Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
Stably upregulating expression of chondromodulin-Ⅰ in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Zhou Lian-zhong1, Cui Cheng-hua2, Feng Ya3, Xing Shuang-chun3, Zhai Li-jie3
- 1Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery Hospital of Tianjin, Tianjin 4th Centre Hospital, Tianjin 300161, China; 2Beijing Cancer Hospital & Beijing Institute for Cancer Research, Peking University, Beijing 100036, China; 3First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116011, Liaoning Province, China
-
Revised:2013-04-27Online:2013-11-05Published:2013-11-05 -
Contact:Zhai Li-jie, Professor, Master’s supervisor, First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116011, Liaoning Province, China lijiezhai@yahoo.com.cn -
About author:Zhou Lian-zhong★, Master, Physician, Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery Hospital of Tianjin, Tianjin 4th Centre Hospital, Tianjin 300161, China zhoulianzhong18@126.com -
Supported by:Funding: the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81271720 2012*; the General Program of Science Research of Liaoning Educational Bureau, No. L2012326 2012*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Lian-zhong, Cui Cheng-hua, Feng Ya, Xing Shuang-chun, Zhai Li-jie. Stably upregulating expression of chondromodulin-Ⅰ in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.45.005.
share this article
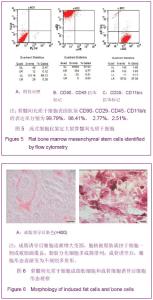
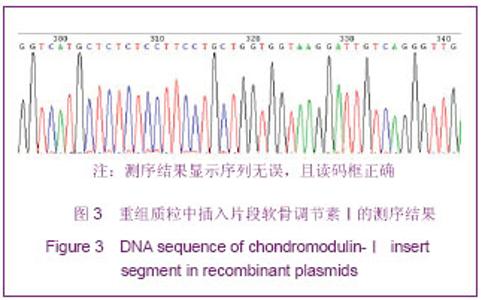
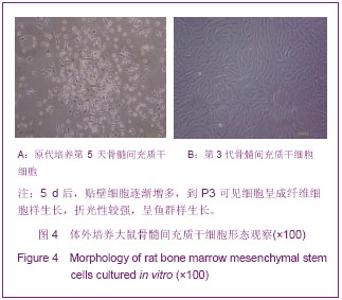
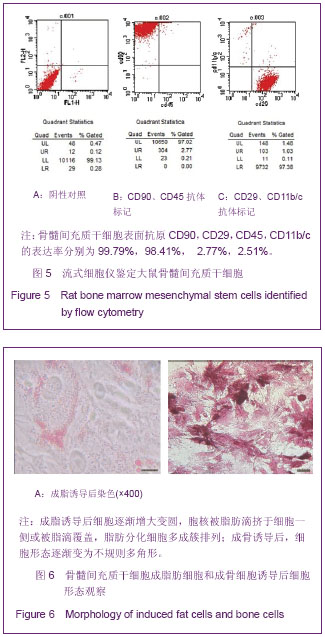
2.5 大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的鉴定结果 流式细胞仪鉴定结果:骨髓间充质干细胞表面抗原CD90、CD29、CD45、CD11b/c的表达率分别为99.79%、98.41%、 2.77%、2.51%;骨髓间充质干细胞表面阳性抗原表达均在97%以上。见图5A-C。 2.6 成脂分化及成骨分化的细胞形态和染色结果 经成脂诱导培养3 d即可见少数细胞在核周出现细小脂肪滴,折光性强。随着诱导时间的延长,胞质内脂滴增多,并彼此融合成大的脂滴。同时细胞逐渐增大变圆,胞核被脂肪滴挤于细胞一侧或被脂滴覆盖。脂肪分化细胞多成簇排列,散在偶见。培养2周后油红染色,脂滴为橙红色。经成骨诱导后,细胞形态逐渐变为不规则多角形。诱导2周后于倒置显微镜下可见细胞外小结晶,为成骨诱导后细胞分泌的钙盐结晶。培养3周后,行茜素红染色,倒置显微镜下呈现为红色斑片。见图6A,B。"
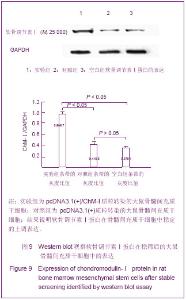
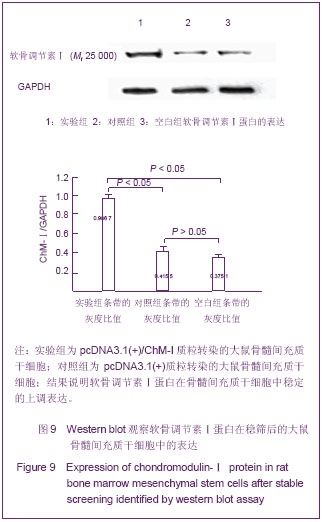
RT-PCR结果:采用软骨调节素Ⅰ/GAPDH灰度比值作为评定指标,实验组、对照组和空白组软骨调节素Ⅰ/GAPDH灰度比值的平均值分别为1.081 7± 0.223 3,0.360 1± 0.126 0,0.368 7±0.008 6;实验组与对照组和空白组间比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),对照组和空白组间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 2.9 蛋白鉴定结果 Western blot结果显示采用转骨调节素Ⅰ/ GAPDH灰度比值作为评定指标,实验组、对照组和空白组软骨调节素Ⅰ/GAPDH灰度比值的平均值分别为0.986 7± 0.020 4,0.415 5±0.020 6,0.375 1± 0.008 1;实验组与对照组和空白组间比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),对照组和空白组间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。见图9。"
| [1] Kafienah W,Mistry S,Dickinson SC,et al.Three-dimensional cartilage tissue engineering using adult stem cells from osteoarthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum.2007;56(1): 177-187. [2] Zhang J, Liu L, Gao Z,et al. Novel approach to engineer implantable nasal alar cartilage employing marrow precursor cell sheet and biodegra-dable scaffold. J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2009;67(2):257-264. [3] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC,et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147. [4] Cui L, Wu Y, Cen L, et al. Repair of articular cartilage defect in n-on-weight bearing areas using adipose derived stem cells loaded polyglycolic acid mesh. Biom-aterials.2009;30(14): 2683-2693. [5] Fan H, Hu Y, Li X,et al. Ectopic cartilage formation induced by m-esenchymal stem cells on porous gelatin-chondroitin- hyaluronate scaffold containing microsph- eres loaded with TGF-beta1. Int J Artif Organs.2006;29(6):602-611. [6] Sekiya I, Larson BL, Vuoristo JT, et al. Comparison of effect of BMP-2,-4,and-6 on invitro cartelage formation of human adult stem cells from bone marrow stroma. Cell T-issue Res.2005; 320(2):269-276. [7] An C, Cheng Y, Yuan Q, et al. IGF-1 and BMP-2 Induces Differentiatio-n of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Chondrocytes-Like Cells. Annal Biomed Eng.2010;38 (10):1647-1654. [8] Hu JC, Athanasiou KA.Low-density cultures of bovine chondrocytes: effect of scaffold material and culture system. Biomaterials.2005;26(14):2001-2012. [9] Liu X, Huang CB, Feng YJ, et al.Reinforcement of a porous collagen scaffold with surface-act-ivated PLA fibers. J Biomat Sci Polym Ed.2010;21 (6): 963-977. [10] Park H, Temenoff JS, Tabata Y,et al. Effect of dual growth factor delivery on chondrogenic differentiation of rabbit marrow mesenchymal stem cell-s encapsulated in injectable hydrogel composites. J Biomed Mater Res A.2009; 88(4): 889-897. [11] Varshney RR, Zhou R, Hao J,et al. Chondrogenesis of synovium-derived mesenchymal stem cells in gene-transf-erred co-culture system. Biomaterials.2010;31 (26):6876-6891. [12] 冯来,翟立杰,王志强. 基因芯片筛选大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞及软骨细胞的差异表达基因[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009,13(10):1886-1890 [13] 邢双春,翟立杰,王志强,等.软骨调节素I和结缔组织生长因子蛋白在骨髓间充质干细胞和软骨细胞中的差异表达[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(41):8085-8089. [14] Zhai LJ, Zhao KQ, Wang ZQ, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells display different gene expression profiles compared to hyaline and elastic chondrocytes. Int J Clin Exp Med.2011;4(1):81-90. [15] Hiraki Y, Tanaka H, Inoue H,et al.Molecular cloning of a new class of cartilage-specific matrix,chondromodulin-I,which stimulates growth of cultured chondrocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.1991;175(3):971-977. [16] Hiraki Y, Inoue H, Iyama K, et al.Identification of chondromodulin I as a novel endothelial cell growth inhibitor. Purification and its localization in the avascular zone of epiphyseal cartilage. J Biol Chem.1997;272(51): 32419-32426. [17] Inoue H, Kondo J, Koike T, et al.Identification of an autocrine chondrocyte colony-stimulating factor: chondromodulin-I stimulates the colony formation of growth plate chondrocytes in agarose culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.1997; 241(2):395-400. [18] Yoshioka M, Yuasa S, Matsumura K,et al.Chondromodulin-I maintains cardiac valvular function by preventing angiogenesis. Nat Med.2006;12(10):1151-1159. [19] Fang W, Friis TE, Long X, et al, Expression of chondromodulin-1 in the temporomandibular joint condylar cartilage and disc.J Oral Patholo Med.2010;39(4):356-360. [20] Shukunami C, Hiraki Y. Expression of cartilage-specific functional matrix chondromodulin-I mRNA in rabbit growth plate chondrocytes and its responsi-veness to growth stimuli in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.1998;249(3): 885-890. [21] Cedar SH.The function of stem cells and their future roles in healthcare .Br J Nurs.2006;15(2):104-107. [22] 王彤.骨髓间充质干细胞临床研究进展[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2010:3-13. [23] Barry FP,Murphy JM.Mesenchymal stem cells: clinical applications and biological characterization. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.2004;36(4):568-584. [24] 周文武,胡建国,马燕琳,等.人VEGF基因转染大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的实验研究[J].生命科学研究,2005,9(4).301-307. [25] Wang T,Tang W,Sun S,et al.Intravenous infusion of bonemarrow mesenchyma- l stem cells improves myocardial function in a rat model of myocardial ischemia.Crit Care Med. 2007;35(11):2587-2593. [26] Tropel P,Noel D,Platet N,et al.Isolation and characterisation of mesenchymal stem cells from adult mouse bone marrow.Exp Cell Res.2004;295(2):395-406. [27] Picinich SC,Mishra PJ,et al.The therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells.Cell tissue-based therapy.Expert Opin Biol Ther.2007;7(7):965-973. [28] 冯作化.医学分子生物学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2005: 177-194. [29] Andersson S,Davis DL,Dahlback H,et al.Cloning, structure,and expression of the mitochondrial cytochrome P-450 sterol 26-hydroxylase,a bile acid biosynthetic enzyme.J Biol Chem.1989;264(14):8222-8229. [30] Forsythe JA, Jiang BH, Iyer NV,et al.Activation of vascular endothelial growth factor gene transcription by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 1996;16(9):4606-4613. [31] Waltenberger J, Mayr U, Pentz S, et al.Functional upregulation of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor KDR by hypoxia.Circulation.1996;94(7):1647-1654. |
| [1] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(在线): 3-. |
| [2] | Chen Jinsong, Wang Zhonghan, Chang Fei, Liu He. Tissue engineering methods for repair of articular cartilage defect under special conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1272-1279. |
| [3] | Liu Chundong, Shen Xiaoqing, Zhang Yanli, Zhang Xiaogen, Wu Buling. Effects of strontium-modified titanium surfaces on adhesion, migration and proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and expression of bone formation-related genes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1009-1015. |
| [4] | Lin Ming, Pan Jinyong, Zhang Huirong. Knockout of NIPBL gene down-regulates the abilities of proliferation and osteogenic differentiation in mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1002-1008. |
| [5] | Zhang Wen, Lei Kun, Gao Lei, Li Kuanxin. Neuronal differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via lentivirus-mediated bone morphogenetic protein 7 transfection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 985-990. |
| [6] | Wu Zhifeng, Luo Min. Biomechanical analysis of chemical acellular nerve allograft combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for repairing sciatic nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 991-995. |
| [7] | Huang Yongming, Huang Qiming, Liu Yanjie, Wang Jun, Cao Zhenwu, Tian Zhenjiang, Chen Bojian, Mai Xiujun, Feng Enhui. Proliferation and apoptosis of chondrocytes co-cultured with TDP43 lentivirus transfected-human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1016-1022. |
| [8] | Qin Xinyu, Zhang Yan, Zhang Ningkun, Gao Lianru, Cheng Tao, Wang Ze, Tong Shanshan, Chen Yu. Elabela promotes differentiation of Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells into cardiomyocyte-like cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1046-1051. |
| [9] | Liu Mengting, Rao Wei, Han Bing, Xiao Cuihong, Wu Dongcheng. Immunomodulatory characteristics of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1063-1068. |
| [10] |
Cen Yanhui, Xia Meng, Jia Wei, Luo Weisheng, Lin Jiang, Chen Songlin, Chen Wei, Liu Peng, Li Mingxing, Li Jingyun, Li Manli, Ai Dingding, Jiang Yunxia.
Baicalein inhibits the biological behavior of hepatocellular
carcinoma stem cells by downregulation of Decoy receptor 3 expression |
| [11] | Zhang Peigen, Heng Xiaolai, Xie Di, Wang Jin, Ma Jinglin, Kang Xuewen. Electrical stimulation combined with neurotrophin 3 promotes proliferation and differentiation of endogenous neural stem cells after spinal cord injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1076-1082. |
| [12] | Huang Cheng, Liu Yuanbing, Dai Yongping, Wang Liangliang, Cui Yihua, Yang Jiandong. Transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor gene for spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1037-1045. |
| [13] | Han Bo, Yang Zhe, Li Jing, Zhang Mingchang . Regulation of limbal stem cells via Wnt signaling in the treatment of limbal stem cell deficiency [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1057-1062. |
| [14] | Li Jia, Tang Ying, Zhu Qi, Zhang Yanping, Zhou Peigang, Gu Yongchun. Transplantation of human stem cells from the apical papilla for treating dextran sulfate sodium-induced experimental colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1069-1075. |
| [15] | Zhang Shengmin, Liu Chao. Research progress in osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells induced by bioscaffold materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1107-1116. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||