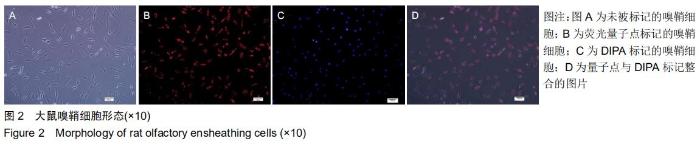
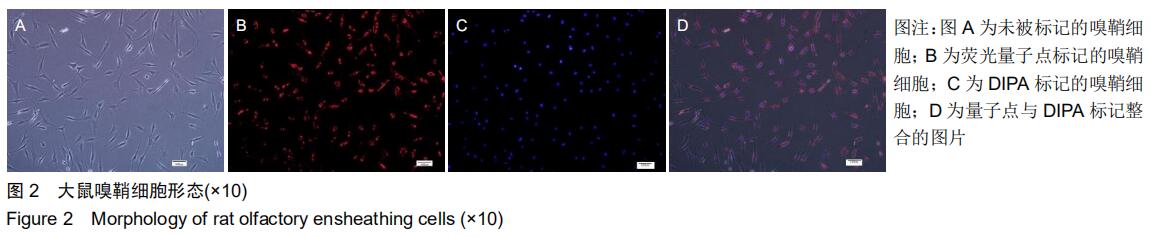
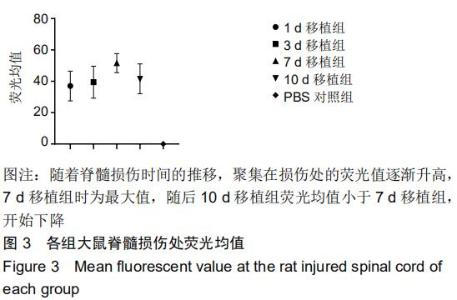
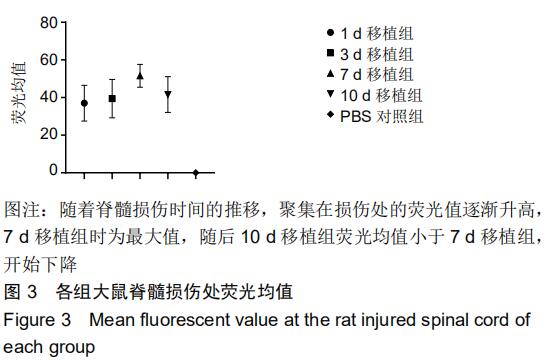
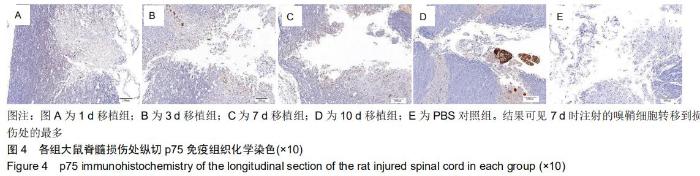
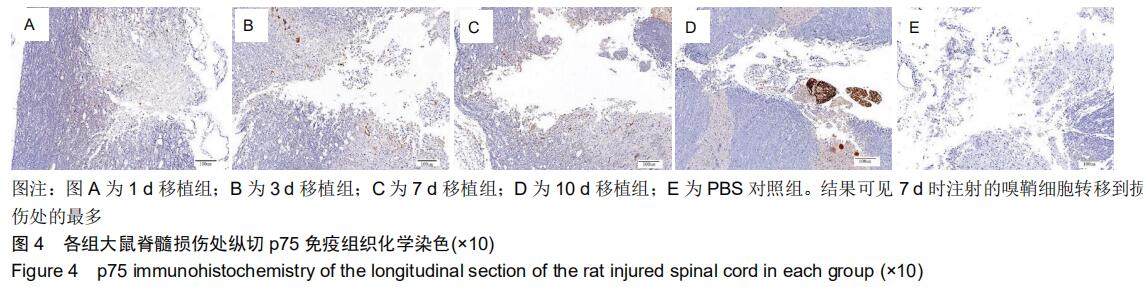
|
[1] STENUDD M, SABELSTROM H, FRISEN J. Role of endogenous neural stem cells in spinal cord injury and repair. JAMA Neurol. 2015;72(2):235-237.
[2] KANNO H, PEARSE D D, OZAWA H, et al. Schwann cell transplantation for spinal cord injury repair: its significant therapeutic potential and prospectus. Rev Neurosci.2015;26(2):121-128.
[3] LIN L, LIN H, BAI S, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) improved functional recovery of spinal cord injury partly by promoting axonal regeneration.Neurochem Int.2018;115:80-84.
[4] ANNA Z, KATARZYNA J, JOANNA C, et al. Therapeutic Potential of Olfactory Ensheathing Cells and Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Spinal Cord Injuries.Stem Cells International.2017;2017:1-6.
[5] YANG H, HE BR, HAO DJ. Biological roles of olfactory ensheathing cells in facilitating neural regeneration: a systematic review.Mol Neurobiol. 2015;51(1):168-179.
[6] LIU Y, GONG Z, LIU L, et al. Combined effect of olfactory ensheathing cell (OEC) transplantation and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) intravitreal injection on optic nerve injury in rats.Mol Vis.2010; 16:2903-2910.
[7] 王珺,张利剑,夏鹤春,等.低氧诱导的大鼠嗅黏膜来源嗅鞘细胞自噬及其对细胞增殖能力的影响[J].吉林大学学报(医学版), 2016,42(03):430-434.
[8] ZHANG L, ZHUANG X, CHEN Y, et al. Intravenous transplantation of olfactory bulb ensheathing cells for a spinal cord hemisection injury rat model.cell transplantation.Cell Transplant. 2019;28(12):1585-1602.
[9] 赵启军,刘燕青,张朝.嗅鞘细胞治疗脊髓损伤的现状及移植途径[J].中国医学创新, 2014,11(6):154-156.
[10] GÓMEZ RM, SÁNCHEZ MY, PORTELA LOMBA M, et al. Cell therapy for spinal cord injury with olfactory ensheathing glia cells (OECs).Glia. 2018;66(7):1267-1301.
[11] RAO YJ, ZHU WX, DU ZQ, et al. Effectiveness of olfactory ensheathing cell transplantation for treatment of spinal cord injury. Genet Mol Res. 2014;13(2):4124-4129.
[12] CHEN L, HUANG H, XI H, et al. A Prospective Randomized Double- Blind Clinical Trial Using a Combination of Olfactory Ensheathing Cells and Schwann Cells for the Treatment of Chronic Complete Spinal Cord Injuries.Cell Transplantation.2014;23(1_suppl):35-44.
[13] RAO Y, ZHU W, LIU H, et al. Clinical application of olfactory ensheathing cells in the treatment of spinal cord injury.J Int Med Res. 2013;41(2):473-481.
[14] SUN T, YE C, ZHANG Z, et al. Cotransplantation of Olfactory Ensheathing Cells and Schwann Cells Combined with Treadmill Training Promotes Functional Recovery in Rats with Contused Spinal Cords. Cell Transplantation.2013;22(1_suppl):27-38.
[15] RAISMAN G, BARNETT SC, RAMON-CUETO A. Repair of central nervous system lesions by transplantation of olfactory ensheathing cells.Handb Clin Neurol.2012;109:541-549.
[16] KHANKAN R R, GRIFFIS KG, HAGGERTY-SKEANS JR, et al. Olfactory Ensheathing Cell Transplantation after a Complete Spinal Cord Transection Mediates Neuroprotective and Immunomodulatory Mechanisms to Facilitate Regeneration.J Neurosci.2016;36(23): 6269-6286.
[17] ZHONG W, BIAN K, HU Y, et al. Lysophosphatidic acid guides the homing of transplanted olfactory ensheathing cells to the lesion site after spinal cord injury in rats.Exp Cell Res.2019;379(1):65-72.
[18] ARMULIK A, GENOVE G, MAE M, et al. Pericytes regulate the blood-brain barrier.Nature.2010;468(7323):557-561.
[19] GU J, XU H, XU YP, et al.Olfactory ensheathing cells promote nerve regeneration and functional recovery after facial nerve defects.Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(1):124-131.
[20] 贾全章,李东君,陈玉丙,等.骨髓间充质干细胞向脊髓损伤区的迁徙[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(45):8390-8393.
[21] YU M, ZHAO K, ZHU X, et al. Development of near-infrared ratiometric fluorescent probe based on cationic conjugated polymer and CdTe/CdS QDs for label-free determination of glucose in human body fluids. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;95:41-47.
[22] XU G, ZENG S, ZHANG B, et al. New Generation Cadmium-Free Quantum Dots for Biophotonics and Nanomedicine.Chem Rev.2016; 116(19):12234-12327.
[23] 王强,于霞,焦延超,等.嗅鞘细胞静脉移植治疗陈旧性脊髓损伤的实验研究[J].泰山医学院学报, 2017,38(1):8-12.
[24] 巫九官,李艳敏,郑晓晖.嗅鞘细胞移植对脊髓损伤大鼠的作用[J].齐鲁医学杂志, 2016,31(4):424-427.
|