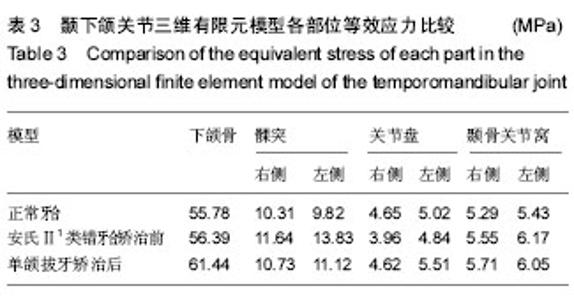
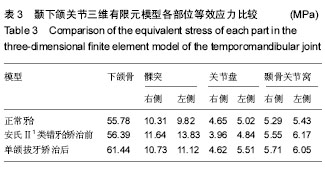
| [1] 杨红,廉翔,樊晶.成人正畸的临床特点及治疗方法分析[J].中国实用医药,2015,10(27):87-88.[2] 罗尚叠.单颌与双颌拔牙矫治成人安氏Ⅱ类1分类的疗效对比研究[D].暨南大学, 2014.[3] Kalha AS. Early orthodontic treatment reduced incisal trauma in children with class II malocchsions. Evid Based Dent, 2014, 15(1):18-20.[4] 奉晓斌.安氏Ⅱ1错(牙合)上颌单颌拔牙矫治前后咀嚼效率对比研究[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2012,5(8):495-497.[5] 黄红亮,安爱群,卢红飞,等.上颌单颌拔牙矫治成人安氏Ⅱ错(牙合)的头影测量研究[J].北京口腔医学,2012,19(6):346-348.[6] 陆盛.不同拔牙矫治模式矫治安氏Ⅱ类伴下切牙缺失错合畸形疗效的PAR指数评价[J].浙江医学,2014,26(10):857-862.[7] 闫阔.Tip-Edge矫治技术中尖牙外展弯相对位置对尖牙移动趋势影响的有限元分析[D].吉林大学,2012.[8] Kim KN, Cha BK, Choi DS, et al. A finite element study on the effects of midsymphyseal distraction osteogenesis on the mandibule and articular disc. Angle Orthod, 2012,82(3): 464-471.[9] 周子凌,张渊,石利强,等.咬合接触对颞下颌关节应力分布影响的三维有限元分析[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2015,50(5):302-306.[10] Koolstra JH, vanEijden TM. Three-dimensional dynamical capabilities of the human masticatory muscles. J Biomech. 1999;32(2):145-152.[11] 刘梦超. 颞下颌关节骨骼肌肉系统三维有限元模型的建立[D]. 温州医科大学, 2014.[12] 王杰睿,潘旭,米丛波.维吾尔族错颌畸形患者髁突位置及颞下颌关节形态的锥形束CT研究[J].上海口腔医学,2016,25(4): 461-464.[13] 车蓓,张昊,钱才梅,等.不同垂直骨面型安氏Ⅱ类1分类错合患者颞下颌关节三维形态结构的比计较[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2014, 49(7):399-402.[14] Fang HJ, Tao L. Evaluation of sagittal temporomandibular condyle position in adolescent Angle Class II division 1 patients by cone-beam CT. Shanghai Kouqiang Yixue. 2014; 23(6):740-743.[15] 赖晓宇,林雪峰,吴夏怡.青年安氏Ⅱ类1分类错合患者下颌咀嚼运动轨迹特征的研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2016,32(1): 115-119.[16] 葛胜将.不同骨性错(牙合)患者髁突形态及位置的CBCT研究[D].青岛大学,2015.[17] Savoldelli C, Bouchard PO, Maniere-Ezvan A, et al. Comparison of stress distribution in the temporomandibular joint during jaw closing before and after symphyseal distraction:a finite element study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012;41(12): 1474-1482.[18] Meloto CB, Serrano PO, Ribeiro-DaSilva MC, et a1.Genomics and the new Perspectives for temporomandibular disorders. Arch Oral Biol. 2011;56(11):1181-1191.[19] Papageorgiou SN, Keilig L, Vandevska-Radunovic V, et al. Torque differences due to the material variation of the orthodontic appliance: a finite element study. Prog Orthod. 2017;18(1):6.[20] Jo AR, Mo SS, Lee KJ, et al. Finite-element analysis of resistance of the mandibular dentition. Korean J Orthod. 2017;47(1):21-30.[21] Mathew A, Nagachandran KS, Vijayalakshmi D. Stress and displacement pattern evaluation using two different palatal expanders in unilateral cleft lip and palate: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. Prog Orthod. 2016;17(1):2-10.[22] Savoldelli C, Bouchard PO, Loudad R, et al.Stress distribution in the temporomandibular joint discs during jaw closing:a high-resolution three-dimensional finite-element model analysis. Surg Radiol Anat. 2012;4(5):404-413.[23] Mori H, Horiuchi S, Nishimura S,et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of cartilaginous tissues in human temporomandibular joint during prolonged clenching. Arch Oral Biol. 2010;55(11):879-886.[24] 邓潇,万哲,何姝姝,等.成人安氏II类错合正畸人群正中关系位与最大牙尖交错位你不调的研究[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2011, 29(1):48-52.[25] Vitral RWF, Telles CS. Computed tomography evaluation of temporomandibular joint alterations in ClassⅡDivisioon 1subdivision patients:condylar symmetry. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2002;121(4):369-374.[26] Vitral RW, Telles Cde S, Fraga MR, et al. Computed tomography evaluation of temporomandibular joint alterations in patients with class II division 1 subdivision malocclusions:condyle-fossa relationship. Am J Oahod Dentofacial Oahop. 2004;126(1): 48-52.[27] 孙岩.安氏Ⅱ类1分类错合患者颞下颌关节CBCT测量值分析[D].中山大学,2010.[28] 方海军,陶列.青春期安氏Ⅱ类1分类患者髁突矢状向位置的锥形束CT测量分析[J].上海口腔医学,2014,23(6):740-743.[29] 张亚楠,雷勇华,邹双双,等.双合垫矫治器治疗青少年安氏Ⅱ1错合患者颞下颌关节变化的初步研究[J].中华口腔正畸学杂志, 2016,23(1):12-16.[30] 顾永佳,陆胜男,高美琴,等.青少年安氏I、II类错合畸形患者髁突位置的比较[J].上海口腔医学,2016,25(6):694-696.[31] 刘展,钱英莉,张远理,等.关节盘移位对颞下颌关节内应力分布的影响[J].医用生物力学,2013,28(5):528-532.[32] 王晓宇,厉松.安氏II1类青少年髁突运动轨迹与颞下颌关节形态的研究[J].北京口腔医学,2011,19(3):164-166.[33] Piehslinger E, Celar A,Celar RM, et al. Orthopetic jaw movement observations, Part V: Transversal condylar shift in protrusive and retrusive movement. Cranio.1994;12(4): 247-251.[34] Tomonari H, Kubota T, Yagi T, et al. Posterior scissorsbite: Masticatory jaw movement and muscle activity. J Oral Rehabil. 2014;41(4):257-265.[35] Nakamura A, Zeredo JL, Utsumi D, et al. Influence of malocclusion on the development of masticatory function and mandibular growth. Angle Orthod. 2013;83(5):749-757.[36] 方颖,孙雯,施洁珺,等.安氏Ⅱ1类下颌后缩颞下颌关节结构与垂直骨面型、覆牙合覆盖的相关性研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志, 2008,24(6):886-889.[37] 王天丛,闫翔,何冬梅,等.安氏Ⅱ类1分类错殆上牙列单颌拔牙矫治后颞下颌关节间隙变化的研究[J].实用临床医药杂志,2016, 20(15):198-199.[38] 张学军,周传丽,白玉兴,等.安氏Ⅱ类1分类错合髁突运动轨迹与关节盘位置的相关性研究[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2010,45(1): 16-19.[39] Aoun M, Mesnard M, Monede-Hocquard L, et al. Stress analysis of temporpm-andibular joint disc during maintained clenching using a viscohyperelastic finite element model. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014;72(6):1070-1077.[40] 唐顼晶,刘月华,王冬梅,等.两种加载方式前牙闭锁性深覆合颞下颌关节的三维有限元分析[J].中国美容医学,2012,21(6): 982-985. |