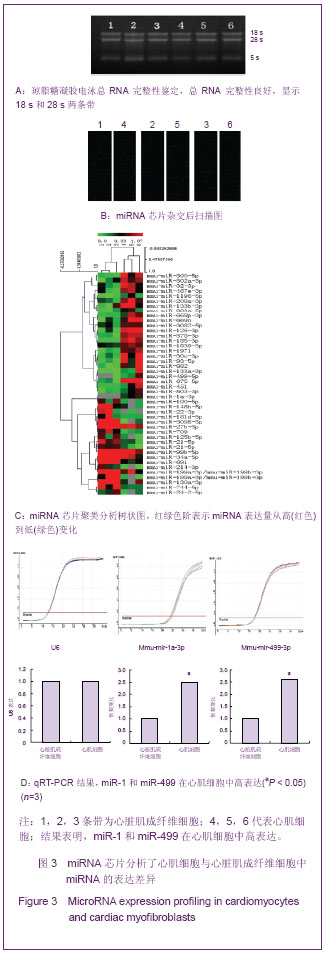
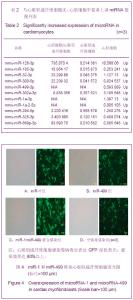
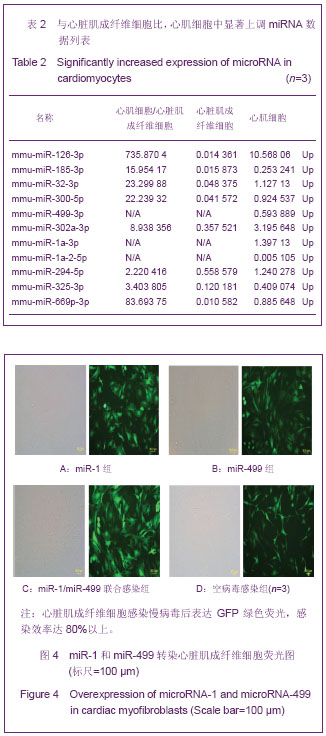
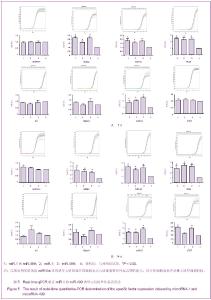
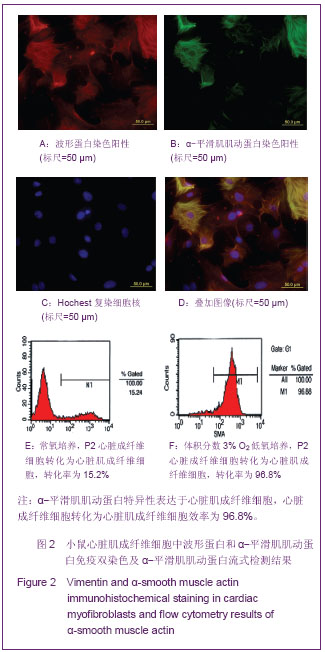
心脏成纤维细胞常氧传代至P2代,37 ℃低氧(体积分数3%O2)培养48 h,免疫荧光双染色观察波形蛋白和α-平滑肌肌动蛋白,流式细胞技术检测α-平滑肌肌动蛋白表达量。结果显示,α-平滑肌肌动蛋白特异性表达于心脏肌成纤维细胞,心脏成纤维细胞转化为心脏肌成纤维细胞效率为96.8%,见图2。 琼脂糖电泳和A260/A280的比值测定结果显示,所得RNA样本浓度和纯度达到了miRNA芯片和反转录为cDNA和real-time qPCR的实验要求。miRNA芯片分析了心肌细胞与心脏肌成纤维细胞中miRNA的表达差异,结果表明,miR-1和miR-499在心肌细胞中高表达。real-time qPCR对芯片验证结果也显示,与心脏肌成纤维细胞相比,心肌细胞中miR-1和miR-499表达量显著增加(P < 0.05),见图3,表2。 2.2 miR-1和miR-499转染心脏肌成纤维细胞的效率 携带特定miRNA的慢病毒(MOI=40)转染心脏肌成纤维细胞,3 d后,荧光显微镜下可见细胞表达绿色荧光,细胞计数检测病毒转染成功率约为80%,见图4。 2.3 心脏肌成纤维细胞中过表达miR-1和miR-499对心肌细胞发育不同阶段特异性因子的影响 Real-time qPCR检测结果显示,心脏肌成纤维细胞中过表达miR-1和miR-499后,与对照组相比,单纯转染miR-1、miR-499和联合转染miR-1/miR-499后第7天,GATA4、Tbx5、Mef-2c表达明显增高,与转染第7天比较,转染第14天时,GATA4、Tbx5、Mef-2c表达进一步增高(P < 0.05)。与对照组相比,转染第7及14天,单纯转染miR-1、miR-499和联合转染miR-1/miR-499组Mesp1、Isl1表达均无显著变化(P > 0.05)。转染第7天,与对照组相比,单纯转染miR-1、miR-499和联合转染miR-1/miR-499组α-MHC表达显著增高,在第14天时,α-MHC表达进一步增高(P < 0.05),cTnT在转染第14天开始增高。"
| [1] Karl T, Weber MD.Extracellularmatrix remodeling in heart failure: A role for DeNovo Angiotensin II generation . Circulation. 1997; 96 (11): 4065-4082. [2] Tomasek JJ, Gabbiani G, Hinz B, et al. Myofibroblasts and mechano regulation of connective tissue remodeling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.2002; 3(5): 349-363. [3] Zile MR, Mehurg SM, Arroyo JE, et al. Relationship between the temporal profile of plasma microRNA and left ventricular remodeling in patients after myocardial infarction. Circ Cardiovasc Genet.2011; 4:614-619. [4] Barrel DP.MicroRNA:genomics, biogenesis, mechanism and function.Cell 2004;116(2):281-297. [5] Felekkis K,Touvana E,Stefanou CH,et al.MicroRNAs:a newly described class of encoded molecules that play a role in health and disease.Hippokmm, 2010;14(4):236-240. [6] Chen T, Liao XP, Wen GQ, et al. Influence of RNA interference on the mitochondrial subcellular localization of alpha-synuclein and on the formation of Lewy body-like inclusions in the cytoplasm of human embryonic kidney 293 cells induced by the overexpression of alpha-synuclein. Neural Regen Res. 2012;7(2):85-90. [7] Costinean S,Zanesi N,Pekarsky Y,et al.Pre-B cell proliferation and lymphoblastic leukemia/high-grade lymphoma in E(mu)-miR155 transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(18):7024-7029. [8] O'Donnell KA,Wentzel EA,Zeller KI,et al.c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1 expression. Nature.2005; 435 (7043):839-843. [9] Ivey KN, Muth A, Arnold J, et al. MicroRNA regulation of cell lineages in mouse and human embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell.2008;2(3): 219-229. [10] Zhao Y, Samal E,Srivastava D.Serum response factor regulates a muscle speci?c microRNA that targets Hand2 during cardiogenesis. Nature.2005;436(7048):214-220. [11] Wilson K D, Hu S, Venkatasubrahmanyam S,et al. Dynamic MicroRNA Expression Programs during Cardiac Differentiation of Human Embryonic Stem Cells: Role for miR-499. Circ Cardiovasc Genet.2010;3(5): 426-435. [12] Sluijter JP,van Mil A,van Vliet P,et al.Doevendans PA,Goumans MJ .MicroRNA-1 and -499 Regulate Differentiation and Proliferation in Human-Derived Cardiomyocyte Progenitor Cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.2010;30(4):859-868. [13] Ross JS,Carlson JA,Brock G. miRNA: the new gene silencer. Am J Clin Pathol 2007;128(5):830-836. [14] Yue J.miRNA and vascular cell movement. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2011;63(8):616-622. [15] Tie Y,Liu B,Fu H,Zheng X. Circulating miRNA and cancer diagnosis.Sci China C Life Sci.2009;52(12):1117-1122. [16] Jakob P,Landmesser U . Role of microRNAs in stem/ progenitor cells and cardiovascular repair. Cardiovasc Res 2012;93(4):614-622 [17] Landgraf P, Rusu M,Sheridan R, et al. A mammalian, microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell.2007;129(7): 1401-1414 [18] Zhang C. MicroRNAs: role in cardiovascular biology and disease. Clin Sci (Lond).2008;114 (12):699-706. [19] Suh MR, Lee Y, Kim JY, et al. Human embryonic stem cells express a unique set of microRNAs. Dev Biol.2004;270(2): 488-498. [20] Chen JF,Mandel EM,Thomson JM.et a1.The role of microRNA-1 and microRNA-133 in skeletal muscle proliferation and differentiation.Nat Genet.2006;38 (2): 228-233. [21] Zhao Y,Samal E,Srivastava D.Serum response factor regulates a muscle-specific microRNA that targets Hand2 during cardiogenesis. Nature.2005; 436(7048):214-220 [22] Cordes KR,Srivastava D.MicroRNA reguIation of cardiovascular development.Circ Res.2009;104(6):724-732. [23] Ivey KN, Muth A, Arnold J, et al. MicroRNA regulation of cell lineages in mouse and human embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell.2008;2(3): 219-229. [24] van Rooij E, Sutherland LB, Liu N, et al. A signature pattern of stressres ponsive microRNAs that can evoke cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2006; 103 (48):182552 18260. [25] van Rooij E, Sutherland LB,Qi X, et al. Control of stress dependent cardiac growth and gene expression by a micr oRNA . Science.2007;316(5824):575-579. [26] I keda S, He A, Kong SW, et al. MicroRNA-1 negatively regulates expression of the hypertrophy associated cal modulin and Mef2a genes. Mol Cell Biol.2009;29 (8): 2193-2204. [27] da Costa Martins PA, BourajjajM, Gladka M, et al. Conditional dicer gene deletion in the postnatal myocardium p rovokes spontaneous cardiac remodeling. Circulation.2008;118 (15): 1567-1576. [28] Maitra M, Schluter man MK, Nichols HA. Interaction of Gata4 and Gata6 with Tbx5 is critical for normal cardiac development. Dev Biol.2009;326(2): 368-377. |
| [1] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(在线): 3-. |
| [2] | Chen Jinsong, Wang Zhonghan, Chang Fei, Liu He. Tissue engineering methods for repair of articular cartilage defect under special conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1272-1279. |
| [3] | Liu Chundong, Shen Xiaoqing, Zhang Yanli, Zhang Xiaogen, Wu Buling. Effects of strontium-modified titanium surfaces on adhesion, migration and proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and expression of bone formation-related genes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1009-1015. |
| [4] | Lin Ming, Pan Jinyong, Zhang Huirong. Knockout of NIPBL gene down-regulates the abilities of proliferation and osteogenic differentiation in mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1002-1008. |
| [5] | Zhang Wen, Lei Kun, Gao Lei, Li Kuanxin. Neuronal differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via lentivirus-mediated bone morphogenetic protein 7 transfection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 985-990. |
| [6] | Wu Zhifeng, Luo Min. Biomechanical analysis of chemical acellular nerve allograft combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for repairing sciatic nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 991-995. |
| [7] | Huang Yongming, Huang Qiming, Liu Yanjie, Wang Jun, Cao Zhenwu, Tian Zhenjiang, Chen Bojian, Mai Xiujun, Feng Enhui. Proliferation and apoptosis of chondrocytes co-cultured with TDP43 lentivirus transfected-human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1016-1022. |
| [8] | Qin Xinyu, Zhang Yan, Zhang Ningkun, Gao Lianru, Cheng Tao, Wang Ze, Tong Shanshan, Chen Yu. Elabela promotes differentiation of Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells into cardiomyocyte-like cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1046-1051. |
| [9] | Liu Mengting, Rao Wei, Han Bing, Xiao Cuihong, Wu Dongcheng. Immunomodulatory characteristics of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1063-1068. |
| [10] |
Cen Yanhui, Xia Meng, Jia Wei, Luo Weisheng, Lin Jiang, Chen Songlin, Chen Wei, Liu Peng, Li Mingxing, Li Jingyun, Li Manli, Ai Dingding, Jiang Yunxia.
Baicalein inhibits the biological behavior of hepatocellular
carcinoma stem cells by downregulation of Decoy receptor 3 expression |
| [11] | Zhang Peigen, Heng Xiaolai, Xie Di, Wang Jin, Ma Jinglin, Kang Xuewen. Electrical stimulation combined with neurotrophin 3 promotes proliferation and differentiation of endogenous neural stem cells after spinal cord injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1076-1082. |
| [12] | Huang Cheng, Liu Yuanbing, Dai Yongping, Wang Liangliang, Cui Yihua, Yang Jiandong. Transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor gene for spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1037-1045. |
| [13] | Han Bo, Yang Zhe, Li Jing, Zhang Mingchang . Regulation of limbal stem cells via Wnt signaling in the treatment of limbal stem cell deficiency [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1057-1062. |
| [14] | Li Jia, Tang Ying, Zhu Qi, Zhang Yanping, Zhou Peigang, Gu Yongchun. Transplantation of human stem cells from the apical papilla for treating dextran sulfate sodium-induced experimental colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1069-1075. |
| [15] | Zhang Shengmin, Liu Chao. Research progress in osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells induced by bioscaffold materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1107-1116. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||