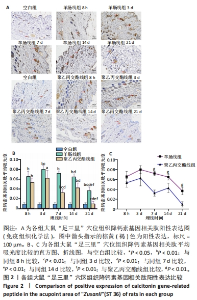
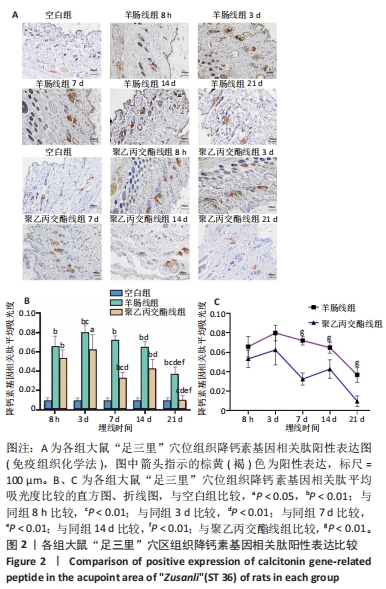
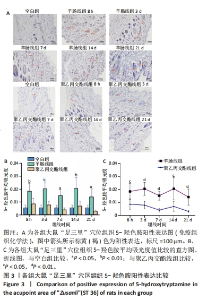
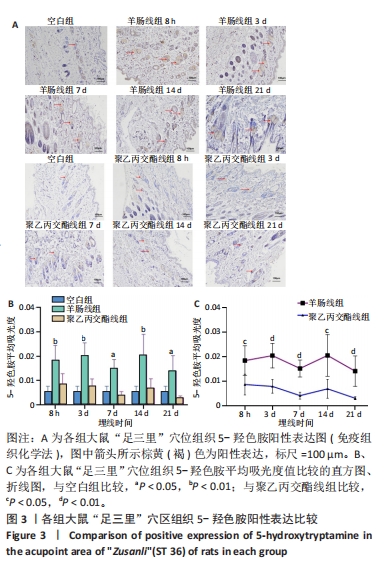
[1] ZHANG K, ZHAO X, DING S, et al. Applying Complex Network and Cell-Cell Communication Network Diagram Methods to Explore the Key Cytokines and Immune Cells in Local Acupoint Involved in Acupuncture Treating Inflammatory Pain. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020:2585960.
[2] 张国山,邱冉冉,潘江,等.艾灸对哮喘大鼠“肺俞”穴局部皮肤中组胺和神经肽的影响[J].针刺研究,2020,45(2):117-121.
[3] 刘惠,徐东升,陈虹,等.拔罐对大鼠环跳穴区皮肤组织相关神经肽及化学物质表达变化的影响[J].世界中医药,2021,16(5):769-774.
[4] 王莹莹,陈虹,张豪斌,等.刮痧对皮肤组织形态和GCS、SP、SOD表达的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2019,34(7):3204-3208.
[5] 陈虹,杨金生,徐东升,等.电针对“阳陵泉”穴区局部皮肤组织伤害性神经肽SP、CGRP及活性物质5-HT、HA表达的影响[C]//2017世界针灸学术大会暨2017中国针灸学会年会论文集.北京:中国针灸学会,2017:2.
[6] CHEN LZ, KAN Y, ZHANG ZY, et al. Neuropeptide Initiated Mast Cell Activation by Transcutaneous Electrical Acupoint Stimulation of Acupoint LI4 in Rats. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):13921.
[7] 吕柳,葛永铮.足三里在不同疾病中的单穴应用概况[J].中国中医药现代远程教育,2016,14(13):143-145.
[8] 吴莹辉,念峰,李燚,等.刺激足三里穴对人体免疫功能影响的Meta分析[J].当代医学,2020,26(2):108-111.
[9] 刘立公,顾杰.古代文献中胃经及其腧穴主治的统计报告[J].上海针灸杂志,2003,22(4):41-42.
[10] 狄忠.足三里针灸适宜病症古代文献研究[D].济南:山东中医药大学,2009.
[11] 陈小丽,岳增辉,刘丽,等.足三里穴的古今应用与研究[J].针灸临床杂志,2016,32(7):80-83.
[12] 杨涛,赵舒蒙,赵雪,等.近6年针灸基础实验中大鼠腧穴使用情况的计量研究[J].河北中医,2018,40(8):1248-1251.
[13] 梁欣,聂红昉,候珣瑞,等.运用磁共振T2图动态观察正常人体足三里穴微创埋线后线体对局部的刺激效应[J].针刺研究,2016,41(4): 356-360.
[14] 梁欣,聂红昉,侯珣瑞,等.PGLA线体微创埋线后对正常人体足三里穴刺激效应的时效性观察[J].中国针灸,2019,39(4):391-395.
[15] 程玲,梁欣,侯珣瑞,等.近10年穴位埋线关键要素特征的临床文献计量研究[J].针刺研究,2022,47(9):830-836.
[16] MINGFU L, XIAOTONG D, XIAOJING S, et al. Study on the dynamic compound structure composed of mast cells, blood vessels, and nerves in rat acupoint. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013: 160651.
[17] 刘芸,余芝,姜劲峰,等.基于神经血管耦联视域下的针刺调控途径探析[J].针刺研究,2022,47(1):83-87.
[18] 余曙光,郭义.实验针灸学[M].上海: 上海科学技术出版社,2009: 15.
[19] 马伊磊,孙文善,姜国芳.微创埋线对椎动脉型颈椎病椎动脉血流的影响[J].上海针灸杂志,2017,36(4):449-452.
[20] 李永明.关于肥大细胞与经穴现象的“宋氏理论”及研究方向[J].中国针灸,2016,36(10):1063-1068.
[21] 姜同菲,郭静.应用脑功能磁共振成像技术对经穴特异性研究概况[J].中华中医药杂志,2021,36(8):4820-4823.
[22] 吴艳英,任晓暄,吉毛先,等.浅析经穴效应特异性的相对性与整体性[J].中国针灸,2018,38(7):729-733.
[23] 刘存志.针灸研究的科学问题[M].北京: 人民卫生出版社,2022:13.
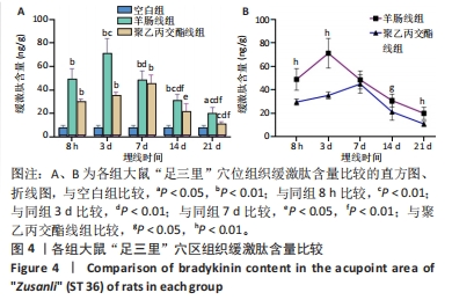
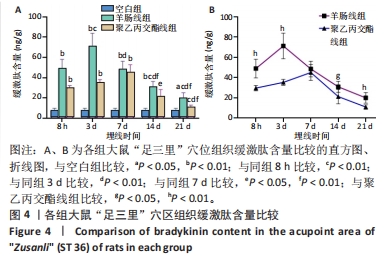
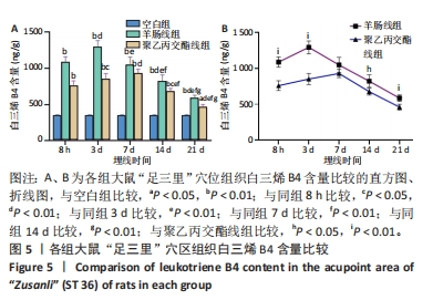
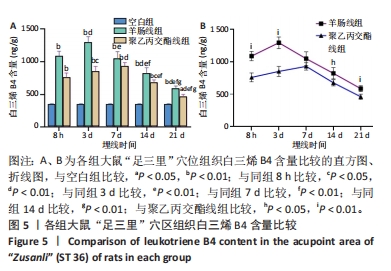
[24] 王钰嘉,李丽红,侯珣瑞,等.羊肠线、PGLA线埋入对健康大鼠“足三里”穴区皮肤肥大细胞、P物质及组胺的影响[J].中国针灸, 2023,43(8):944-950.
[25] IYENGAR S, OSSIPOV MH, JOHNSON KW. The role of calcitonin gene–related peptide in peripheral and central pain mechanisms including migraine. Pain. 2017;158(4):543-559.
[26] 潘丽佳,赵雪,郭义.CGRP与针刺效应相关性的研究进展[J].上海针灸杂志,2016,35(1):117-120.
[27] LUNDEBERG T. Acupuncture mechanisms in tissue healing: contribution of NO and CGRP. Acupunct Med. 2013;31(1):7-8.
[28] FAN Y, KIM DH, RYU Y, et al. Neuropeptides SP and CGRP Underlie the Electrical Properties of Acupoints. Front Neurosci. 2018;12:907.
[29] BENARROCH EE. CGRP: Sensory neuropeptide with multiple neurologic implications. Neurology. 2011;77(3):281-287.
[30] POYNER DR. Calcitonin gene-related peptide: Multiple actions, multiple receptors. Pharmacol Ther. 1992;56(1):23-51.
[31] LÄMMERMANN T, AFONSO PV, ANGERMANN BR, et al. Neutrophil swarms require LTB4 and integrins at sites of cell death in vivo. Nature. 2013;498(7454):371-375.
[32] LEY K, LAUDANNA C, CYBULSKY MI, et al. Getting to the site of inflammation: the leukocyte adhesion cascade updated. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7(9):678-689.
[33] 周爽,李慧敏,张行行,等.基于LTB4/BLTR通路探讨黄芩苷-栀子苷配伍对局灶性脑缺血大鼠再灌注损伤的影响[J].中南药学, 2022,20(6):1255-1261.
[34] 陈小菊.白三烯与慢性阻塞性肺疾病的研究进展[J].国外医学(呼吸系统分册),2003,23(1):12-14.
[35] 李丽莎,杨泳,刘星玲,等.白三烯B4在单肺通气致肺微血管内皮细胞通透性增加中的作用机制[J].南方医科大学学报,2017,37(11): 1523-1528.
[36] 周竞颖,来奕恬,丁攀婷,等.针灸对克罗恩病模型大鼠天枢穴局部皮肤中缓激肽、CGRP和NPY的影响[J]. 湖南中医药大学学报, 2023,43(1):100-105.
[37] 马圣尧,王伟瑜,王怀杰,等.缓激肽上调豚鼠肠道黏膜下神经丛环氧合酶2的表达(英文)[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2022,49(1): 62-71.
[38] 戴红良,张慧云,何韶衡.缓激肽在过敏性疾病发病机制中的作用[J].中华临床免疫和变态反应杂志,2014,8(4):306-311.
[39] 刘小燕,刘汉平,张鹤鸣,等.穴位埋线局部刺激效应动态变化的激光多普勒微循环研究[J].中华中医药杂志,2012,27(6):1503-1507.
[40] 代巧妹,王美峤,颜培宇,等.针刺“足三里”对免疫抑制大鼠的作用及穴区CGRP表达影响的研究[J].针灸临床杂志,2018,34(5): 49-52.
[41] 石冬一,姜宇晴,王哲,等.眼针对眼周穴区皮下肥大细胞活化作用的实验研究[J].辽宁中医杂志,2022,49(2):182-186,226-227.
[42] 梁宜,方剑乔. 5-羟色胺痛觉调制与针灸镇痛相关研究[J].上海针灸杂志,2009,28(8):492-495.
[43] 张春燕,李亚明,张巧艳.苍耳子、辛夷药对挥发油化学成分及对抗组胺、五羟色胺所致的皮肤过敏反应[J].老年医学与保健, 2008,14(3):172-174.
[44] 汪芳,萧伟,王振中,等. 5-羟色胺监控中药注射剂过敏反应的可行性研究[J].中成药,2015,37(2):457-459.
[45] 陈虹,徐东升,杨金生,等.艾灸对阳陵泉穴区皮肤组织五羟色胺和组胺的影响[J].上海针灸杂志,2018,37(7):813-817.
[46] 杨昆吾,杨金生,徐东升,等.不同刮痧力度对大鼠皮肤形态及5-羟色胺、肥大细胞表达变化的比较研究[J].中国中医基础医学杂志, 2021,27(4):587-591.
|