Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (39): 6970-6977.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.39.017
Previous Articles Next Articles
Plating versus intramedullary nail fixation for the treatment of humeral shaft fractures in adults: A systematic review update
Li Lian-hua, Wang Hao, Zhang Yan, Cai Yan-hong, Zhang Hao, Liu Zhi, Sun Tian-sheng
- PLA Institute of Traumatic Orthopedics, General Hospital of Beijing Military Region, Beijing 100700, China
-
Online:2013-09-24Published:2013-09-24 -
About author:Li Lian-hua☆, M.D., Attending physician, PLA Institute of Traumatic Orthopedics, General Hospital of Beijing Military Region, Beijing 100700, China lilianhua@medmail.com.cn
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Lian-hua, Wang Hao, Zhang Yan, Cai Yan-hong, Zhang Hao, Liu Zhi, Sun Tian-sheng. Plating versus intramedullary nail fixation for the treatment of humeral shaft fractures in adults: A systematic review update[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(39): 6970-6977.
share this article

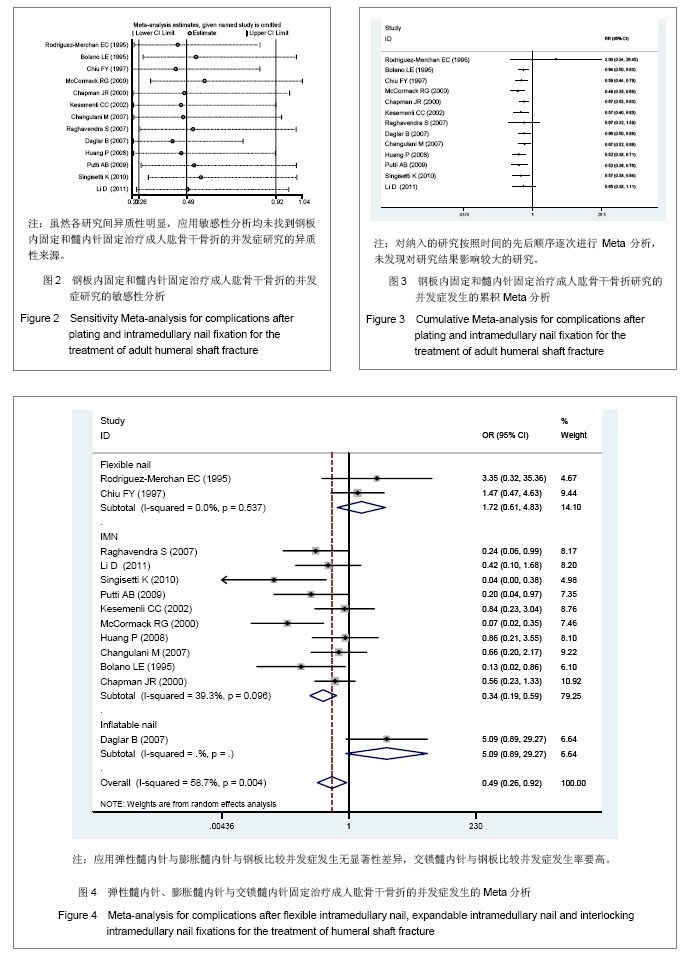
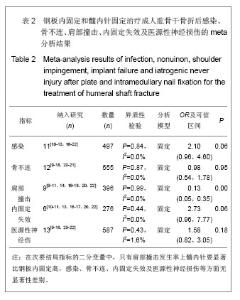
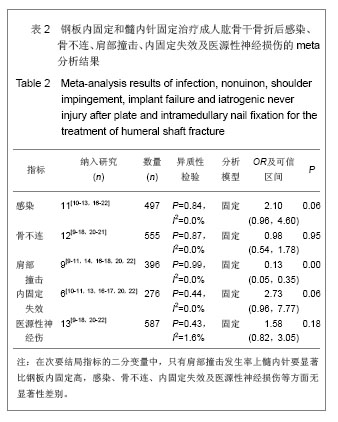
2.1 检索结果分析及基线质量评价 共查到相关文献312篇。按纳入标准进行筛选后获取15篇文献[8-22]。其中研究地点3篇在中国大陆[15, 21-22],1篇在中国台湾省[12];11篇在其他国家[8-11,13-14,16-20],13 篇为英文[8-20],2 篇为中文[21-22]。各纳入研究的基本情况见表1。 2.2 Meta分析结果 2.2.1 主要结果指标 并发症:实验关注的并发症主要是指肱骨干骨折中、肱骨干骨折后发生医源性神经损伤、肱骨干骨折后感染、内固定失效、肩部撞击及活动受限、骨不连等事件发生的总和。有13个研究报告了钢板与髓内针治疗成人肱骨干骨折后并发症的发生率[9-14, 16-22],共866例患者,其中钢板固定420例,髓内针固定446例,钢板固定组发生并发症108例,髓内针固定组发生并发症169例。各研究间异质性明显(P=0.00,I2=55%),应用敏感性分析及累积Meta分析,见图2,3,均未找到异质性来源。将髓内针类型、钢板类型、研究性质、研究地点分别进行Meta回归分析,结果显示,钢板类型、髓内针类型、研究性质、研究地点的P值分别为0.34,0.02,0.96,0.76。这说明髓内针类型对异质性的影响较为明显,究其原因可能与不同髓内针的手术操作复杂程度及固定效果对并发症的发生造成影响。为消除髓内针类型对Meta分析造成的异质性,实验按照髓内针类型进行亚组Meta分析,分析模型采用随机模型,如图4所示,总体的Meta分析结果显示OR=0.49(0.26,0.92),P=0.01,髓内针发生并发症的风险要高于钢板。由于OR可信区间的上限0.92接近1,因此在接受这一结论还需要谨慎。再看亚组分析结果,弹性髓内针、膨胀髓内针与交锁髓内针亚组OR分别为1.72(0.61-4.83),5.09(0.88,29.27)及0.37(0.19,0.59),对应的P值分别为0.30,0.07及0.00。"
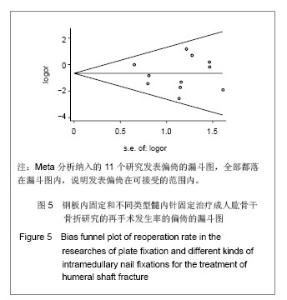
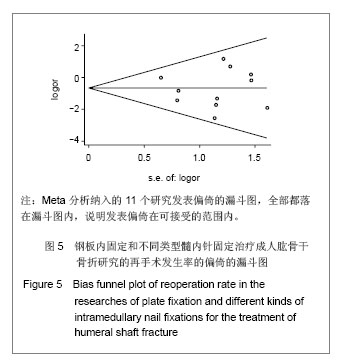
这种结果提示只有交锁髓内针亚组具有显著性统计学差异,选择钢板或交锁髓内针治疗成人肱骨干骨折与肱骨干骨折后并发症发生率之间存在中等联系强度,并且有统计学上差异有显著性意义。采用弹性髓内针及膨胀髓内针与钢板治疗相比较并发症发生率相当。采用 Egger’s 方法检验纳入文献的发表偏倚,P=0.91,无显著性发表偏倚。 再手术:研究关注的再手术主要是由于发生医源性神经损伤、肱骨干骨折后感染、内固定失效、肩部撞击及活动受限、骨不连等并发症需要手术治疗的病例。有11个研究报告了钢板与髓内针治疗成人肱骨干骨折再手术的发生率[9-14, 16-20],共498例患者,其中钢板固定252例,髓内针固定246例,钢板固定组发生并发症22例,髓内针固定组发生并发症40例。各研究间无明显异质性(P=0.36,I2=5.3%),按照髓内针类型进行亚组Meta分析,分析模型采用固定模型,总体的Meta分析结果显示OR=0.49(0.28,0.85),P=0.01,髓内针治疗后再手术的风险要高于钢板。亚组分析弹性髓内针、膨胀髓内针与交锁髓内针亚组OR分别为1.21(0.40-3.70),3.40(0.36,36.27)及0.28(0.14,0.57),对应的P值分别为0.73,0.31及0.00,这种结果提示只有交锁髓内针亚组差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),选择钢板或交锁髓内针治疗成人肱骨干骨折与肱骨干骨折后再手术发生率之间存在中等联系强度,并且有统计学上的显著性差异。采用弹性髓内针及膨胀髓内针与钢板治疗相比较并发症发生率相当。采用Egger’s方法检验纳入文献的发表偏倚(漏斗图见图5),从图形上可见各个研究基本对称,P=0.69,无显著性发表偏倚。"
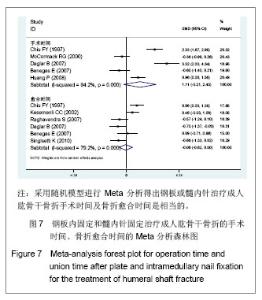
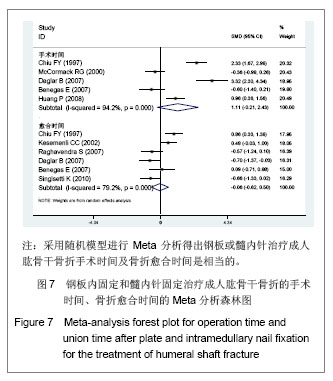
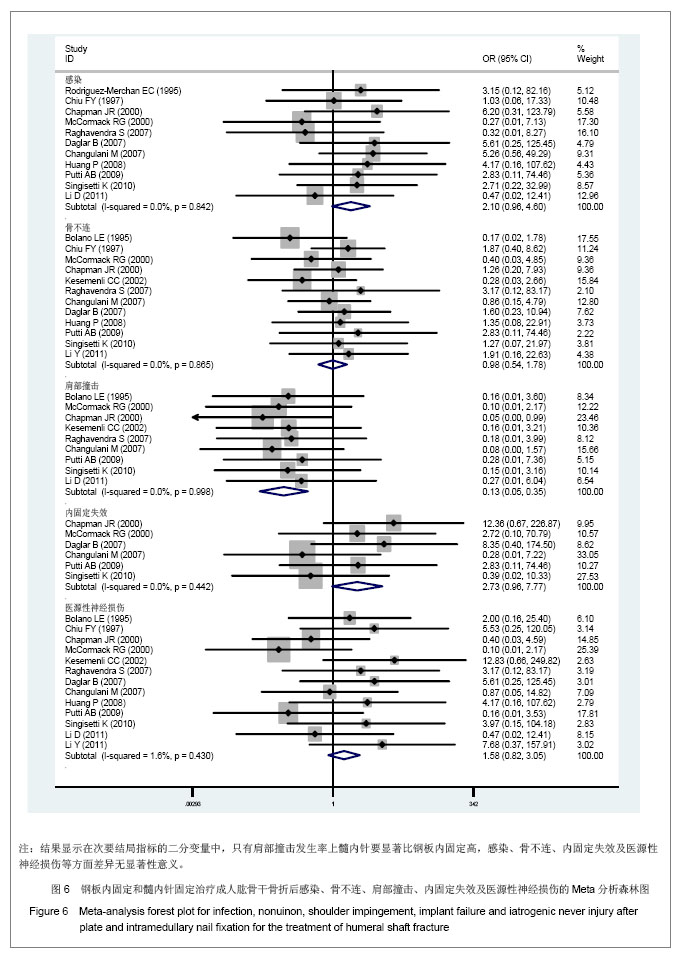
只有肩部撞击有显著性差异,OR及可信区间0.13(0.05,0.35),P=0.00,髓内针治疗与肱骨干骨折后肩部撞击发生率之间存在较强的联系强度,且差异有显著性意义。在感染及内固定失败发生上,虽然两者的P值都大于0.05,但两者的OR分别为2.1和2.73,且OR的下限接近1,说明钢板固定与肱骨干骨折后感染、内固定失效发生为中等联系强度,接受“钢板或髓内针治疗成人肱骨干骨折后发生感染及内固定失败的概率相当”这一结论仍要持谨慎态度。 连续变量:在次要结局指标中连续变量包括手术时间(min)[8, 12-13, 16, 21]、骨折愈合时间(周)[8, 12-14, 18, 20]。研究中没有提供算术均数与标准差,但提供了最大、最小值者,用cochrane手册中处理缺失值的方法进行换算。异质性检验显示手术时间、愈合时间都具有异质性,考虑可能与每个研究计算手术时间、愈合时间的方法和标准不同有关,而这种异质性无法消除。采用随机模型进行Meta分析得出的两者的P值分别为0.10和0.84,说明钢板或髓内针治疗成人肱骨干骨折手术时间及骨折愈合时间是相当的,见图7。"
| [1]Day CS, Yeh AC, Franko O, et al. Musculoskeletal medicine: an assessment of the attitudes and knowledge of medical students at Harvard Medical School. Acad Med. 2007;82(5):452-457.
[2]Sarmiento A, Waddell JP, Latta LL. Diaphyseal humeral fractures: treatment options. Instr Course Lect. 2002;51: 257-269.
[3]Kreb DL, Blokhuis TJ, van Wessem KJ, et al. Intramedullary nailing without interlocking screws for femoral and tibial shaft fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;133(8):1109-1113.
[4]Heineman DJ, Poolman RW, Nork SE, et al. Plate fixation or intramedullary fixation of humeral shaft fractures. Acta Orthop. 2010;81(2):216-223.
[5]Tsourvakas S, Alexandropoulos C, Papachristos I, et al. Treatment of humeral shaft fractures with antegrade intramedullary locking nail. Musculoskelet Surg. 2011;95(3): 193-198.
[6]Steffner RJ, Lee MA. Emerging concepts in upper extremity trauma: humeral shaft fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 2013; 44(1):21-33.
[7]Strohm PC, Reising K, Hammer T, et al. Humerus shaft fractures - where are we today? Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2011;78(3):185-189.
[8]Benegas E, Amódio DT, Correia LFM, et al. Prospective randomized comparative study between surgical treatment of humeral shaft fractures with bridging plate and interlocking nail (preliminary). Acta Ortop Bras. 2007;15(2):87-92.
[9]Bolano LE, Vasicek V. Operative treatment of humerus shaft fractures: A prospective randomized study comparing intramedullary nailing with dynamic compression plating. Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 1995.
[10]Changulani M, Jain UK, Keswani T. Comparison of the use of the humerus intramedullary nail and dynamic compression plate for the management of diaphyseal fractures of the humerus. A randomised controlled study. Int Orthop. 2007; 31(3):391-395.
[11]Chapman JR, Henley MB, Agel J, et al. Randomized prospective study of humeral shaft fracture fixation: intramedullary nails versus plates. J Orthop Trauma. 2000; 14(3):162-166.
[12]Chiu FY, Chen CM, Lin CF, et al. Closed humeral shaft fractures: a prospective evaluation of surgical treatment. J Trauma. 1997;43(6):947-951.
[13]Da?lar B, Delialio?lu OM, Ta?ba? BA, et al. Comparison of plate-screw fixation and intramedullary fixation with inflatable nails in the treatment of acute humeral shaft fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2007;41(1):7-14.
[14]Kesemenli CC, Suba?i M, Arslan H, et al. Comparison between the results of intramedullary nailing and compression plate fixation in the treatment of humerus fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2003;37(2):120-125.
[15]Li Y, Wang C, Wang M, et al. Postoperative malrotation of humeral shaft fracture after plating compared with intramedullary nailing. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(6): 947-954.
[16]McCormack RG, Brien D, Buckley RE, et al. Fixation of fractures of the shaft of the humerus by dynamic compression plate or intramedullary nail. A prospective, randomised trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000;82(3):336-339.
[17]Putti AB, Uppin RB, Putti BB. Locked intramedullary nailing versus dynamic compression plating for humeral shaft fractures. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2009;17(2):139-141.
[18]Raghavendra S, Bhalodiya HP. Internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the humerus by dynamic compression plate or intramedullary nail: A prospective study. Indian J Orthop. 2007; 41(3):214-218.
[19]Rodríguez-Merchán EC. Compression plating versus hackethal nailing in closed humeral shaft fractures failing nonoperative reduction. J Orthop Trauma. 1995;9(3):194-197.
[20]Singisetti K, Ambedkar M. Nailing versus plating in humerus shaft fractures: a prospective comparative study. Int Orthop. 2010;34(4):571-576.
[21]黄鹏,唐佩福,姚琦,等.带锁髓内钉与锁定加压钢板内固定治疗肱骨干骨折的随机对比研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2008, 23(9):3.
[22]李丹,王刚,谷贵山,等.髓内钉与钢板治疗肱骨干骨折患者的疗效及安全性比较[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2011,37(2):342-344.
[23]An ZQ, He XJ, Jiang CL, et al. Treatment of middle third humeral shaft fractures: minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis versus expandable nailing. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2012;22(3):193-199.
[24]Chao TC, Chou WY, Chung JC, et al. Humeral shaft fractures treated by dynamic compression plates, Ender nails and interlocking nails. Int Orthop. 2005;29(2):88-91.
[25]Chen F, Wang Z, Bhattacharyya T. Outcomes of nails versus plates for humeral shaft fractures: a Medicare cohort study. J Orthop Trauma. 2013;27(2):68-72.
[26]Denies E, Nijs S, Sermon A, et al. Operative treatment of humeral shaft fractures. Comparison of plating and intramedullary nailing. Acta Orthop Belg. 2010;76(6):735-742.
[27]Flinkkilä T, Hyvönen P, Siira P, et al. Recovery of shoulder joint function after humeral shaft fracture: a comparative study between antegrade intramedullary nailing and plate fixation. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2004;124(8):537-541.
[28]Khan AS, Afzal W, Anwar A. Comparison of shoulder function, radial nerve palsy and infection after nailing versus plating in humeral shaft fractures. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2010; 20(4):253-257.
[29]Lin J. Treatment of humeral shaft fractures with humeral locked nail and comparison with plate fixation. J Trauma. 1998;44(5):859-864.
[30]Bhandari M, Devereaux PJ, McKee MD, et al. Compression plating versus intramedullary nailing of humeral shaft fractures--a meta-analysis. Acta Orthop. 2006;77(2):279-284.
[31]李连华,孙天胜,刘智,等.钢板内固定和髓内针固定比较治疗成人肱骨干骨折疗效的系统评价[J].中国循证医学杂志,2008, 8(8): 662-667.
[32]Kurup H, Hossain M, Andrew JG. Dynamic compression plating versus locked intramedullary nailing for humeral shaft fractures in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;(6): CD005959.
[33]Ouyang H, Xiong J, Xiang P, et al. Plate versus intramedullary nail fixation in the treatment of humeral shaft fractures: an updated meta-analysis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013;22(3): 387-395.
[34]Wang X, Chen Z, Shao Y, et al. A meta-analysis of plate fixation versus intramedullary nailing for humeral shaft fractures. J Orthop Sci. 2013;18(3):388-397.
[35]Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. 1996;17(1):1-12. |
| [1] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [2] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [3] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [4] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [5] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [6] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [7] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [8] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [9] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [10] | Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976. |
| [11] | Zhan Fangbiao, Cheng Jun, Zou Xinsen, Long Jie, Xie Lizhong, Deng Qianrong. Intraoperative intravenous application of tranexamic acid reduces perioperative bleeding in multilevel posterior spinal surgery: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 977-984. |
| [12] | Zhong Yuanming, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng, Wu Zhuotan, He Bingkun, Wu Sixian. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty and unilateral pedicle approach percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 456-462. |
| [13] | Li Yang, Zhang Mingyong. Meta-analysis of the effect of double Endobutton and clavicular hook plate on the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 463-470. |
| [14] | Li Yanle, Yue Xiaohua, Wang Pei, Nie Weizhi, Zhang Junwei, Tan Yonghai, Jiang Hongjiang. Intramedullary nail fixation versus plate fixation in the treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 471-476. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Han Shufeng. Interlocking intramedullary nail for proximal femur versus proximal femoral anti-rotation intramedullary nail or proximal femoral anti-rotation intramedullary nail of Asian for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 477-485. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||