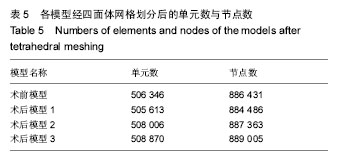
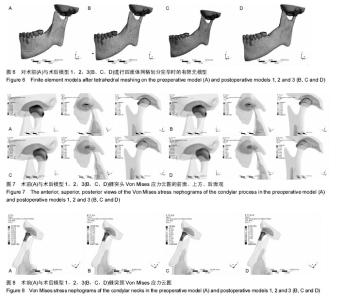
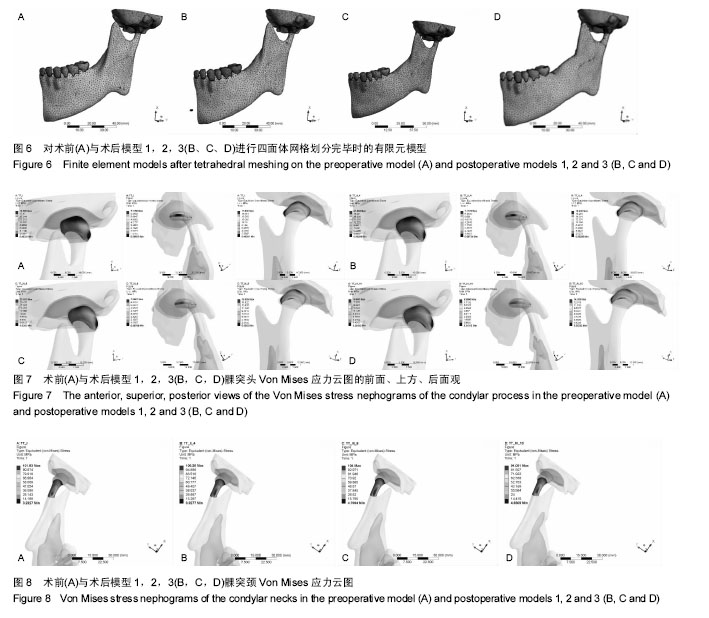
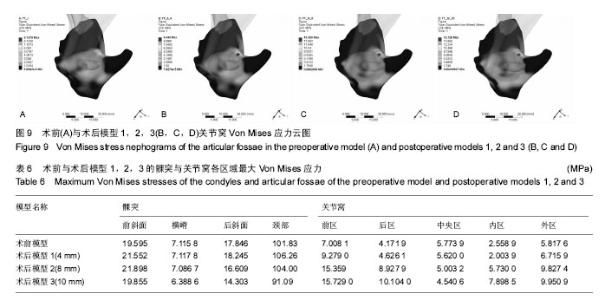
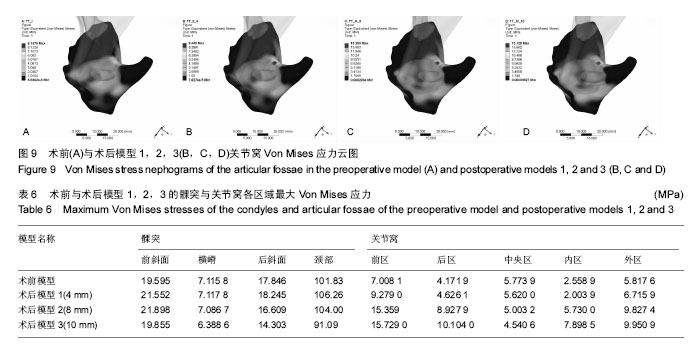
| [1] McNamara JA Jr,Peterson JE Jr,Alexander RG.Three-Dimensional Diagnosis and Management of Class II Malocclusion in the Mixed Dentition.Semin Orthod. 1996;2(2): 114-137.[2] 谢丽丽,左艳萍,董福生.安格尔Ⅱ类错牙合的生长发育特点[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2003,17(5):468-470.[3] Baccetti T,Franchi L,McNamara JA JR,et al.Early dentofacial features of classⅡmalocclusion: A longitudinal study from the deciduous through the mixed dentition.Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 1997;111:502-509.[4] Bishara SE,Hoppens BJ,Jakobsen JR,et al.Changes in the molar relationship between the deciduous and permanent dentitions:a longitudinal study.Am J Orthod. 1988;93(1):19-28.[5] 王美青,何三纲.口腔解剖生理学(第7版)[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2014:111.[6] MasBarb RF,Chen AL,Hu JC,et al.Engineering Functional Anisotropy in Fibrocartilage Neotissues. Biomaterials. 2013; 34(38):9980-9989.[7] 胡凯,周继林,胡敏,等.颞下颌关节负荷研究方法及其评价[J].国外医学:生物医学工程分册,1997,20(4):228-232.[8] Koolstra JH,van Eijden TM. Combined finite-element and rigid-body analysis of human jaw joint dynamics.J Biomech. 2005;38: 2431-2439.[9] 周祺,蔡中,房兵.正颌手术与颞下颌关节的关系研究进展[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2003,12(1):35-38.[10] 张震康,张熙恩,傅民魁.正颌外科学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,1994: 180-185.[11] 房兵,周祺,沈国芳,等.下颌支矢状劈开后退术对颞下颌关节影响的有限元研究[J].上海口腔医学,2004,13(1):51-55.[12] 段嫄嫄,王忠义,张寿华,等.有限元方法及其在口腔医学中的应用[J].医学与哲学,2004,25(10):48-50.[13] Turner MJ,Clough RW,Martin HC,et al.Stiffness an deflection analysis of complex structure.J Aero Soc. 1956;23(9):805.[14] 张红,殷新民,吴凤鸣,等.牙尖交错位紧咬时颞下颌关节接触特征及应力分布的三维有限元研究[J].口腔医学,2007,27(12):617-619.[15] Aoun M,Mesnard M, Monede-Hocquard L,et al.Stress Analysis of Temporomandibular Joint Disc During Maintained Clenching Using a Viscohyperelastic Finite Element Model. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014;72:1070-1077.[16] 于世凤.口腔组织病理学(第6版)[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2011:80.[17] 陈新明,汪说之,熊世春,等.人髁突软骨组织各带厚度的测量[J].解剖学杂志,1997,20(1):87-90.[18] Hansson T,Oberg T,Carlsson GE,et al.Thickness of the soft tissue layers and the articular disk in the temporomandibular joint.Acta Odont.Scand. 1977;35:77-83.[19] 王美青,何三纲.口腔解剖生理学(第7版)[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2014:131-133.[20] Hart RT,Hennebel VV,Thongpreda N,et al.Modeling the biomechanics of the mandible:A three-dimensional finite element study.J Biomechanics. 1992;25(3):261-286.[21] Tanaka E,del Pozo R,Tanaka M,et al.Three-dimensional finite element analysis of human temporomandibular joint with and without disc displacement during jaw opening.Med Eng Phys. 2004;26:503-511.[22] 刘啸殷.关节盘前位移颞下颌关节生物力学研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2013.[23] Weijs WA,Hillen B.Cross-seetional areas and estimated intrinsic strength of the human jaw muscles.Acta Morph Neerl Scand. 1985;23:267.[24] 尹翰文,林娜,关键,等.双侧下颌支矢状劈开坚固内固定的三维有限元分析[J].上海口腔医学,2012,21(2):194-198.[25] 殷学民,张君伟,任晓旭,等.下颌支矢状骨劈开术数字模型的建立及不同固定方式的稳定性分析[J].上海口腔医学,2013,22(3): 241-245.[26] 周学军,赵志河,赵美英,等.包括下颌骨的颞下颌关节三维有限元模型的建立[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2000,16(1):17-19.[27] 苏忠平,何黎升,白石柱,等.应用Mimics和HyperMesh 软件建立人体下颌骨三维有限元模型[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2012,28(2): 192-195.[28] Standlee JP,Caputo AA,Ralph JP.The condyle as a stress-distributing component of the temp-oromandibular joint.J Oral Rehabil.1981;8:391-400.[29] 郭宏,刘洪臣,张润荃,等.正常颞下颌关节应力分布的三维有限元研究[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2004,20(3):134-137.[30] 胡凯,张晔缨,柳春明,等.模拟功能咬合时人颞下颌关节内的应力分布和位移特征[J].解放军医学杂志,2003,28(1):63-65.[31] 陈硕,刘筱菁,李自力,等.下颌后缩畸形患者正颌外科术后髁突改建的三维影像评价[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2015,47(4):703-707.[32] 雷涛,张纲,谭颖徽.有限元法在颌骨生物力学研究中的应用研究进展[J].重庆医学,2009,38(3):350-352. |