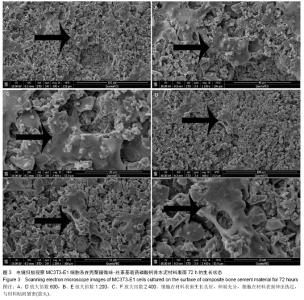
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (16): 2519-2525.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.16.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Cytocompatibility and cytotoxicity of a novel composite bone cement material composed of chitosan microsphere, alpha-tricalcium phosphate and silk fibroin
Wang Jin-ning, Pi Bin, Wang Peng, Zhu Xue-song, Yang Hui-lin
- Department of Orthopedic Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Revised:2014-02-01Online:2014-04-16Published:2014-04-16 -
Contact:Zhu Xue-song, Associate investigator, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China Yang Hui-lin, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Wang Jin-ning, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China Pi Bin, M.D., Physician, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China Wang Jin-ning and Pi Bin contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81071451, 81171689, 81301559; the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, No. BK2011264, SBK201341421; the Graduate Innovative Plan of Jiangsu Provincial Educational Bureau, No. CXZZ11_0123
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Jin-ning, Pi Bin, Wang Peng, Zhu Xue-song, Yang Hui-lin. Cytocompatibility and cytotoxicity of a novel composite bone cement material composed of chitosan microsphere, alpha-tricalcium phosphate and silk fibroin[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(16): 2519-2525.
share this article
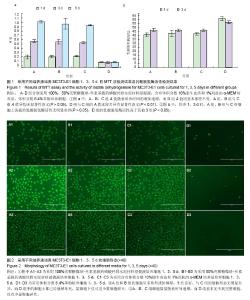
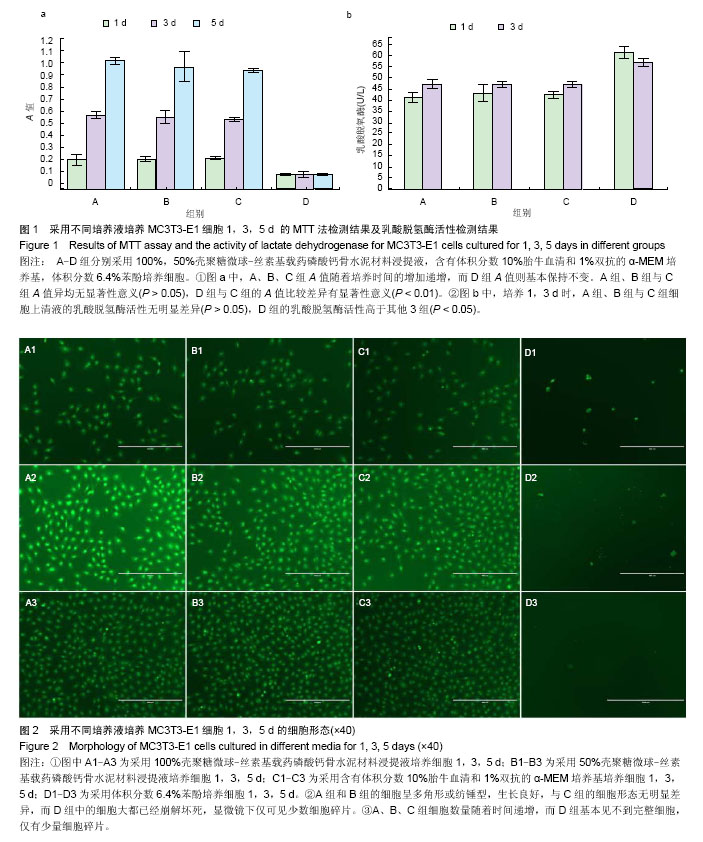
2.1 壳聚糖微球-丝素基载药磷酸钙骨水泥材料浸提液的MTT检测结果 各组在培养1,3,5 d后的MTT法检测结果见图1a,100%浸提液组、50%浸提液组、阴性对照组A值随着培养时间的增加递增,而阳性对照组A值则基本保持不变。100%浸提液组、50%浸提液组与阴性对照组1,3,5 d的A值比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),阳性对照组与阴性对照组的A值比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01)。 2.2 各组细胞上清液乳酸脱氢酶活性检测 各组在培养1,3 d后的乳酸脱氢酶活性检测结果见图1b。培养 1,3 d时,100%浸提液组、50%浸提液组与阴性对照组细胞上清液的乳酸脱氢酶活性比较差异无显著性意义 (P > 0.05),阳性对照组的乳酸脱氢酶活性高于其他3组 (P < 0.05)。 2.3 各组细胞光镜检测 在培养1,3,5 d时采用荧光倒置显微镜对各组细胞进行观察(图2),结果显示1,3,5 d时,100%浸提液组、50%浸提液组的细胞呈多角形或纺锤型,生长良好,与阴性对照组的细胞形态无明显差异,而阳性对照组中的细胞大都已经崩解坏死,显微镜下仅可见少数细胞碎片。 100%浸提液组、50%浸提液组、阴性对照细胞数量随着时间递增,而阳性对照组基本见不到完整细胞,仅有少量细胞碎片。"
| [1] Kolk A,Handschel J,Drescher W,et al.Current trends and future perspectives of bone substitute materials - from space holders to innovative biomaterials.J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2012;40(8):706-718. [2] Wang G,Yang H,Li M,et al.The use of silk fibroin/hydroxyapatite composite co-cultured with rabbit bone-marrow stromal cells in the healing of a segmental bone defect.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2010;92(2):320-325. [3] 毛海青,耿德春,朱雪松,等.椎间盘骨水泥颗粒对人髓核细胞增殖的影响并非无足轻重[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(12): 26-33. [4] Bermúdez O,Boltong MG,Driessens FCM,et al.Development of some calcium phosphate cements from combinations of α-TCP, MCPM and CaO.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 1994;5(3): 160-163. [5] Driessens FCM,Boltong MG,Zapatero MI,et al.In vivo behaviour of three calcium phosphate cements and a magnesium phosphate cement.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 1995; 6(5):272-278. [6] Koshino T,Kubota W,Morii T.Bone formation as a reaction to hydraulic hydroxyapatite thermal decomposition product used as bone cement in rabbits. Biomaterials.1995;16(2): 125-128. [7] Kurashina K,Kurita H,Hirano M,et al.Calcium phosphate cement: in vitro and in vivo studies of the α-tricalcium phosphate-dicalcium phosphate dibasic-tetracalcium phosphate monoxide system.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 1995; 6(6): 340-347. [8] Liu C,Shen W.Effect of crystal seeding on the hydration of calcium phosphate cement.J Mater Sci Mater Med.1997;8(12): 803-807. [9] Mirtchi AA,Lemaitre J,Terao N.Calcium phosphate cements: study of the beta-tricalcium phosphate--monocalcium phosphate system.Biomaterials. 1989;10(7):475-480. [10] Miyamoto Y,Ishikawa K,Fukao H,et al.In vivo setting behaviour of fast-setting calcium phosphate cement. Biomaterials. 1995;16(11):855-860. [11] Miyamoto Y,Ishikawa K,Takechi M,et al.Non-decay type fast-setting calcium phosphate cement: setting behaviour in calf serum and its tissue response. Biomaterials.1996;17(14): 1429-1435. [12] Munting E,Mirtchi AA,Lemaitre J.Bone repair of defects filled with a phosphocalcic hydraulic cement: an in vivo study.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 1993;4(3):337-344. [13] Nishimura N,Yamamuro T,Taguchi Y,et al.A new bioactive bone cement: its histological and mechanical characterization. J Appl Biomater. 1991;2(4):219-229. [14] Mirtchi AA,Lemaitre J,Munting E.Calcium phosphate cements: action of setting regulators on the properties of the beta-tricalcium phosphate-monocalcium phosphate cements. Biomaterials.1989;10(9):634-638. [15] Mirtchi AA,Lemaitre J,Munting E.Calcium phosphate cements: study of the beta-tricalcium phosphate--dicalcium phosphate--calcite cements.Biomaterials. 1990;11(2):83-88. [16] Gu Y,Chen L,Yang HL,et al.Evaluation of an injectable silk fibroin enhanced calcium phosphate cement loaded with human recombinant bone morphogenetic protein-2 in ovine lumbar interbody fusion.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2011;97(2): 177-185. [17] Qu Y,Yang Y,Li J,et al.Preliminary evaluation of a novel strong/osteoinductive calcium phosphate cement.J Biomater Appl.2011;26(3):311-325. [18] Wang L,Li C,Chen Y,et al.Poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid/nanohydroxyapatite scaffold containing chitosan microspheres with adrenomedullin delivery for modulation activity of osteoblasts and vascular endothelial cells. BioMed Res Tnt.2013;2013:530712. [19] Mao HQ,Roy K,Troung-Le VL,et al.Chitosan-DNA nanoparticles as gene carriers: synthesis, characterization and transfection efficiency.J Control Release.2001; 70(3): 399-421. [20] Varshosaz J.The promise of chitosan microspheres in drug delivery systems. Expert Opin Drug Deliv.2007;4(3):263-273. [21] Preda R,Leisk G,Omenetto F,et al.Bioengineered silk proteins to control cell and tissue functions. Methods Mol Biol. 2013; 996: 19-41. [22] Budiraharjo R,Neoh KG,Kang ET.Hydroxyapatite-coated carboxymethyl chitosan scaffolds for promoting osteoblast and stem cell differentiation. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2012;366 (1):224-232. [23] 鲁红,田宇,吴织芬.珊瑚转化羟基磷灰石应用于牙周组织工程的细胞相容性和细胞毒性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(16): 2955-2958. [24] Aubin JE. Regulation of osteoblast formation and function. Rev Endocr Metab Disord.2001;2(1):81-94. [25] Czekanska EM,Stoddart MJ,Richards RG,et al.In search of an osteoblast cell model for in vitro research.Eur Cell Mater.2012; 24:1-17. [26] Billiau A,Edy VG,Heremans H,et al.Human interferon: mass production in a newly established cell line, MG-63.Antimicrob Agents Chemother.1977;12(1):11-15. [27] Kuhn LT,Liu Y,Advincula M,et al.A nondestructive method for evaluating in vitro osteoblast differentiation on biomaterials using osteoblast-specific fluorescence. Tissue Eng Part C Methods.2010;16(6):1357-1366. [28] Roman I,Vilalta M,Rodriguez J,et al.Analysis of progenitor cell-scaffold combinations by in vivo non-invasive photonic imaging.Biomaterials. 2007;28(17):2718-2728. [29] Wang YH,Liu Y,Buhl K,et al.Comparison of the action of transient and continuous PTH on primary osteoblast cultures expressing differentiation stage-specific GFP.J Bone Miner Res.2005;20(1):5-14. [30] Wang YH, Liu Y, Rowe DW.Effects of transient PTH on early proliferation, apoptosis, and subsequent differentiation of osteoblast in primary osteoblast cultures.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.2007;292(2):E594-603. [31] Kalajzic Z,Liu P,Kalajzic I,et al.Directing the expression of a green fluorescent protein transgene in differentiated osteoblasts: comparison between rat type I collagen and rat osteocalcin promoters.Bone.2002;31(6):654-660. [32] Harrison JR,Huang YF,Wilson KA,et al.Col1a1 promoter-targeted expression of p20 CCAAT enhancer-binding protein beta (C/EBPbeta), a truncated C/EBPbeta isoform, causes osteopenia in transgenic mice.J Biol Chem.2005;280(9):8117-8124. [33] Sher LB,Harrison JR,Adams DJ,et al.Impaired cortical bone acquisition and osteoblast differentiation in mice with osteoblast-targeted disruption of glucocorticoid signaling. Calcif Tissue Int.2006;79(2):118-125. [34] Han YJ,Loo SC,Lee J,et al.Investigation of the bioactivity and biocompatibility of different glass interfaces with hydroxyapatite, fluorohydroxyapatite and 58S bioactive glass. Biofactors.2007; 30(4):205-216. [35] Fu Q,Rahaman MN,Bal BS,et al.Silicate, borosilicate, and borate bioactive glass scaffolds with controllable degradation rate for bone tissue engineering applications. II. In vitro and in vivo biological evaluation.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;95(1): 172-179. [36] Blaker JJ,Nazhat SN,Boccaccini AR.Development and characterisation of silver-doped bioactive glass-coated sutures for tissue engineering and wound healing applications. Biomaterials.2004;25(7-8):1319-1329. [37] Fu Q,Rahaman MN,Fu H,et al.Silicate, borosilicate, and borate bioactive glass scaffolds with controllable degradation rate for bone tissue engineering applications. I. Preparation and in vitro degradation.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;95(1): 164-171. [38] Lu HH,El-Amin SF,Scott KD,et al.Three-dimensional, bioactive, biodegradable, polymer-bioactive glass composite scaffolds with improved mechanical properties support collagen synthesis and mineralization of human osteoblast-like cells in vitro.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2003; 64(3): 465-474. [39] Matsuoka H,Akiyama H,Okada Y,et al.In vitro analysis of the stimulation of bone formation by highly bioactive apatite- and wollastonite-containing glass-ceramic: released calcium ions promote osteogenic differentiation in osteoblastic ROS17/2.8 cells.J Biomed Mater Res.1999;47(2):176-188. [40] Luo SH,Xiao W,Wei XJ,et al.In vitro evaluation of cytotoxicity of silver-containing borate bioactive glass.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2010;95(2):441-448. |
| [1] | Sun Qing-zhi . Nano-hydroxyapatite/silk fibroin bone substitute for repairing bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(8): 1190-1194. |
| [2] | He Yan-ping, Ma De-chun, Li Lei, Zhang Li, Zheng Shuang, Dong Ke-xin. Hemocompatibility and surface modification of artificial blood vessel materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(8): 1272-1276. |
| [3] | Li Bing-ting, Jia Ying-zhen, Liu Zhi-fang, Song Yuan, Hou Xiao-wei. Effect of freeze-dried bone xenograft and platelet-rich fibrin compound on osteogenesis and osseointegration of alveolar bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8376-8381. |
| [4] | Wu Tao, Wu Jin-hui, Zheng Guo-dong, Lu Zhi-qin, Zeng Hai-yan, Lv Jun, Xing Jian-zhou. Release behavior of icariin-chitosan/hydroxyapatite scaffolds in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8399-8404. |
| [5] | Wang Xiao-dong, Zhang Yong-hong. Preparation and performance of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2-poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyoctanoate) nanospheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8405-8408. |
| [6] | Feng Chao, Li Zhe, Lv Xiang-guo, Xu Yue-min, Fu Qiang. In vitro preparation and biochemical evaluation of oxygen generative keratin/silk fibroin compound biomaterial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8480-8486. |
| [7] | Li Tian-shi, Zeng Wen-ni, He Jun-jun. Chitin and its derivatives inhibit scar formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8504-8508. |
| [8] | Ma Song-feng, Cao Hui, Zheng Feng, Qiao Jun, Zhang Guo-ming. Concomitant cardiac valve replacement and coronary artery bypass grafting [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(5): 699-704. |
| [9] | Ning Xiao-ting, Shao Bo, Gong Zhong-cheng, Liu Hui, Ling Bin, Keremu Abass, Lin Zhao-quan, . Chondrogenesis of synovial mesenchymal stem cells co-cultured with chondrocytes on the three-dimensional scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(34): 5434-5440. |
| [10] | Lu Zhao, Jiang Xue-jun, Feng Gao-ke, Zheng Xiao-xin, Li Jun, Qin Chao-shi, Gu Wei-wang, Wang Qun, Xu Qing-ru, Huang Yi-mei, Chen Jiu-hao. Safety and histocompatibility of a novel biogradable stent implanted into the coronary artery in a porcine model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(34): 5429-5433. |
| [11] | Lu Hua-ding, Lian Li-yi, Chen Ming-wei, Dai Yu-hu. Cloning and expression of Asperguillus endo-chitosanase gene in Escherichia coli [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(34): 5490-5496. |
| [12] | Fan Zhong-bao, Rong Da-qing, Liu Qing-feng. Prolene hernia system versus polypropylene mesh plug in tension-free hernia repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(34): 5535-5539. |
| [13] | Li A-li. Absorbable ligating clip in laparoscopic hysterectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(34): 5561-5565. |
| [14] | Huang Xiao-nan. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures: high-viscosity versus low-viscosity bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(16): 2461-2467. |
| [15] | Liu Li-xia, Chen Lin. Comparison of fluoride release and solubility for different glass ionomer cements [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(16): 2480-2486. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||