Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (39): 6954-6961.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.39.015
Previous Articles Next Articles
Biomechanical factors in the design of new femoral neck screw in children
Huang Xuan-huai, Liao Ying, Fan Wei-jie, Chen Zhi-wei
- Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of University of South China, Hengyang 421001, Hunan Province, China
-
Online:2013-09-24Published:2013-09-24 -
Contact:Liao Ying, Professor, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of University of South China, Hengyang 421001, Hunan Province, China liaoying8281462@163.com -
About author:Huang Xuan-huai★, Master, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of University of South China, Hengyang 421001, Hunan Province, China huangxuanhuai@163.com -
Supported by:Program of China Hunan Science & Technology Department, No. 2009SK3136*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Huang Xuan-huai, Liao Ying, Fan Wei-jie, Chen Zhi-wei . Biomechanical factors in the design of new femoral neck screw in children[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(39): 6954-6961.
share this article
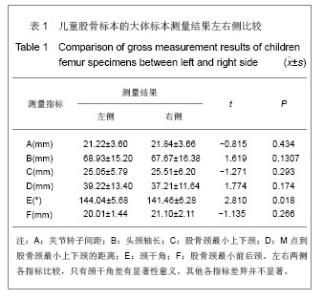
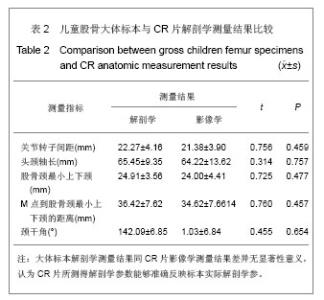
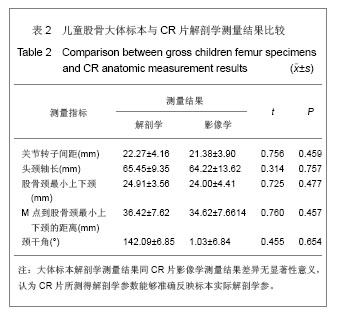
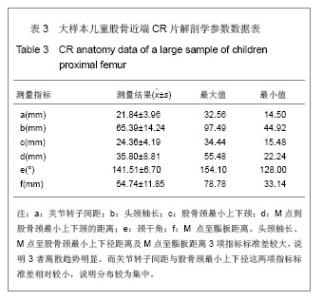
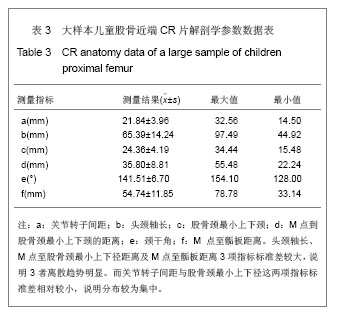
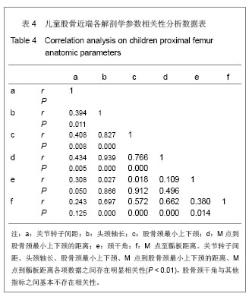
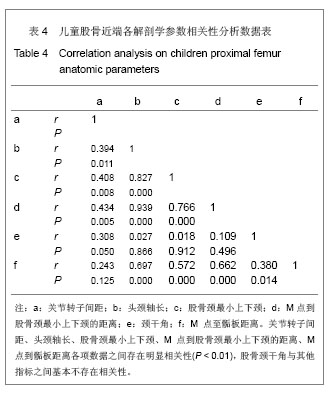
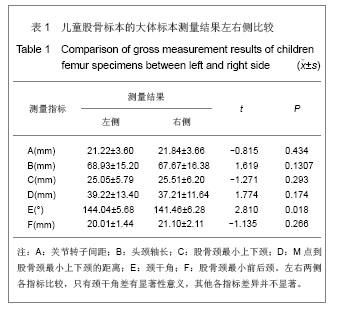
2.1 大体标本观察结果 本年龄段儿童股骨近端发育变化差异较大。和成人相比,儿童的股骨颈较为细小,狭窄,尚且发育不完善,小转子的位置较成人更为偏向后方。股骨头大部分为关节软骨所覆盖,股骨大、小转子没有完全骨化,股骨头关节软骨和大小转子的软骨在股骨颈的后方连接到一起。颈干角明显较成人偏大。 2.2 大体标本、CR片解剖学测量结果及统计学分析 所测量的儿童股骨近端各项指标均符合正态分。将大体标本所得数据左右两侧配对进行t检验,结果显示左右两侧股骨标本在关节转子间距、头颈轴长、股骨颈最小上下颈、M点到股骨颈最小上下颈的距离、这些指标上差异并无显著性意义(P > 0.05),而左右两侧在颈干角差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),但并不排除因为测量工具限制所导致系统误差(P > 0.01),具体数据见表1。"
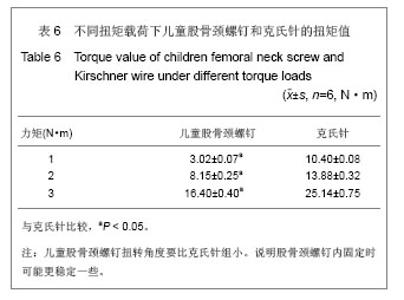
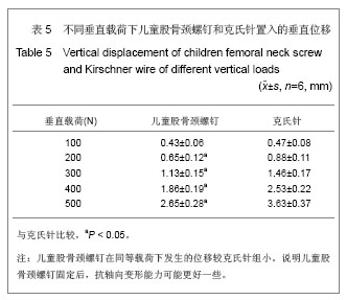
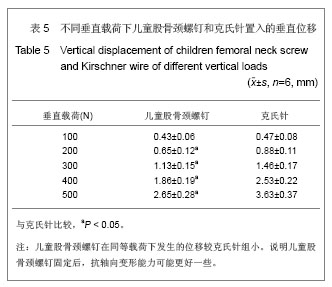
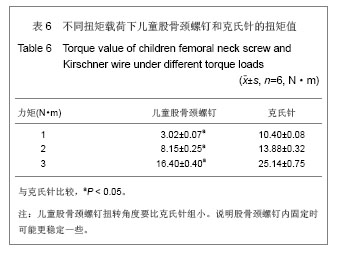
按其生物力学意义:EF=P/DL,式中EF表示刚度,P为轴向载荷,DL为压缩位移。在500 N载荷作用下,儿童股骨颈螺钉组的刚度为(190.74±20.88) N/mm,克氏针组的刚度为(138.95±15.19) N/mm,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。在抗压缩能力上儿童股骨颈螺钉要强于克氏针。 在同样加载3 N•m的力矩作用下,儿童股骨颈螺钉组扭转角度为(16.40±0.40)°,克氏针组为(25.14±0.75)°,儿童股骨颈螺钉扭转角度要比克氏针组小,两者比较,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。扭转刚度是指股骨在扭矩载荷作用下,抵抗扭转变形的能力大小,它是反映内固定是否稳定的一重要指标,骨折端的旋转移位常导致骨折畸形愈合或不愈合。见表6。 按其生物力学意义表示:为GJp=Mn/¢,式中GJp表示扭转刚度,Mn为扭矩大小,¢为绝对扭角。在3 N•m扭矩作用下,儿童股骨颈螺钉组的扭转刚度为(0.180± 0.045) N•m/(°),克氏针组的扭转刚度(0.120± 0.036) N•m/(°),两者比较,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。由此看来在抗扭能力上儿童股骨颈螺钉要强于克氏针。 "
| [1]Shrader MW, Jacofsky DJ, Stans AA,et al. Femoral neck fractures in pediatric patients: 30 years experience at a level 1 trauma center. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;454: 169-173.
[2]Li Y, Heyworth BE, Glotzbecker M, et al. Comparison of titanium elastic nail and plate fixation of pediatric subtrochanteric femur fractures. J Pediatr Orthop. 2013; 33(3):232-238.
[3]王满宜,杨庆铭,曾烦芳,等.骨折治疗的AO原则[M].北京:华夏出版社.2003:682-683.
[4]吉士俊.小儿髋关节外科学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社. 2005:15-23.
[5]赵炬才,张铁良,髋关节外科学[M].北京:中国医药科技出版社出版.1992:32-42.
[6]马若凡,刘尚礼,许杰.国人股骨上段测量及其临床意义[J].临床骨科杂志,2002,5 (3):164-166.
[7]Heidari N, Eberl R, Wiklicky S, et al. Anatomical landmarks in the paediatric distal radius: a new method for measuring epiphyseal height. Surg Radiol Anat. 2011;33(8):683-687.
[8]陈振光,余国荣,喻爱喜,等.儿童股骨头骺板的解剖定位及其临床意义[J].中华实验外科,1997,14(2):92-93.
[9]Ogden JA. Changing patterns of proximal femoral vascularity. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974;56(5):941-950.
[10]郭世绂.临床骨科解剖学[M].天津:天津科学技术出版社,1991: 707-734.
[11]王启华,孙博.临床解剖学丛书—四肢分册[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,1998: 246-258.
[12]Akahane T, Fujioka F, Shiozawa R. A transepiphyseal fracture of the proximal femur combined with a fracture of the mid-shaft of ipsilateral femur in a child: a case report and literature review. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2006;126(5):330-334.
[13]Morsy HA. Complications of fracture of the neck of the femur in children. A long-term follow-up study. Injury. 2001;32(1): 45-51.
[14]Mirdad T. Operative treatment of femoral shaft fractures in children: a nine-year experience in a Saudi Arabian population. Injury. 2000;31(10):769-771.
[15]Flynn JM, Wong KL, Yeh GL, et al. Displaced fractures of the hip in children. Management by early operation and immobilisation in a hip spica cast. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002; 84(1):108-112.
[16]Hedin H, Hjorth K, Rehnberg L, et al. External fixation of displaced femoral shaft fractures in children: a consecutive study of 98 fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2003;17(4):250-256.
[17]Cheng JC, Tang N. Decompression and stable internal fixation of femoral neck fractures in children can affect the outcome. J Pediatr Orthop. 1999;19(3):338-343.
[18]Yeranosian M, Horneff JG, Baldwin K, et al. Factors affecting the outcome of fractures of the femoral neck in children and adolescents: a systematic review. Bone Joint J. 2013; 95-B (1):135-142.
[19]Eberl R, Singer G, Ferlic P, et al. Post-traumatic coxa vara in children following screw fixation of the femoral neck. Acta Orthop. 2010;81(4):442-445.
[20]Pape HC, Krettek C, Friedrich A, et al. Long-term outcome in children with fractures of the proximal femur after high-energy trauma. J Trauma. 1999;46(1):58-64.
[21]Plánka L, Chalupová P, Charvátová M, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging for detection of rotational deformities in children with femoral shaft fractures treated by the ESIN method. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2010;77(1):39-42.
[22]Gopinathan NR, Chouhan D, Akkina N, et al. Case report: Bilateral femoral neck fractures in a child and a rare complication of slipped capital epiphysis after internal fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(10):2941-2945.
[23]Zhang H, Jin L, Li W, et al. Anterior dislocation of the sacroiliac joint with complex fractures of the pelvis and femur in children: a case report. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2013 Mar 22.
[24]Park SS, Noh H, Kam M. Risk factors for overgrowth after flexible intramedullary nailing for fractures of the femoral shaft in children. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(2):254-258.
[25]Bandyopadhyay R, Mukherjee A. Short term complications of titanium elastic nail in the treatment of diaphyseal fracture of the femur in children. Open Orthop J. 2013;7:12-17.
[26]Brousil J, Hunter JB. Femoral fractures in children. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2013;25(1):52-57.
[27]Bieger R, Ignatius A, Reichel H, et al. Biomechanics of a short stem: In vitro primary stability and stress shielding of a conservative cementless hip stem.J Orthop Res. 2013;31(8): 1180-1186.
[28]Wouters I, Almonroeder T, Dejarlais B, et al. Effects of a movement training program on hip and knee joint frontal plane running mechanics. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2012;7(6): 637-646.
[29]Allen MJ. Advances in total joint replacement in small animals. J Small Anim Pract. 2012;53(9):495-506.
[30]Probst A, Schneider T, Hankemeier S, et al. The prosthesis nail -- a new stable fixation device for periprosthetic fractures and critical fractures of the proximal femur. Unfallchirurg. 2003;106(9):722-731.
[31]Yu YX, Ma JZ, Zhu LB, et al. Failure of internal fixation on displaced femoral neck fractures in adults under fifty-five years old. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2012;25(7):542-545.
[32]马元璋,郑祖根,万鹏,等.临床骨内固定学[M].合肥:安徽科学技术出版社,1999.
[33]Khan SK, Khanna A, Parker MJ. Posterior multifragmentation of the femoral neck: does it portend a poor outcome in internally fixed intracapsular hip fractures? Injury. 2009;40(3): 280-282.
[34]Gao K, Gao W, Li F, et al. Treatment of ipsilateral concomitant fractures of proximal extra capsular and distal femur. Injury. 2011;42(7):675-681. Injury. 2011;42(7):675-681.
[35]Bonnaire F, Lein T, Hohaus T,et al. Prosthetic care of proximal femur fractures. Unfallchirurg. 2005;108(5):387-399.
[36]秦步平,王以进,黄圣达,等.三枚双头空心加压钉(DECS)治疗股骨颈骨折的生物力学研究与临床应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2002,10(8):810-812.
[37]康少英,张克亮.旋髂深血管骨瓣移植治疗小儿股骨颈骨折骨不连[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2006,21(3):220.
[38]李坚,唐尚权,付纳新,等.儿童青少年股骨颈colonnaⅡ型骨折的两种内固定方法比较研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2008, 23(3):253-254.
[39]朱通伯,戴克戎.骨科手术学[M].第2版.北京:人民卫生出版社, 1998:790-793.
[40]Quick TJ, Eastwood DM.Pediatric fractures and dislocations of the hip and pelvis.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2005;432:87-96.
[41]周健,卜海富.儿童股骨颈骨折的临床研究[J].安徽医科大学学报,1997,32(3): 235-237.
[42]Mecham N. Pediatric proximal femur fractures--what the trauma nurse should know. J Trauma Nurs. 2003;10(2):52-55.
[43]Togrul E, Bayram H, Gulsen M,et al. Fractures of the femoral neck in children: long-term follow-up in 62 hip fractures. Injury. 2005;36(1):123-130.
[44]Mirdad T. Fractures of the neck of femur in children: an experience at the Aseer Central Hospital, Abha, Saudi Arabia. Injury. 2002;33(9):823-827. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [3] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [4] | Luo Lin, Song Naiqing, Huang Jin, Zou Xiaodong. Review and prospect of international research on preschool children’s movement development assessment: a CiteSpace-based visual analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1270-1276. |
| [5] | Xu Yulin, Shen Shi, Zhuo Naiqiang, Yang Huilin, Yang Chao, Li Yang, Zhao Heng, Zhao Lu. Biomechanical comparison of three different plate fixation methods for acetabular posterior column fractures in standing and sitting positions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 826-830. |
| [6] | Cai Qunbin, Zou Xia, Hu Jiantao, Chen Xinmin, Zheng Liqin, Huang Peizhen, Lin Ziling, Jiang Ziwei. Relationship between tip-apex distance and stability of intertrochanteric femoral fractures with proximal femoral anti-rotation nail: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 831-836. |
| [7] | Song Chengjie, Chang Hengrui, Shi Mingxin, Meng Xianzhong. Research progress in biomechanical stability of lateral lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 923-928. |
| [8] | Xie Chongxin, Zhang Lei. Comparison of knee degeneration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with or without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 735-740. |
| [9] | Nie Shaobo, Li Jiantao, Sun Jien, Zhao Zhe, Zhao Yanpeng, Zhang Licheng, Tang Peifu. Mechanical stability of medial support nail in treatment of severe osteoporotic intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 329-333. |
| [10] | Tan Jiachang, Yuan Zhenchao, Wu Zhenjie, Liu Bin, Zhao Jinmin. Biomechanical analysis of elastic nail combined with end caps and wire fixation for long oblique femoral shaft fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 334-338. |
| [11] | Chen Lu, Zhang Jianguang, Deng Changgong, Yan Caiping, Zhang Wei, Zhang Yuan. Finite element analysis of locking screw assisted acetabular cup fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 356-361. |
| [12] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of multiple implants in treatment of traumatic dislocation of sternoclavicular joint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 443-448. |
| [13] | Li Kun, Li Zhijun, Zhang Shaojie, Gao Shang, Sun Hao, Yang Xi, Wang Xing, Dai Lina . A 4-year-old child model of occipito-atlanto-axial joints established by finite element dynamic simulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3773-3778. |
| [14] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||