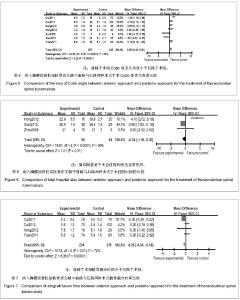
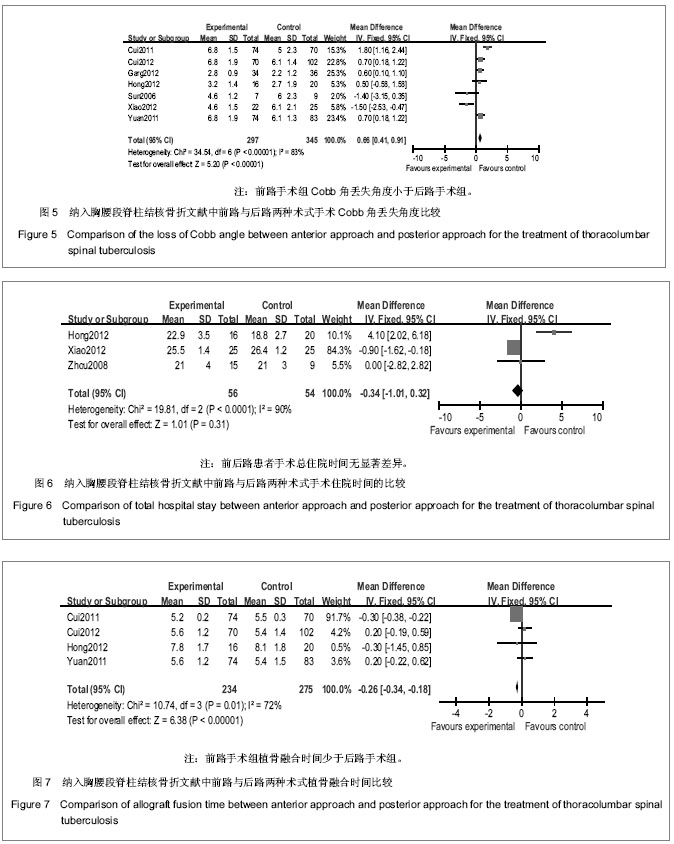
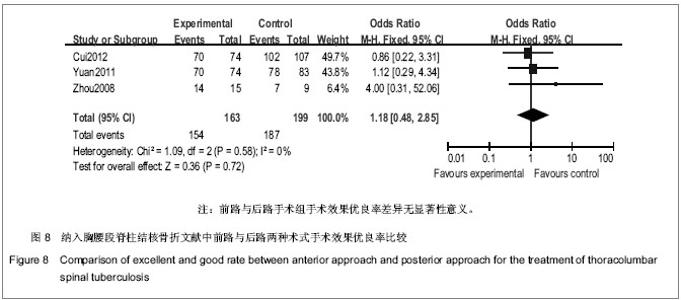
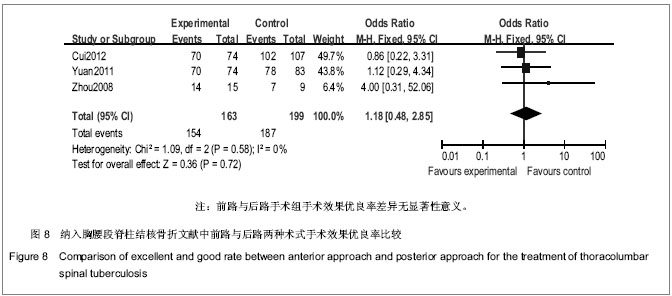
| [1] Nagashima H, Yamane K, Nishi T, et al. Recent trends in spinal infections: retrospective analysis of patients treated during the past 50 years. Int Orthop. 2010;34(3):395-399.
[2] Rasouli MR, Mirkoohi M, Vaccaro AR, et al. Spinal tuberculosis: diagnosis and management. Asian Spine J. 2012;6(4):294-308.
[3] Jin D, Qu D, Chen J,et al. One-stage anterior interbody autografting and instrumentation in primary surgical management of thoracolumbar spinal tuberculosis. Eur Spine J. 2004;13(2):114-121.
[4] Hirakawa A, Miyamoto K, Masuda T, et al. Surgical outcome of 2-stage (posterior and anterior) surgical treatment using spinal instrumentation for tuberculous spondylitis. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2010;23(2):133-138.
[5] Harimaya K, Lenke LG, Son-Hing JP, et al. Safety and accuracy of pedicle screws and constructs placed in infantile and juvenile patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(20): 1645-1651.
[6] Zhang HQ, Li JS, Guo CF,et al. Two-stage surgical management using posterior instrumentation, anterior debridement and allografting for tuberculosis of the lower lumbar spine in children of elementary school age: minimum 3-year follow-up of 14 patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132(9):1273-1279.
[7] Fuentes Ferrer M, Gutiérrez Torres L, Ayala Ramírez O, et al. Tuberculosis of the spine. A systematic review of case series. Int Orthop. 2012;36(2):221-231.
[8] Goni V, Thapa BR, Vyas S, et al. Bilateral psoas abscess: atypical presentation of spinal tuberculosis. Arch Iran Med. 2012;15(4):253-256.
[9] Buyukbebeci O, Seckiner I, Karsli B, et al. Retroperitoneoscopic drainage of complicated psoas abscesses in patients with tuberculous lumbar spondylitis. Eur spine j. 2012;21(3):470-473.
[10] Wang XB, Li J, Lu GH, Wang B, Lu C, Kang YJ. Single-stage posterior instrumentation and anterior debridement for active tuberculosis of the thoracic and lumbar spine with kyphotic deformity. Int Orthop. 2012;36(2):373-380.
[11] Ma YZ, Cui X, Li HW, et al. Outcomes of anterior and posterior instrumentation under different surgical procedures for treating thoracic and lumbar spinal tuberculosis in adults. Int Orthop. 2012;36(2):299-305.
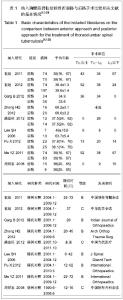
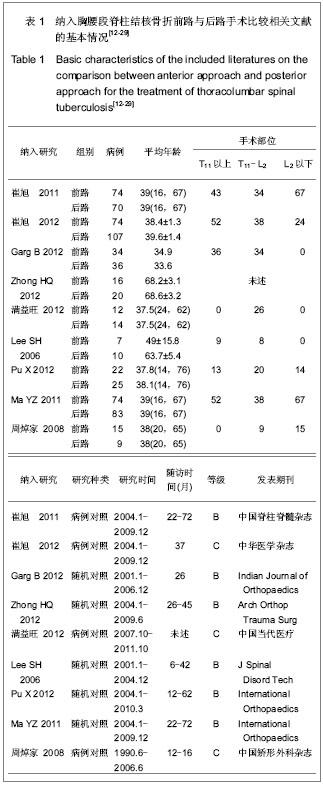
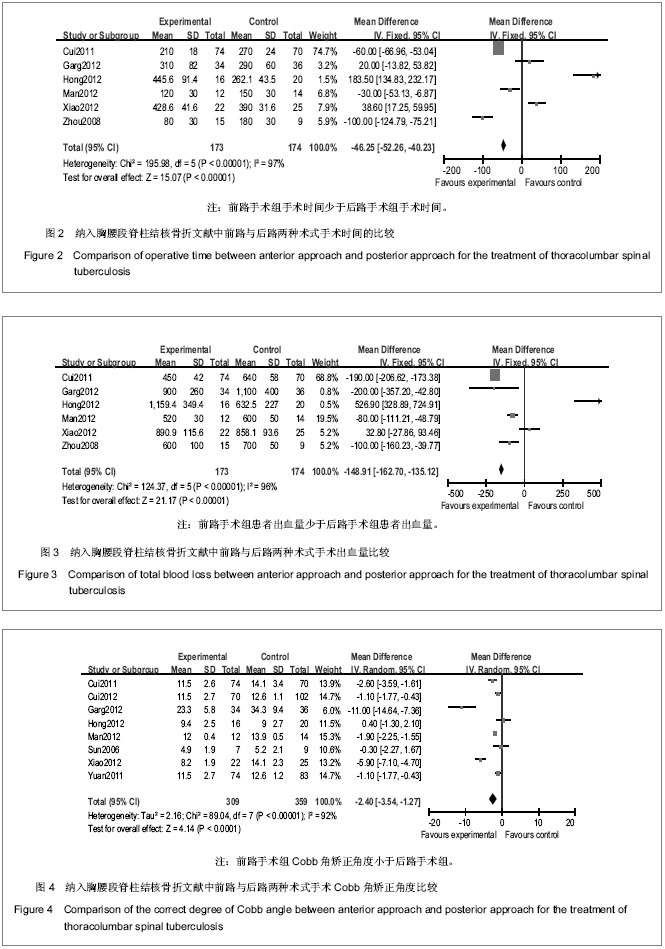
[12] 崔旭,马远征,陈兴,等.脊柱结核前后路不同术式的选择及其疗效[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志. 2011,21(10):807-812.
[13] 崔旭,马远征,李宏伟,等.前路和后路内固定治疗胸腰椎结核的疗效比较[J].中华医学杂志,2012,92(19):1325-1329.
[14] Garg B, Kandwal P, Nagaraja UB, et al. Anterior versus posterior procedure for surgical treatment of thoracolumbar tuberculosis: A retrospective analysis. Indian J Orthop. 2012; 46(2):165-170.
[15] Zhang HQ, Li JS, Zhao SS, et al. Surgical management for thoracic spinal tuberculosis in the elderly: posterior only versus combined posterior and anterior approaches. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132(12):1717-1723.
[16] 满益旺,唐接福,唐永太,等.前、后路内固定手术治疗胸腰段脊柱结核的对比研究[J].中国当代医药,2012,19(3):42-43.
[17] Lee SH, Sung JK, Park YM. Single-stage transpedicular decompression and posterior instrumentation in treatment of thoracic and thoracolumbar spinal tuberculosis: a retrospective case series. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2006;19(8):于595-602.
[18] Pu X, Zhou Q, He Q, et al. A posterior versus anterior surgical approach in combination with debridement, interbody autografting and instrumentation for thoracic and lumbar tuberculosis. Int Orthop. 2012;36(2):307-313.
[19] Ma YZ, Cui X, Li HW, et al. Outcomes of anterior and posterior instrumentation under different surgical procedures for treating thoracic and lumbar spinal tuberculosis in adults. Int Orthop. 2012;36(2):299-305.
[20] 周焯家,简月奎,李波,等.腰骶椎结核治疗的方法选择(附65例分析)[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2008,16(15):1141-1143.
[21] Waterman BR, Belmont PJ Jr, Schoenfeld AJ. Low back pain in the United States: incidence and risk factors for presentation in the emergency setting. Spine J. 2012;12(1): 63-70.
[22] Blöndal K, Viiklepp P, Guðmundsson LJ, et al. Predictors of recurrence of multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2012; 16(9):1228-1233.
[23] Dunn R, Zondagh I, Candy S. Spinal tuberculosis: magnetic resonance imaging and neurological impairment. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(6):469-473.
[24] He B, Hu Z, Hao J, et al. Posterior transpedicular debridement, decompression and instrumentation for thoracic tuberculosis in patients over the age of 60. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132(10):1407-1414.
[25] Zhang HQ, Wang YX, Guo CF, et al. One-stage posterior focus debridement, fusion, and instrumentation in the surgical treatment of cervicothoracic spinal tuberculosis with kyphosis in children: a preliminary report. Childs Nerv Syst. 2011; 27(5): 735-742.
[26] Jain AK. Tuberculosis of the spine: a fresh look at an old disease. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(7):905-913.
[27] Hodgson AR, Stock FE, Fang HS, et al. Anterior spinal fusion. The operative approach and pathological findings in 412 patients with Pott's disease of the spine. Br J Surg. 1960;48: 172-178.
[28] Mehta JS, Bhojraj SY. Tuberculosis of the thoracic spine. A classification based on the selection of surgical strategies. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001;83(6):859-863.
[29] Zhang HQ, Lin MZ, Shen KY, et al. Surgical management for multilevel noncontiguous thoracic spinal tuberculosis by single-stage posterior transforaminal thoracic debridement, limited decompression, interbody fusion, and posterior instrumentation (modified TTIF). Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132(6):751-757.
[30] Li J, Lü GH, Wang B, et al. Pedicle screw implantation in the thoracic and lumbar spine of 1-4-year-old children: evaluating the safety and accuracy by a computer tomography follow-up. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013;26(2):E46-52.
[31] Abuaku BK, Tan H, Li X, et al. A comparative analysis of tuberculosis treatment success between Hunan Province of China and Eastern Ghana. Med Princ Pract. 2010;19(6): 451-456.
[32] Arora S, Sabat D, Maini L, et al. Isolated involvement of the posterior elements in spinal tuberculosis: a review of twenty-four cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(20):e151. |