Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (8): 1556-1564.doi: 10.12307/2025.322
Previous Articles Next Articles
Causal relationship between circulating inflammatory cytokines and bone mineral density based on two-sample Mendelian randomization
Chen Shuai, Jin Jie, Han Huawei, Tian Ningsheng, Li Zhiwei
- Department of Orthopaedics, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine (Jiangsu Second Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine), Nanjing 210017, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2024-01-19Accepted:2024-04-19Online:2025-03-18Published:2024-07-05 -
Contact:Li Zhiwei, Professor, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopaedics, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine (Jiangsu Second Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine), Nanjing 210017, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Chen Shuai, Master candidate, Department of Orthopaedics, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine (Jiangsu Second Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine), Nanjing 210017, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:Jiangsu Provincial Science and Technology Plan Special Fund for Key Social R&D Plan Project, No. BE2023787 (to LZW); the Elderly Health Research Project of Jiangsu Commission of Health, No. LKZ2022008 (to LZW)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Shuai, Jin Jie, Han Huawei, Tian Ningsheng, Li Zhiwei . Causal relationship between circulating inflammatory cytokines and bone mineral density based on two-sample Mendelian randomization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1556-1564.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
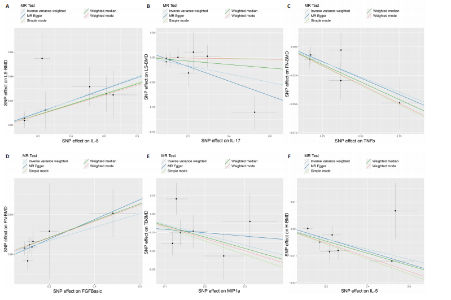
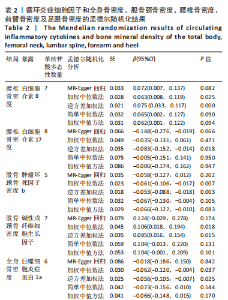
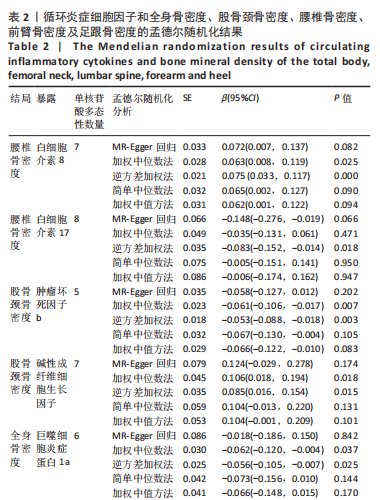
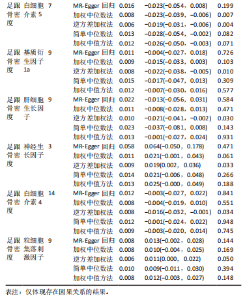
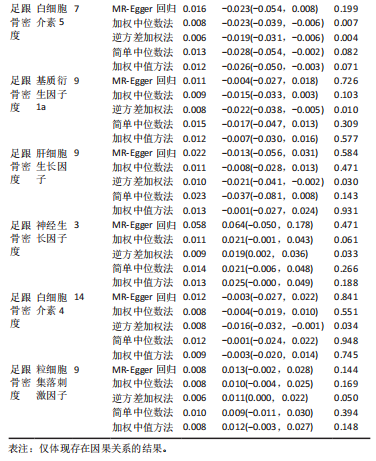
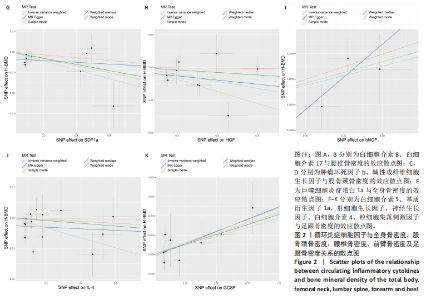
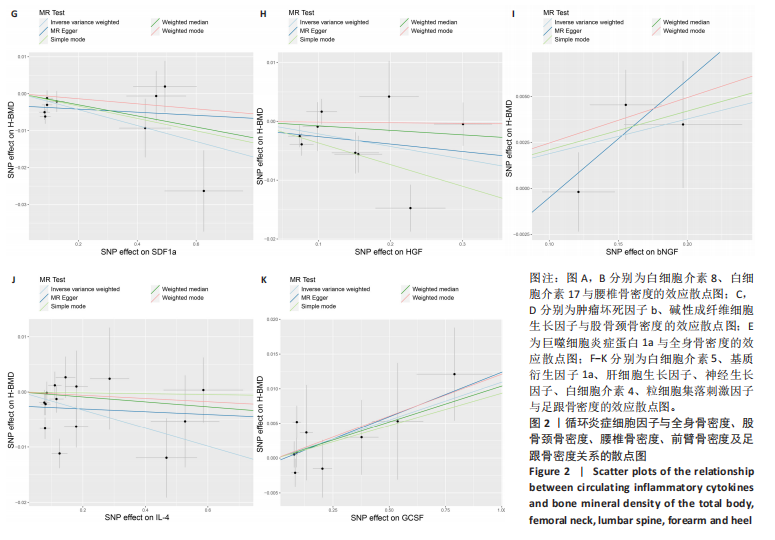
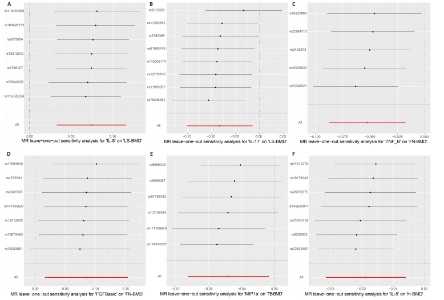
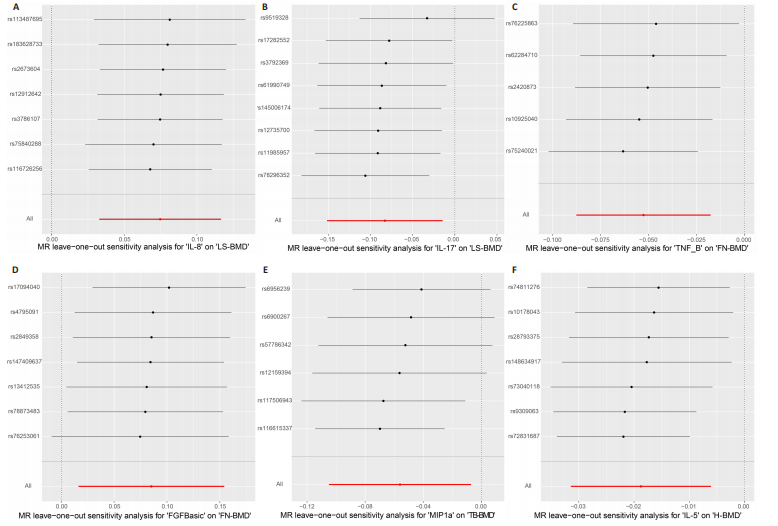
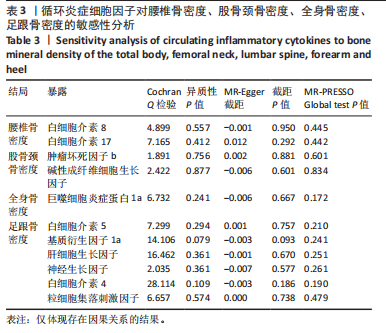
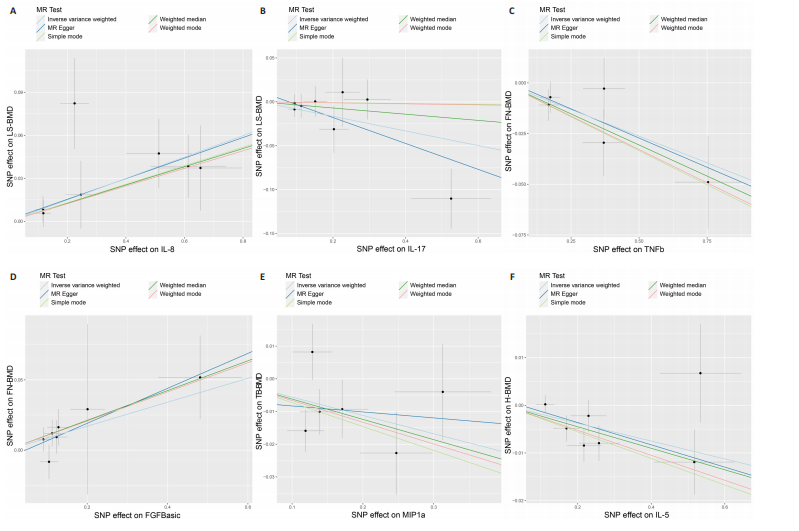
2.2 循环炎症细胞因子与腰椎骨密度的因果关系 IVW法分析结果显示,遗传预测的白细胞介素8与腰椎骨密度之间呈正向因果关系(β=0.075,95%CI:0.033-0.117,P=0.000 5);而遗传预测的白细胞介素17与腰椎骨密度之间呈负向因果关系(β=-0.083,95%CI:-0.152至-0.014,P=0.018)。同时经Bonferroni校正后发现,白细胞介素8与腰椎骨密度之间存在强因果关系(表2)。此外,MR-Egger法、加权中位数法、简单中位数法和加权中值法分析结果方向一致,见图2。 2.3 循环炎症细胞因子与股骨颈骨密度、前臂骨密度的因果关系 IVW法分析结果显示,遗传预测的肿瘤坏死因子b与股骨颈骨密度之间可能存在负向因果效应(β=-0.053,95%CI:-0.088至-0.018,P=0.003),遗传预测的碱性成纤维细胞生长因子与股骨颈骨密度之间可能存在正向因果关系(β=0.085,95%CI:0.016-0.154,P=0.015)(表2)。并且MR-Egger法、加权中位数法、简单中位数法和加权中值法分析结果方向一致(图2)。此外根据IVW法分析结果,未发现遗传预测的循环炎症细胞因子与前臂骨密度之间存在因果关系。 2.4 循环炎症细胞因子与全身骨密度的因果关系 IVW法分析结果显示,遗传预测的巨噬细胞炎症蛋白1a与全身骨密度之间可能存在负向因果效应(β=-0.056,95%CI:-0.105至-0.007,P=0.025)(表2)。并且MR-Egger法、加权中位数法、简单中位数法和加权中值法分析结果方向一致(图2)。 2.5 循环炎症细胞因子与足跟骨密度的因果关系 IVW法分析结果显示,遗传预测的白细胞介素5(β=-0.019,95%CI:-0.031至-0.006,P=0.004)、基质衍生因子1a(β=-0.022,95%CI:-0.038至-0.005,P=0.010)、肝细胞生长因子(β=-0.021,95%CI:-0.041至-0.002,P=0.030)、白细胞介素4(β=-0.016,95%CI:-0.032至-0.001,P=0.034)与足跟骨密度之间存在负向因果效应;遗传预测的神经生长因子(β=0.019,95%CI:0.002-0.036,P=0.033)、粒细胞集落刺激因子(β=0.011,95%CI:0.000-0.022,P=0.050)与足跟骨密度之间存在正向因果关系(表2)。并且MR-Egger法、加权中位数法、简单中位数法和加权中值法分析结果方向一致(图2)。 2.6 敏感性分析 研究进行了一系列敏感性分析,以检验结果是否存在异质性和水平多效性(表 3)。根据Cochran’s Q检验结果,没有观察到显著的异质性(P > 0.05)。同时,MR-Egger回归的截距均接近于0且检验P值均 > 0.05,表示结果不存在水平多效性。此外留一法检验分析显示,在逐个剔除单核苷酸多态性后结果相对稳定,无单核苷酸多态性对因果关系具有较大影响,见图3。"
|
[1] CLYNES MA, HARVEY NC, CURTIS EM, et al. The epidemiology of osteoporosis. Br Med Bull. 2020;133(1):105-117. [2] KANIS JA, COOPER C, RIZZOLI R, et al. European guidance for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Osteoporos Int. 2019;30(1):3-44. [3] TEIGLAND C, PULUNGAN Z, SCHINKEL J, et al. Economic and Humanistic Burden Among Medicare-Aged Women With Fragility Fracture in the United States. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2023;24(10):1533-1540. [4] LEBOFF MS, GREENSPAN SL, INSOGNA KL, et al. The clinician’s guide to prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 2022; 33(10):2049-2102. [5] SAXENA Y, ROUTH S, MUKHOPADHAYA A. Immunoporosis: Role of Innate Immune Cells in Osteoporosis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:687037. [6] ALIPPE Y, MBALAVIELE G. Omnipresence of inflammasome activities in inflammatory bone diseases. Semin Immunopathol. 2019;41(5):607-618. [7] WANG L, HUANG S, LI S, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: A Prospective Phase I/II Study. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019;13: 4331-4340. [8] YOKOTA K, SATO K, MIYAZAKI T, et al. Characterization and Function of Tumor Necrosis Factor and Interleukin-6-Induced Osteoclasts in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021;73(7):1145-1154. [9] YAO Z, GETTING SJ, LOCKE IC. Regulation of TNF-Induced Osteoclast Differentiation. Cells. 2022;11(1):132. [10] ILESANMI-OYELERE BL, SCHOLLUM L, KUHN-SHERLOCK B, et al. Inflammatory markers and bone health in postmenopausal women: a cross-sectional overview. Immun Ageing. 2019;16:15. [11] BARBOUR KE, BOUDREAU R, DANIELSON ME, et al. Inflammatory markers and the risk of hip fracture: the Women’s Health Initiative. J Bone Miner Res. 2012;27(5):1167-1176. [12] SKRIVANKOVA VW, RICHMOND RC, WOOLF BAR, et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology Using Mendelian Randomization: The STROBE-MR Statement. JAMA. 2021; 326(16):1614-1621. [13] DAVIES NM, HOLMES MV, DAVEY SMITH G. Reading Mendelian randomisation studies: a guide, glossary, and checklist for clinicians. BMJ. 2018;362:k601. [14] BOURAS E, KARHUNEN V, GILL D, et al. Circulating inflammatory cytokines and risk of five cancers: a Mendelian randomization analysis. BMC Med. 2022;20(1):3. [15] WEI T, ZHU Z, LIU L, et al. Circulating levels of cytokines and risk of cardiovascular disease: a Mendelian randomization study. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1175421. [16] BOWDEN J, DAVEY SMITH G, BURGESS S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44(2):512-525.
[17] XIANG M, WANG Y, GAO Z, et al. Exploring causal correlations between inflammatory cytokines and systemic lupus erythematosus: A Mendelian randomization. Front Immunol. 2022;13:985729.
[18] LIU H, LIU Z, HUANG Y, et al. Exploring causal association between circulating inflammatory cytokines and functional outcomes following ischemic stroke: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Eur J Neurol. 2024;31(2):e16123. [19] LAI R, YIN B, FENG Z, et al. The causal relationship between 41 inflammatory cytokines and hypothyroidism: bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023; 14:1332383. [20] BOWDEN J, DAVEY SMITH G, HAYCOCK PC, et al. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet Epidemiol. 2016;40(4):304-314. [21] BOWDEN J, DEL GRECO MF, MINELLI C, et al. A framework for the investigation of pleiotropy in two-sample summary data Mendelian randomization. Stat Med. 2017;36(11):1783-1802. [22] VERBANCK M, CHEN CY, NEALE B, et al. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat Genet. 2018;50(5):693-698. [23] PIERCE BL, BURGESS S. Efficient design for Mendelian randomization studies: subsample and 2-sample instrumental variable estimators. Am J Epidemiol. 2013;178(7):1177-1184. [24] ZHANG W, GAO R, RONG X, et al. Immunoporosis: Role of immune system in the pathophysiology of different types of osteoporosis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:965258. [25] CHARO IF, RANSOHOFF RM. The many roles of chemokines and chemokine receptors in inflammation. N Engl J Med. 2006;354(6):610-621. [26] BAGGIOLINI M, CLARK-LEWIS I. Interleukin-8, a chemotactic and inflammatory cytokine. FEBS Lett. 1992;307(1):97-101. [27] FOUSEK K, HORN LA, PALENA C. Interleukin-8: A chemokine at the intersection of cancer plasticity, angiogenesis, and immune suppression. Pharmacol Ther. 2021;219:107692. [28] KANY S, VOLLRATH JT, RELJA B. Cytokines in Inflammatory Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(23):6008. [29] 卢守亮.绝经后骨质疏松症妇女血清IL-8、10水平及雌激素对去势大鼠血清IL-8、10水平影响[D]. 天津:天津医科大学,2013. [30] LAM GY, DESAI S, FU J, et al. IL-8 correlates with reduced baseline femoral neck bone mineral density in adults with cystic fibrosis: a single center retrospective study. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):15405. [31] LEWIS DB, LIGGITT HD, EFFMANN EL, et al. Osteoporosis induced in mice by overproduction of interleukin 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993;90(24):11618-11622. [32] FISCHER V, HAFFNER-LUNTZER M. Interaction between bone and immune cells: Implications for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022;123:14-21. [33] PARRA-TORRES AY, ENRíQUEZ J, JIMéNEZ-ORTEGA RF, et al. Expression profiles of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling-related extracellular antagonists during proliferation and differentiation in human osteoblast-like cells. Exp Ther Med. 2020;20(6):254. [34] KRSTIĆ J, MOJSILOVIĆ S, MOJSILOVIĆ SS, et al. Regulation of the mesenchymal stem cell fate by interleukin-17: Implications in osteogenic differentiation. World J Stem Cells. 2021;13(11):1696-1713. [35] BHADRICHA H, PATEL V, SINGH AK, et al. Increased frequency of Th17 cells and IL-17 levels are associated with low bone mineral density in postmenopausal women. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):16155. [36] LU L, LIU Y, NAZIERHAN S, et al. Expression changes of IL-17 in zoledronic acid combined with PVP technology in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture and its predictive value of relapse. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2020;20(4):563-569. [37] PENG R, DONG Y, ZHENG M, et al. IL-17 promotes osteoclast-induced bone loss by regulating glutamine-dependent energy metabolism. Cell Death Dis. 2024;15(2):111. [38] PUN S, FLORIO CL, WRONSKI TJ. Anabolic effects of basic fibroblast growth factor in the tibial diaphysis of ovariectomized rats. Bone. 2000;27(2):197-202. [39] YAO W, HADI T, JIANG Y, et al. Basic fibroblast growth factor improves trabecular bone connectivity and bone strength in the lumbar vertebral body of osteopenic rats. Osteoporos Int. 2005;16(12):1939-1947. [40] ZHOU S, ZILBERMAN Y, WASSERMANN K, et al. Estrogen modulates estrogen receptor alpha and beta expression, osteogenic activity, and apoptosis in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) of osteoporotic mice. J Cell Biochem Suppl. 2001;Suppl 36:144-155. [41] KAYGUSUZ MA, TURAN CC, AYDIN NE, et al. The effects of G-CSF and naproxen sodium on the serum TGF-beta1 level and fracture healing in rat tibias. Life Sci. 2006;80(1):67-73. [42] SOSHI S, TAKAHASHI HE, TANIZAWA T, et al. Effect of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (rh G-CSF) on rat bone: inhibition of bone formation at the endosteal surface of vertebra and tibia. Calcif Tissue Int. 1996;58(5):337-340. [43] ROSEREN F, PITHIOUX M, ROBERT S, et al. Systemic Administration of G-CSF Accelerates Bone Regeneration and Modulates Mobilization of Progenitor Cells in a Rat Model of Distraction Osteogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(7):3505. |
| [1] | Wu Zhilin, , He Qin, Wang Pingxi, Shi Xian, Yuan Song, Zhang Jun, Wang Hao . DYRK2: a novel therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis combined with osteoporosis based on East Asian and European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1569-1579. |
| [2] | Liu Hongtao, Wu Xin, Jiang Xinyu, Sha Fei, An Qi, Li Gaobiao. Causal relationship between age-related macular degeneration and deep vein thrombosis: analysis based on genome-wide association study data [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1602-1608. |
| [3] | Guo Ying, Tian Feng, Wang Chunfang. Potential drug targets for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: large sample analysis from European databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1549-1557. |
| [4] | Gao Zengjie, , Pu Xiang, Li Lailai, Chai Yihui, Huang Hua, Qin Yu. Increased risk of osteoporotic pathological fractures associated with sterol esters: evidence from IEU-GWAS and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1302-1310. |
| [5] | Liu Fengzhi, Dong Yuna, Tian Wenyi, Wang Chunlei, Liang Xiaodong, Bao Lin. Gene-predicted associations between 731 immune cell phenotypes and rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1311-1319. |
| [6] | Zhang Cuicui, Chen Huanyu, Yu Qiao, Huang Yuxuan, Yao Gengzhen, Zou Xu. Relationship between plasma proteins and pulmonary arterial hypertension and potential therapeutic targets [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1331-1340. |
| [7] | Yang Zhijie, Zhao Rui, Yang Haolin, Li Xiaoyun, Li Yangbo, Huang Jiachun, Lin Yanping, Wan Lei, HuangHongxing. Postmenopausal osteoporosis: predictive values of muscle mass, grip strength, and appendicular skeletal muscle index [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1073-1080. |
| [8] | Zeng Hao, Sun Pengcheng, Chai Yuan, Huang Yourong, Zhang Chi, Zhang Xiaoyun. Association between thyroid function and osteoporosis: genome-wide data analysis of European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1019-1027. |
| [9] | Rong Xiangbin, , Zheng Haibo, Mo Xueshen, Hou Kun, Zeng Ping, . Plasma metabolites, immune cells, and hip osteoarthritis: causal inference based on GWAS data from European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1028-1035. |
| [10] | He Qiwang, , , Chen Bo, Liang Fuchao, Kang Zewei, Zhou Yuan, Ji Anxu, Tang Xialin, . Relationship between Alzheimer’s disease and sarcopenia and body mass index: analysis of GWAS datasets for European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1036-1046. |
| [11] | Ding Yu, Chen Jingwen, Chen Xiuyan, Shi Huimin, Yang Yudie, Zhou Meiqi, Cui Shuai, . Circulating inflammatory proteins and myocardial hypertrophy: large sample analysis of European populations from GWAS Catalog and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1047-1057. |
| [12] | Zhao Feifan, Cao Yujing. An artificial neural network model of ankylosing spondylitis and psoriasis shared genes and machine learning-based mining and validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 770-784. |
| [13] | Liu Chu, Qiu Boyuan, Tong Siwen, He Linyuwei, Chen Haobo, Ou Zhixue. A genetic perspective reveals the relationship between blood metabolites and osteonecrosis: an analysis of information from the FinnGen database in Finland [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 785-794. |
| [14] | Chen Jiayong, Tang Meiling, Lu Jianqi, Pang Yan, Yang Shangbing, Mao Meiling, Luo Wenkuan, Lu Wei, Zhou Jiatan. Based on Mendelian randomization, the causal relationship between 1400 metabolites and sarcopenia and the correlation analysis of cardiovascular disease were investigated [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-11. |
| [15] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Exploring the causal relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: a Mendel randomized study involving serum metabolites and inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||