Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (4): 839-845.doi: 10.12307/2025.213
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application, research hotspots, and shortcomings of degradable zinc-based alloys in bone defect repair and reconstruction
Liu Haoyang1, Xie Qiang2, Shen Mengran1, Ren Yansong3, Ma Jinhui4, Wang Bailiang4, Yue Debo4, Wang Weiguo4
- 1China-Japan Friendship School of Clinical Medicine, Peking University, Beijing 100029, China; 2Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 400016, China; 3Health Science Center of Peking University, Beijing 100191, China; 4Department of Orthopedic Surgery, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China
-
Received:2023-11-23Accepted:2024-01-12Online:2025-02-08Published:2024-06-04 -
Contact:Ma Jinhui, MD, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China Wang Bailiang, MD, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China -
About author:Liu Haoyang, Master candidate, China-Japan Friendship School of Clinical Medicine, Peking University, Beijing 100029, China -
Supported by:1Research Project on Education and Teaching Reform at Capital Medical University, No. 2023JYY388 (to MJH); 2National High-Level Hospital Clinical Research Funding, Elite Medical Professionals Project of China-Japan Friendship Hospital, No. ZRJY2021-TD01 (to WBL);3 National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 52373273 (to WBL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Haoyang, Xie Qiang, Shen Mengran, Ren Yansong, Ma Jinhui, Wang Bailiang, Yue Debo, Wang Weiguo . Application, research hotspots, and shortcomings of degradable zinc-based alloys in bone defect repair and reconstruction[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 839-845.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
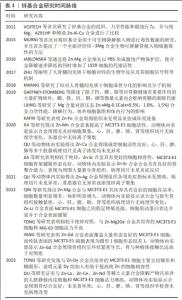
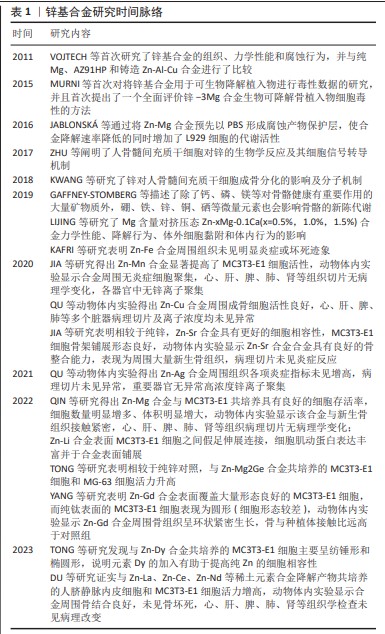
2.1 锌基合金研究时间脉络 见表1。 2.2 锌基合金概述 2.2.1 锌的生理功能 锌作为仅次于铁的人体第二大营养必需微量元素,以参与蛋白、组织构成或以信号因子调控信号通路等形式在人体神经[13]、免疫[14]、心血管[15]、生殖[16]、肌骨等各大系统的发育[17]、代谢中具有不可或缺的作用。当锌缺乏而无法满足机体正常代谢需求时,可能导致如认知功能障碍、骨质疏松等一系列病症发生[18-19]。尽管对于儿童具体补锌剂量依旧有待探讨,但当前对锌有利于儿童成长已得到充分论证[20]。 组织损伤时,锌元素聚集参与止血、炎性反应、细胞增殖、组织重塑在内的组织修复全程[21-22],该效益对于促进骨缺损后的修复重建具有重要意义。在骨缺损处植入锌基合金后的主要降解产物——锌离子通过调节血管内皮细胞[23]、免疫细胞[24]、骨细胞等协同促进骨修复[21],以及参与构建骨基质[25],尚余锌离子在参与维持锌稳态相关蛋白的调控下通过血液转运,最后通过皮肤、汗液、肾脏、尿液、大肠或结肠和粪便中排出,不会发生局部高浓度锌离子聚集而引发不良反应[26-27]。"
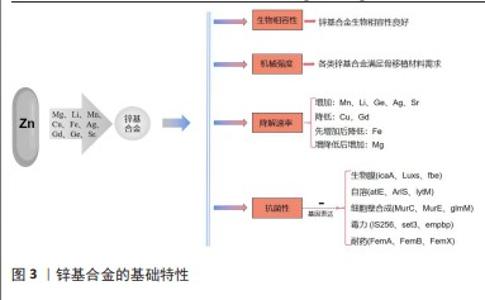
鉴于此前在骨植入中以AZ31、WE43等为代表镁基合金的成功研发,目前骨植入锌基合金以锌镁合金为主[10,37],但锌基合金体系具有相对特殊的机械性能和生物学效应,对于理想化、个性化可降解锌基合金研发的贡献不可忽视。合金的降解速率伴随所加入微量金属元素的种类和量发生改变,例如Mn加入所得的锌基合金降解速率增加[9],而Cu的加入使降解速率降低[10];特殊的是,加入不同质量比Mg的锌基合金降解速率先降低而后升高[38],而加入不同质量比Fe的锌基合金先增高后降低[30],这是合金在降解过程中周围生化环境、金属原电池效应、降解产物包被在内多重因素共同交织影响的结果。此外,Cu和Ag的加入对于提高合金材料抗菌能力具有重要意义,QU研究团队[11-12]通过研究Zn-Ag、Zn-Cu合金对耐甲氧西林金葡菌(ATCC 43300)的抗菌作用,发现该类合金相较于对照组显著抑制了细菌生物膜形成、细菌细胞壁合成、自溶、毒力和耐药等相关基因的表达。锌基合金的基础特性见图3。 综上,鉴于锌基合金的基本特性,通过设置不同组合体系二元、多元合金而实现个性化的骨植入材料研发以适用于不同人群,是锌基合金潜在研究方向。 2.2.3 锌基合金的力学和机械特性 锌基合金医用植入材料具有优异的力学性能、完全可降解性、良好的生物相容性,主要用于骨科植入物、心血管支架的研究,近几年还扩展到胆管支架、气管支架、神经导管等,具有广阔的应用前景。目前锌基合金体外生物相容性的研究主要集中在骨相关细胞、血管相关细胞和成纤维细胞。有研究表明,纯Zn材料的力学性能不足,无法满足植入体的力学强度需求,所以采用粉末冶金法通过添加Mg元素合金化来改善纯Zn的力学性能,添加造孔剂制备了具有多孔结构的锌镁合金,以达到人体松质骨仿生的目的[39]。YANG等[8]的研究通过逐一测试筛选的方法证实,各类锌基合金在机械强度上满足骨植入材料的需求,并且进一步明确了金属Li具有相对最强增加材料机械性能的作用。 "

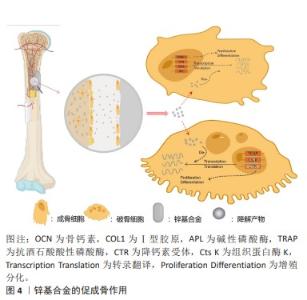
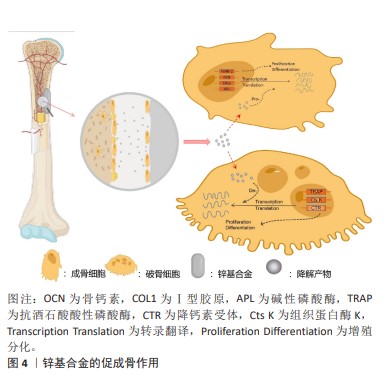
2.3 锌基合金的骨修复作用 可降解锌基合金在骨缺损部位发挥刺激骨修复作用在于降解前和降解后2个阶段,而由于降解发生的持续性它们同时存在并相互影响、促进,降解前主要以固态金属形式表现为骨传导性,降解后则以降解离子参与代谢表现为骨诱导性,见图4。 2.3.1 骨传导性 骨传导性是指植入材料支持骨祖细胞和成骨细胞附着的能力,并且允许这些细胞在移植物的三维结构中增殖、生长和迁移[3]。由于生物可降解特性的存在,骨细胞代谢矿化对降解区及时有效的填充取代决定了缺损修复的进展,材料良好的骨传导性确保了黏附成骨细胞的充分活性,避免了材料降解后填充不及时、不充分进而出现微隙而影响骨缺损的修复重建[40]。对于提高骨传导性,往往通过支架结构的构建及涂层优化。 (1)支架结构:支架结构具有三维立体孔隙,其孔径大小、孔隙率以及表面粗糙程度都将影响细胞的黏附与分化[41-42]。目前构建支架结构的技术主要有直接能量沉积、分层实体制造、选择性激光熔融及电子束熔融,而后两种方法可形成复杂的拓扑结构与精细的微结构,已被作为金属支架结构构建的主导技术[43]。伴随对多孔材料整体性能包括力学、生物学性能要求的提高,在微观表征下新型多孔支架的微观设计依旧有待改进[44]。增加组织与金属的接触面积,细胞可扩散面积更大,多孔支架结构相比于铸型金属表现出更好的骨传导性[45-46]。同时由于健康成年人骨组织代谢活跃,简单锌基合金的降解速率无法达到这类人群对可降解骨植入材料的需求[30],而支架结构的选择扩大了金属体积质量比,能有效缩短金属降解时间使之与成骨代谢速率相当,使实现理想最高速率的骨修复重建成为可能。同时,降解速率的增加将伴随降解产物的加快生成,这与组织对降解产物的吸收速率共同决定了局部产物浓度,大量的蓄积将导致细胞毒性[47]。尽管现有研究表明,组织对于锌基合金降解产物具有良好的吸收速率而不发生组织炎症[48],但若进一步提高材料的降解速率以适应健康人群的骨缺损修复速率,而材料的降解产物是否会局部浓聚而抑制成骨活性值得研究。 研究表明,锌基合金支架结构具有相比于铸型金属更优异的细胞相容性。有研究使用当前相对成熟的激光粉床融化技术构建了Zn-Li和Zn-Mg多孔支架合金,发现成骨细胞前体细胞(MC3T3-E1细胞)在多孔支架合金上拥有更好的细胞形态以及细胞贴附效果,表现为伪足充分展开相连接,这一代谢活跃的表现与块状样品表面的球形细胞差异明显[29,31]。此外,一种含有泡沫气孔的泡沫金属材料孔隙率可达90%以上。一项以电化学沉积法制备Zn-Cu泡沫金属的研究发现,该泡沫合金除了具有抗菌性能外还具有优异的骨传导性,该合金上的细胞渗透率明显优于铸型合金[49]。尽管此前研究已证实铸型锌基合金满足承重区骨植入物标准[8],但鉴于各类锌基合金在支架构架后如抗压强度的机械性能下降[29,49-50],这或导致该型材料仅限于非承重或低负荷区的应用。但从总体上说,锌基合金在构建支架结构方面仍具有明显优势。 (2)表面涂层改性技术:表面涂层改性技术在各类生物材料中都有广泛研究,通过在目标金属表面进行特殊加工处理增加一层特殊材料,以改善材料的降解速率[51]、提高组织相容性以及抑制细菌生物膜形成而提高抗菌性[52-53]。 目前为止,运用锌离子作为涂层材料以优化材料性能的研究屡见不鲜,或是作为抗菌剂,抑或是提高共培养细胞的黏附与生长[54-55]。目前针对锌基合金的表面涂层的研究相对较少,主要集中在对Zn-Mg体系的研究。JABLONSKá等[56]通过将Zn-Mg合金预先以PBS形成腐蚀产物保护层,使其降解速率降低的同时增加了L929细胞的代谢活性。通过化学沉积法在Zn-3Cu-1Mg支架合金表面构建Ca-P涂层,该材料在体外可促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化和钙沉积,体内可促进细胞的黏附与周围新骨形成[57]。同样的,通过磷酸化学转换法在Zn-1Mg-0.5Ga合金表面构建Zn-P涂层和Ca-Zn-P涂层,显著增加了巨噬细胞M2极化,通过调节骨免疫微环境促进了组织再生[58]。此外,有研究通过原子层沉积法在Zn-Li合金表面构建了ZrO2纳米膜层,以此提高MC3T3-E1细胞的黏附力和细胞活力[59]。 尽管对锌基合金涂层的研究相对较少,但优化涂层技术应用于锌基合金以获取更好的骨传导性具有切实可行性[60]。涂层与基体材料的结合以及涂层材料表征决定了材料的生物效应,因此进一步探讨涂层工艺具有重要意义。 2.3.2 骨诱导性 骨诱导性指材料可诱导原始细胞发育为骨形成细胞系,而后继续刺激诱导形成新骨[61]。骨缺损微环境包括成骨、破骨细胞和骨微循环代谢及部分炎症细胞(如巨噬细胞)[62],可降解锌基合金的降解产物将通过影响骨细胞的基因表达代谢以及调节骨缺损处微循环实现促进骨修复重建。 (1)细胞代谢:成骨细胞使胞外基质矿化成骨,成骨细胞代谢活性增加将直接促进成骨的发生。研究发现,锌镁合金降解产物可通过PI3K-AKT和细胞外基质受体等信号通路上调碱性磷酸酶、Ⅰ型胶原、骨钙素和RUNX-2等成骨分化相关基因的表达[38,63]。其中,碱性磷酸酶通过水解焦磷酸创造的碱性环境有利于磷酸盐沉积,以促进骨修复重建,而锌离子在促进碱性磷酸酶表达的同时还作为其辅助因子,对碱性磷酸酶功能的发挥有至关重要的作用[64]。Zn-Sr合金可促进成骨细胞Akt、p-Akt及Erk基因的表达,激活PI3K/Akt和MAPK/ERK信号通路,促使下游成骨相关基因如骨钙素、RUNX-2表达水平显著升高,促进成骨[32]。 对于破骨细胞,尽管骨吸收在骨修复塑形期发挥重要作用,但在修复早期作为不利因素延长了修复时间,因此抑制破骨细胞代谢活性对促进早期的骨修复具有重要意义。在对Zn-Ag合金的研究中,将合金与诱导分化阶段的破骨细胞共培养,发现这不仅抑制了破骨细胞的形成及分化相关基因的表达,还抑制其代谢活性,在扫描电镜下发现含锌组的骨吸收明显减少[12]。 在骨缺损后的重建过程中,人骨髓间充质干细胞可分化为成骨细胞、软骨细胞等以实现骨再生修复。相关研究表明,锌离子可激活人骨髓间充质干细胞的cAMP-PKA-CREB通路,触发细胞内Ca2+反应来诱导MAPK及Gαq-PLC-AKT通路的激活,促使成骨相关基因表达水平增高以及胞外基质矿化效率增加,以促进骨组织修复[65-66]。此外,锌离子刺激的巨噬细胞被激活包括MAPK、蛋白激酶C和核因子kB在内的多种信号通路,从而改变下游基因和蛋白质的表达参与到外泌体中,释放后被成骨细胞摄取可表现为高碱性磷酸酶活性,而被内皮细胞摄取后促进其迁移和分化[67]。 综上所述,锌基合金对于成骨相关基因的调控积极而复杂,进一步研究其调控机制与辨析调控网络有助于对锌基合金诱导成骨更深层次的把控。 (2)微循环:局部微循环对于组织修复重建具有重要意义,其自身与骨诱导无关,但营养物质的获取、细胞因子的传递使骨细胞成骨代谢活跃都有赖于良好的损伤后微循环的重建。锌基合金植入体内后促进局部微循环修复的效益是复杂的,锌离子可通过PI3K/Akt/内皮型一氧化氮合酶途径增强血管内皮细胞形态发生[68],通过增加血管周围细胞缺氧诱导因子1α、血管内皮生长因子A、血管内皮生长因子受体2等蛋白水平促进血管生成,改善局部微环境[69]。值得提出的是,一项锌离子对肿瘤细胞影响的研究发现,锌离子可通过诱导A-20抑制核因子kB表达来减少血管生成因子的表达,进而抑制血管生成[70]。表明锌离子通过多种不同途径在不同细胞可表现为不同作用,而整体是有利于人体病理改变的改善。"
| [1] DIMITRIOU R, JONES E, MCGONAGLE D, et al. Bone regeneration: current concepts and future directions. BMC Med. 2011;9:66. [2] CAMPANA V, MILANO G, PAGANO E, et al. Bone substitutes in orthopaedic surgery: from basic science to clinical practice. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2014;25(10):2445-2461. [3] WANG W, YEUNG KWK. Bone grafts and biomaterials substitutes for bone defect repair: A review. Bioact Mater. 2017;2(4):224-247. [4] HOU X, ZHANG L, ZHOU Z, et al. Calcium Phosphate-Based Biomaterials for Bone Repair. J Funct Biomater. 2022;13(4):187. [5] CHEN K, LU Y, TANG H, et al. Effect of strain on degradation behaviors of WE43, Fe and Zn wires. Acta Biomater. 2020;113:627-645. [6] WANG N, MA Y, SHI H, et al. Mg-, Zn-, and Fe-Based Alloys With Antibacterial Properties as Orthopedic Implant Materials. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:888084. [7] VOJTECH D, KUBASEK J, SERAK J, et al. Mechanical and corrosion properties of newly developed biodegradable Zn-based alloys for bone fixation. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(9):3515-3522. [8] YANG H, JIA B, ZHANG Z, et al. Alloying design of biodegradable zinc as promising bone implants for load-bearing applications. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):401. [9] JIA B, YANG H, HAN Y, et al. In vitro and in vivo studies of Zn-Mn biodegradable metals designed for orthopedic applications. Acta Biomater. 2020;108:358-372. [10] GARCIA-MINTEGUI C, CORDOBA LC, BUXADERA-PALOMERO J, et al. Zn-Mg and Zn-Cu alloys for stenting applications: From nanoscale mechanical characterization to in vitro degradation and biocompatibility. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(12):4430-4446. [11] QU X, YANG H, JIA B, et al. Biodegradable Zn-Cu alloys show antibacterial activity against MRSA bone infection by inhibiting pathogen adhesion and biofilm formation. Acta Biomater. 2020;117: 400-417. [12] QU X, YANG H, JIA B, et al. Zinc alloy-based bone internal fixation screw with antibacterial and anti-osteolytic properties. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(12):4607-4624. [13] MATTEI D, PIETROBELLI A. Micronutrients and Brain Development. Curr Nutr Rep. 2019;8(2):99-107. [14] SINCAN G, ERDEM F, BAY I, et al. Serum Copper and Zinc Levels in Primary Immune Thrombocytopenia. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2022;200(9): 3919-3924. [15] GAC P, CZERWINSKA K, MACEK P, et al. The importance of selenium and zinc deficiency in cardiovascular disorders. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2021;82:103553. [16] NASIADEK M, STRAGIEROWICZ J, KLIMCZAK M, et al. The Role of Zinc in Selected Female Reproductive System Disorders. Nutrients. 2020; 12(8):2464. [17] GAFFNEY-STOMBERG E. The Impact of Trace Minerals on Bone Metabolism. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2019;188(1):26-34. [18] SUN R, WANG J, FENG J, et al. Zinc in Cognitive Impairment and Aging. Biomolecules. 2022;12(7):1000. [19] MIAZGOWSKI T, RYL A, SZYLINSKA A, et al. The Impact of Major and Trace Elements in Serum and Bone on Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry-Derived Hip Strength. Calcif Tissue Int. 2022;110(6): 674-684. [20] CEBALLOS-RASGADO M, LOWE NM, MALLARD S, et al. Adverse Effects of Excessive Zinc Intake in Infants and Children Aged 0-3 Years: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Adv Nutr. 2022;13(6):2488-2518. [21] OGAWA Y, KINOSHITA M, SHIMADA S, et al. Zinc and Skin Disorders. Nutrients. 2018;10(2):199. [22] LIN PH, SERMERSHEIM M, LI H, et al. Zinc in Wound Healing Modulation. Nutrients. 2017;10(1):16. [23] TSURUOKA T, KODAMA A, YAMAGUCHI S, et al. Zinc deficiency impairs ischemia-induced angiogenesis. JVS Vasc Sci. 2021;3:30-40. [24] LI H, LI M, RAN X, et al. The Role of Zinc in Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cell Differentiation. Cell Reprogram. 2022;24(2):80-94. [25] MIAZGOWSKI T, RYŁ A, SZYLIŃSKA A, et al. The Impact of Major and Trace Elements in Serum and Bone on Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry-Derived Hip Strength. Calcif Tissue Int. 2022;110(6): 674-684. [26] KING JC, SHAMES DM, WOODHOUSE LR. Zinc homeostasis in humans. J Nutr. 2000;130(5S Suppl):1360S-1366S. [27] COSTA MI, SARMENTO-RIBEIRO AB, GONÇALVES AC. Zinc: From Biological Functions to Therapeutic Potential. Int J Mol Sci. 2023; 24(5):4822. [28] LIU Y, DU T, QIAO A, et al. Zinc-Based Biodegradable Materials for Orthopaedic Internal Fixation. J Funct Biomater. 2022;13(4):164. [29] QIN Y, LIU A, GUO H, et al. Additive manufacturing of Zn-Mg alloy porous scaffolds with enhanced osseointegration: In vitro and in vivo studies. Acta Biomater. 2022;145:403-415. [30] KAFRI A, OVADIA S, YOSAFOVICH-DOITCH G, et al. The Effects of 4%Fe on the Performance of Pure Zinc as Biodegradable Implant Material. Ann Biomed Eng. 2019;47(6):1400-1408. [31] QIN Y, YANG H, LIU A, et al. Processing optimization, mechanical properties, corrosion behavior and cytocompatibility of additively manufactured Zn-0.7Li biodegradable metals. Acta Biomater. 2022; 142:388-401. [32] JIA B, YANG H, ZHANG Z, et al. Biodegradable Zn-Sr alloy for bone regeneration in rat femoral condyle defect model: In vitro and in vivo studies. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(6):1588-1604. [33] TONG X, HAN Y, ZHOU R, et al. Biodegradable Zn-Dy binary alloys with high strength, ductility, cytocompatibility, and antibacterial ability for bone-implant applications. Acta Biomater. 2023;155:684-702. [34] TONG X, WANG H, ZHU L, et al. A biodegradable in situ Zn-Mg(2)Ge composite for bone-implant applications. Acta Biomater. 2022;146: 478-494. [35] YANG H, JIA B, QU X, et al. Modified Biodegradation Behavior Induced Beneficial Microenvironments for Bone Regeneration by Low Addition of Gadolinium in Zinc. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(21):e2201184. [36] DU S, SHEN Y, ZHENG Y, et al. Systematic in vitro and in vivo study on biodegradable binary Zn-0.2 at% Rare Earth alloys (Zn-RE: Sc, Y, La-Nd, Sm-Lu). Bioact Mater. 2023;24:507-523. [37] LIU J, LIU B, MIN S, et al. Biodegradable magnesium alloy WE43 porous scaffolds fabricated by laser powder bed fusion for orthopedic applications: Process optimization, in vitro and in vivo investigation. Bioact Mater. 2022;16:301-319. [38] YANG L, GUO P, NIU Z, et al. Influence of Mg on the mechanical properties and degradation performance of as-extruded ZnMgCa alloys: In vitro and in vivo behavior. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2019; 95:220-231. [39] 李伟健.医用可降解多孔锌镁合金的制备及性能研究[D].太原:太原理工大学,2019. [40] LI D, ZHANG D, YUAN Q, et al. In vitro and in vivo assessment of the effect of biodegradable magnesium alloys on osteogenesis. Acta Biomater. 2022;141:454-465. [41] LI Z, RAMAY HR, HAUCH KD, et al. Chitosan-alginate hybrid scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2005;26(18):3919-3928. [42] GUO H, XIA D, ZHENG Y, et al. A pure zinc membrane with degradability and osteogenesis promotion for guided bone regeneration: In vitro and in vivo studies. Acta Biomater. 2020;106:396-409. [43] 刘昊,陈靓瑜,张洪岳,等.增材制造多孔金属生物材料研究综述[J].精密成形工程,2022,14(5):121-133. [44] PENG W, LIU Y, WANG C. Definition, measurement, and function of pore structure dimensions of bioengineered porous bone tissue materials based on additive manufacturing: A review. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;10:1081548. [45] HUANG K, YANG MS, TANG YJ, et al. Porous shape memory scaffold of dextran and hydroxyapatite for minimum invasive implantation for bone tissue engineering applications. J Biomater Appl. 2021;35(7): 823-837. [46] LI B, LEI Y, HU Q, et al. Porous copper- and lithium-doped nano-hydroxyapatite composite scaffold promotes angiogenesis and bone regeneration in the repair of glucocorticoids-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Biomed Mater. 2021;16(6):10. [47] AMUKARIMI S, MOZAFARI M. Biodegradable Magnesium Biomaterials-Road to the Clinic. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022;9(3):107. [48] HUSSAIN M, ULLAH S, RAZA MR, et al. Recent Developments in Zn-Based Biodegradable Materials for Biomedical Applications. J Funct Biomater. 2022;14(1):1. [49] TONG X, SHI Z, XU L, et al. Degradation behavior, cytotoxicity, hemolysis, and antibacterial properties of electro-deposited Zn-Cu metal foams as potential biodegradable bone implants. Acta Biomater. 2020;102:481-492. [50] PENG W, LIU Y, WANG C. Definition, measurement, and function of pore structure dimensions of bioengineered porous bone tissue materials based on additive manufacturing: A review. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;10:1081548. [51] AKBARZADEH FZ, GHOMI ER, RAMAKRISHNA S. Improving the corrosion behavior of magnesium alloys with a focus on AZ91 Mg alloy intended for biomedical application by microstructure modification and coating. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2022;236(8):1188-1208. [52] LI K, WANG B, ZHOU J, et al. In vitro corrosion resistance and cytocompatibility of Mg66Zn28Ca6 amorphous alloy materials coated with a double-layered nHA and PCL/nHA coating. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020;196:111251. [53] GUO J, CAO G, WANG X, et al. Coating CoCrMo Alloy with Graphene Oxide and epsilon-Poly-L-Lysine Enhances Its Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Properties. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021;16:7249-7268. [54] ZUO K, WANG L, WANG Z, et al. Zinc-Doping Induces Evolution of Biocompatible Strontium-Calcium-Phosphate Conversion Coating on Titanium to Improve Antibacterial Property. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14(6):7690-7705. [55] CERQUEIRA A, ROMERO-GAVILAN F, GARCIA-ARNAEZ I, et al. Bioactive zinc-doped sol-gel coating modulates protein adsorption patterns and in vitro cell responses. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;121:111839. [56] JABLONSKÁ E, VOJTECH D, FOUSOVA M, et al. Influence of surface pre-treatment on the cytocompatibility of a novel biodegradable ZnMg alloy. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;68:198-204. [57] ZHUANG Y, LIU Q, JIA G, et al. A Biomimetic Zinc Alloy Scaffold Coated with Brushite for Enhanced Cranial Bone Regeneration. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021;7(3):893-903. [58] ZHAO DW, DU CM, ZUO KQ, et al. Calcium-Zinc Phosphate Chemical Conversion Coating Facilitates the Osteointegration of Biodegradable Zinc Alloy Implants by Orchestrating Macrophage Phenotype. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(9):e2202537. [59] YUAN W, XIA D, ZHENG Y, et al. Controllable biodegradation and enhanced osseointegration of ZrO2-nanofilm coated Zn-Li alloy: In vitro and in vivo studies. Acta Biomater. 2020;105:290-303. [60] YUAN W, XIA D, WU S, et al. A review on current research status of the surface modification of Zn-based biodegradable metals. Bioact Mater. 2022;7:192-216. [61] RAGNI E, PERUCCA ORFEI C, BIDOSSI A, et al. Superior Osteo-Inductive and Osteo-Conductive Properties of Trabecular Titanium vs. PEEK Scaffolds on Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Proof of Concept for the Use of Fusion Cages. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2379. [62] JESUS D, PINHO AR, GOMES MC, et al. Emerging modulators for osteogenic differentiation: a combination of chemical and topographical cues for bone microenvironment engineering. Soft Matter. 2022;18(16):3107-3119. [63] MURNI NS, DAMBATTA MS, YEAP SK, et al. Cytotoxicity evaluation of biodegradable Zn-3Mg alloy toward normal human osteoblast cells. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015;49:560-566. [64] VIMALRAJ S. Alkaline phosphatase: Structure, expression and its function in bone mineralization. Gene. 2020;754:144855. [65] PARK KH, CHOI Y, YOON DS, et al. Zinc Promotes Osteoblast Differentiation in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Via Activation of the cAMP-PKA-CREB Signaling Pathway. Stem Cells Dev. 2018;27(16): 1125-1135. [66] ZHU D, SU Y, YOUNG ML, et al. Biological Responses and Mechanisms of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Zn and Mg Biomaterials. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(33):27453-27461. [67] LIU J, ZHAO Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Exosomes derived from macrophages upon Zn ion stimulation promote osteoblast and endothelial cell functions. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(18):3800-3807. [68] GAO B, WANG X, WANG M, et al. Superlow Dosage of Intrinsically Bioactive Zinc Metal-Organic Frameworks to Modulate Endothelial Cell Morphogenesis and Significantly Rescue Ischemic Disease. ACS Nano. 2022;16(1):1395-1408. [69] LI Y, MA T, ZHU X, et al. Zinc improves neurological recovery by promoting angiogenesis via the astrocyte-mediated HIF-1alpha/VEGF signaling pathway in experimental stroke. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022;28(11):1790-1799. [70] PRASAD AS, BECK FW, SNELL DC, et al. Zinc in cancer prevention. Nutr Cancer. 2009;61(6):879-887. [71] BONDAREVA JV, DUBININ ON, KUZMINOVA YO, et al. Biodegradable iron-silicon implants produced by additive manufacturing. Biomed Mater. 2022;17(3):5005. [72] WANG Y, FENG Z, LIU X, et al. Titanium alloy composited with dual-cytokine releasing polysaccharide hydrogel to enhance osseointegration via osteogenic and macrophage polarization signaling pathways. Regen Biomater. 2022;9:rbac003. |
| [1] | Yu Shuangqi, Ding Fan, Wan Song, Chen Wei, Zhang Xuejun, Chen Dong, Li Qiang, Lin Zuoli. Effects of polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer/lysine-grafted graphene oxide nanoparticle composite scaffolds on osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 707-712. |
| [2] | Feng Shuqi, Zhang Shiyong, Yao Keyi, Tang Yufei, Wang Kai, Zhou Xuemei, Xiang Lin. Application of photoresponsive nanomaterials in bone tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(16): 3469-3475. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||