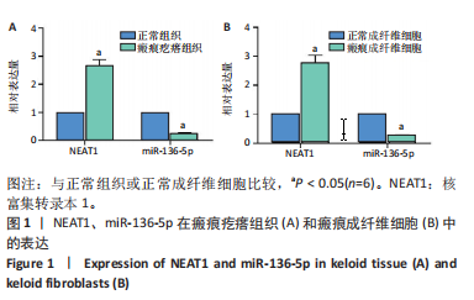
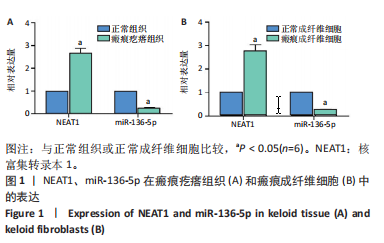
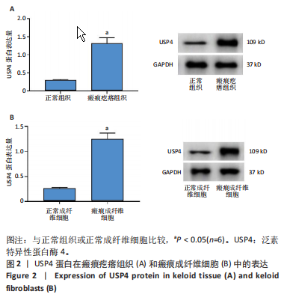
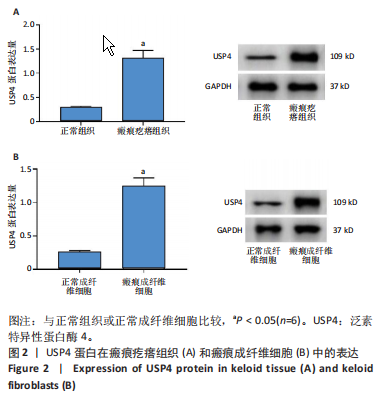
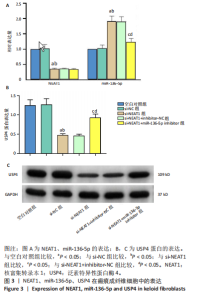
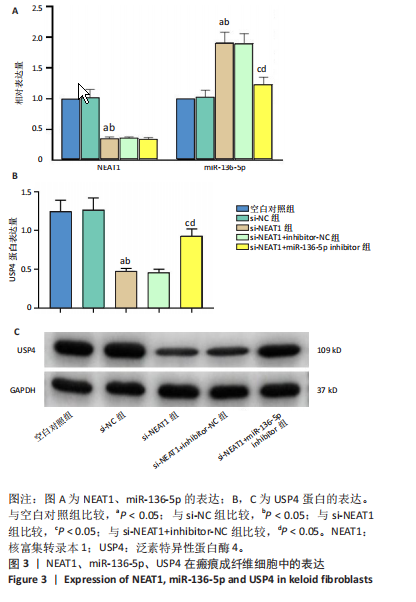
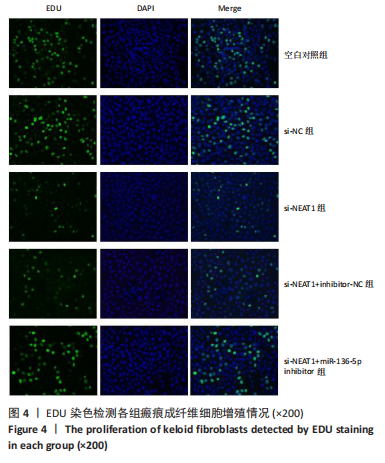
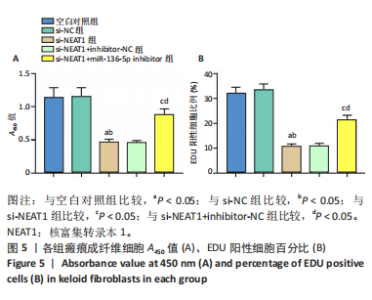
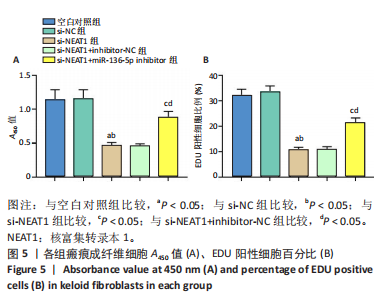
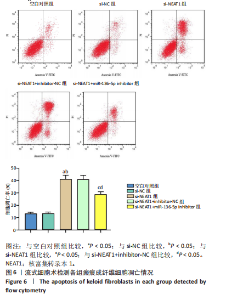
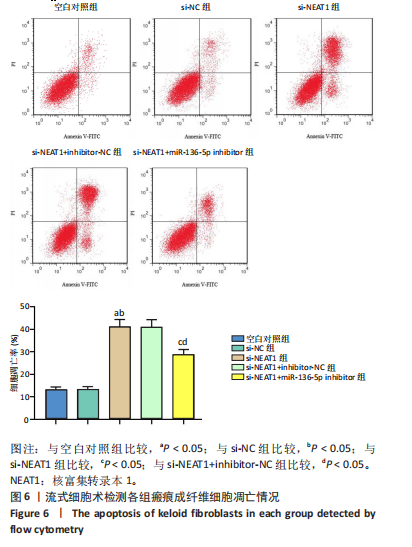
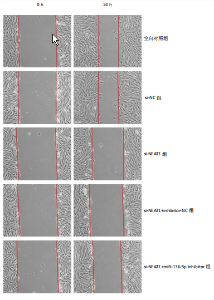
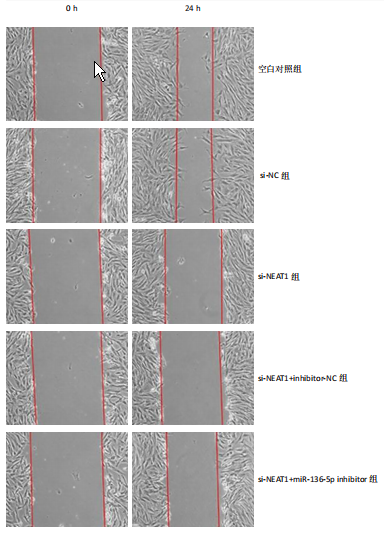
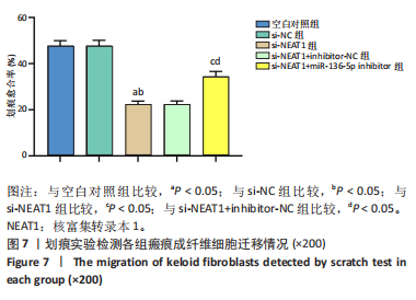
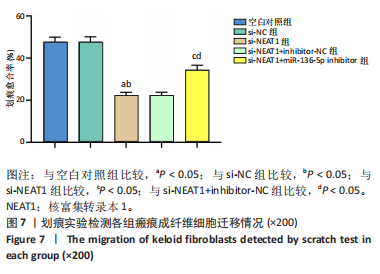
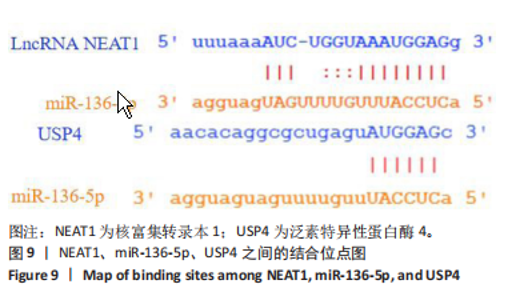
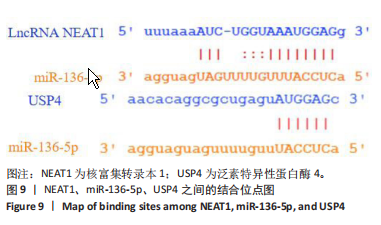
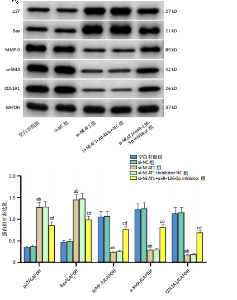
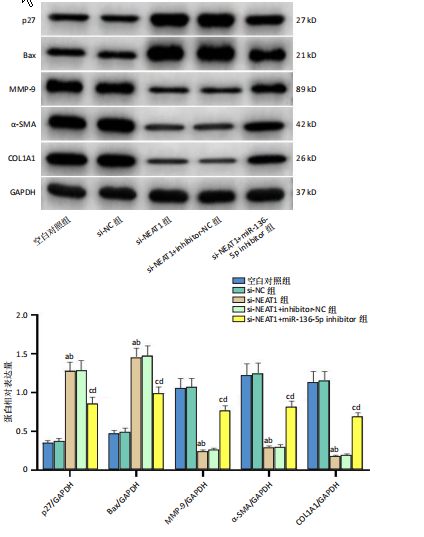
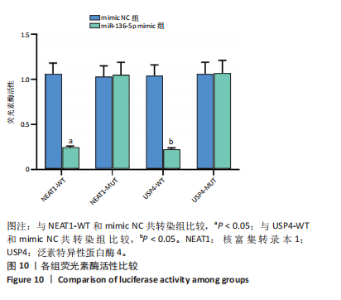
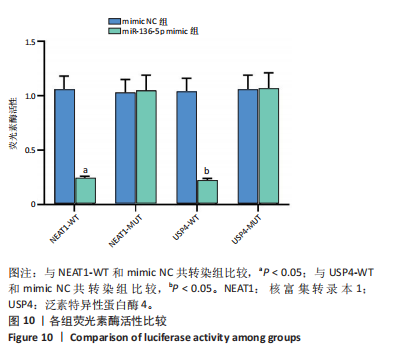
[1] JIANG L, SHI X, WANG M, et al. Study on the Mechanism of miR-34a Affecting the Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Human Keloid Fibroblasts by Regulating the Expression of SATB1. J Healthc Eng. 2021; 2021:8741512.
[2] 李心怡,李茜,张伟,等.miR-148b-3p调控瘢痕疙瘩来源的成纤维细胞增殖的机制研究[J].安徽医科大学学报,2023,58(9):1534-1539.
[3] WEI Y, WANG T, ZHANG N, et al. LncRNA TRHDE-AS1 inhibit the scar fibroblasts proliferation via miR-181a-5p/PTEN axis. J Mol Histol. 2021; 52(2):419-426.
[4] 黄晶晶,蒋英,于静萍.缺氧诱导因子1α与瘢痕疙瘩肿瘤特性及其放疗抵抗[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(29):4728-4734.
[5] 乔晓峰,李昕.手术联合多种方法治疗耳部瘢痕的疗效对比研究[J].临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志,2017,31(17):1341-1343.
[6] 肖传柳,林鸿昌,罗杨,等.小白菊内酯通过调控微小RNA-637表达抑制瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭的研究[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2022,38(16):1915-1919.
[7] DONG P, XIONG Y, YUE J, et al. Long Non-coding RNA NEAT1: A Novel Target for Diagnosis and Therapy in Human Tumors. Front Genet. 2018;9:471.
[8] XU X, LIANG Y, GAREEV I, et al. LncRNA as potential biomarker and therapeutic target in glioma. Mol Biol Rep. 2023;50(1):841-851.
[9] YANG Y, JIN L, HE J, et al. Upregulation LncRNA MEG3 expression suppresses proliferation and metastasis in melanoma via miR-208/SOX4. Mol Cell Biochem. 2023;478(2):407-414.
[10] WU K, MA F, SHEN J, et al. LncRNA FPASL suppresses fibroblast proliferation through its DNA methylation via DNMT3b in hypertrophic scar. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2022;54(12):1-9.
[11] YANG J, DENG P, QI Y, et al. NEAT1 Knockdown Inhibits Keloid Fibroblast Progression by miR-196b-5p/FGF2 Axis. J Surg Res. 2021;259:261-270.
[12] 刘尧尧,孙明立,张帆.过表达miR-136-5p对子宫内膜癌HEC-1A细胞增殖、侵袭以及凋亡的影响[J].解剖科学进展,2021,27(5): 533-537.
[13] ZHANG J, NA S, PAN S, et al. Inhibition of USP4 attenuates pathological scarring by downregulation of the TGF‑β/Smad signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2019;20(2):1429-1435.
[14] WANG J, XIANG Y, YANG SX, et al. MIR99AHG inhibits EMT in pulmonary fibrosis via the miR-136-5p/USP4/ACE2 axis. J Transl Med. 2022; 20(1):426.
[15] ZHAO X, JIE X, GAO YK, et al. Long non-coding RNA CACNA1G-AS1 promotes proliferation and invasion and inhibits apoptosis by regulating expression of miR-205 in human keloid fibroblasts. Biosci Rep. 2020;40(6):BSR20192839.
[16] SHIM J, OH SJ, YEO E, et al. Integrated Analysis of Single-Cell and Spatial Transcriptomics in Keloids: Highlights on Fibrovascular Interactions in Keloid Pathogenesis. J Invest Dermatol. 2022;142(8):2128-2139.e11.
[17] LIU Y, XIONG X, CAO N, et al. Diagnosis and Treatment of Keloid: Method Summary and Effect Evaluation. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023;16:3775-3783.
[18] HU H, MAO G, ZHENG J, et al. Keloid Patient Plasma-Derived Exosomal hsa_circ_0020792 Promotes Normal Skin Fibroblasts Proliferation, Migration, and Fibrogenesis via Modulating miR-193a-5p and Activating TGF-β1/Smad2/3 Signaling. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022;16:4223-4234.
[19] LI Z, GONG C, WEI H. Long non-coding RNA H19 aggravates keloid progression by upregulating SMAD family member 5 expression via miR-196b-5p. Bioengineered. 2022;13(1):1447-1458.
[20] CHEN L, SU Y, YIN B, et al. LARP6 Regulates Keloid Fibroblast Proliferation, Invasion, and Ability to Synthesize Collagen. J Invest Dermatol. 2022;142(9):2395-2405.e7.
[21] ZHU M, LI Y, LIU L, et al. Circ_0057452 sponges miR-7-5p to promote keloid progression through upregulating GAB1. Cell Cycle. 2022; 21(23):2471-2483.
[22] ZHOU J, SHEN JY, TAO LE, et al. The Inhibition of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells on the Invasion of Keloid Fibroblasts. Int J Med Sci. 2022; 19(12):1796-1805.
[23] XU L, SUN N, LI G, et al. LncRNA H19 promotes keloid formation through targeting the miR-769-5p/EIF3A pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021;476(3):1477-1487.
[24] WANG J, SHEN J. LncRNA HOXA11-AS aggravates the keloid formation by targeting miR-148b-3p/IGFBP5 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021;581:60-67.
[25] CHEN Y, HUANG C, DUAN ZB, et al. LncRNA NEAT1 accelerates renal fibrosis progression via targeting miR-31 and modulating RhoA/ROCK signal pathway. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2023;324(2):C292-C306.
[26] LUO J, LIU J, MOU Y, et al. Propofol improves ischemia reperfusion-induced liver fibrosis by regulating lncRNA HOXA11-AS. J Toxicol Sci. 2023;48(6):345-354.
[27] MA T, QIU F, GONG Y, et al. Therapeutic silencing of lncRNA RMST alleviates cardiac fibrosis and improves heart function after myocardial infarction in mice and swine. Theranostics. 2023;13(11):3826-3843.
[28] WU Q, CHEN J, TAN Z, et al. Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1 (NEAT1) regulates fibroblast growth factor receptor substrate 2 (FRS2) by targeting microRNA (miR)-29-3p in hypertrophic scar fibroblasts. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1):5210-5219.
[29] YE J, LIN Y, YU Y, et al. LncRNA NEAT1/microRNA-129-5p/SOCS2 axis regulates liver fibrosis in alcoholic steatohepatitis. J Transl Med. 2020; 18(1):445.
[30] 万瑀,马芳,贺茜,等.长链非编码RNA SNHG1对增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞增殖的影响[J].解放军医学杂志,2022,47(2):118-127.
[31] WU X, WANG Z, WU G, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Proliferation of Hypertrophic Scar-Derived Fibroblasts via Inhibiting the Phosphorylation of AKT. Front Pharmacol. 2020; 11:602.
[32] ZHU W, WU X, YANG B, et al. miR-188-5p regulates proliferation and invasion via PI3K/Akt/MMP-2/9 signaling in keloids. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2019;51(2):185-196.
[33] CHAI CY, TAI IC, ZHOU R, et al. MicroRNA-9-5p inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of human hypertrophic scar fibroblasts through targeting peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor β. Biol Open. 2020;9(12):bio051904.
[34] LUO P, LIU D, ZHANG Q, et al. Celastrol induces ferroptosis in activated HSCs to ameliorate hepatic fibrosis via targeting peroxiredoxins and HO-1. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022;12(5):2300-2314.
[35] DUBEY S, DUBEY PK, UMESHAPPA CS, et al. Inhibition of RUNX1 blocks the differentiation of lung fibroblasts to myofibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 2022;237(4):2169-2182.
[36] PENG H, WAN LY, LIANG JJ, et al. The roles of lncRNA in hepatic fibrosis. Cell Biosci. 2018;8:63.
[37] GUO Y, LI M, LONG J, et al. LncRNA-ZNF252P-AS1/miR-15b-5p promotes the proliferation of keloid fibroblast by regulating the BTF3-STAT3 signaling pathway. J Dermatol Sci. 2022;108(3):146-156.
[38] XU J, WANG J, ZHAO M, et al. LncRNA LINC01018/miR-942-5p/KNG1 axis regulates the malignant development of glioma in vitro and in vivo. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023;29(2):691-711.
[39] ZHANG J, ZHANG L, YAO G, et al. lncRNA-Gm5532 regulates osteoclast differentiation through the miR-125a-3p/TRAF6 axis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2023;56(1):54-61.
[40] ZHOU Y, SHAO Y, HU W, et al. A novel long noncoding RNA SP100-AS1 induces radioresistance of colorectal cancer via sponging miR-622 and stabilizing ATG3. Cell Death Differ. 2023;30(1):111-124.
[41] LIU L, PANG X, SHANG W, et al. miR-136 improves renal fibrosis in diabetic rats by targeting down-regulation of tyrosine kinase SYK and inhibition of TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling pathway. Ren Fail. 2020; 42(1):513-522.
[42] HUANG X, WANG Z, HOU S, et al. Long non-coding RNA DSCAM-AS1 promotes pancreatic cancer progression via regulating the miR-136-5p/PBX3 axis. Bioengineered. 2022;13(2):4153-4165.
[43] ZHANG Z, WANG S, LIU W. EMT-related long non-coding RNA in hepatocellular carcinoma: A study with TCGA database. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;503(3):1530-1536.
[44] HUANG Y, WANG Y, WANG X, et al. The Effects of the Transforming Growth Factor-β1 (TGF-β1) Signaling Pathway on Cell Proliferation and Cell Migration are Mediated by Ubiquitin Specific Protease 4 (USP4) in Hypertrophic Scar Tissue and Primary Fibroblast Cultures. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e920736. |