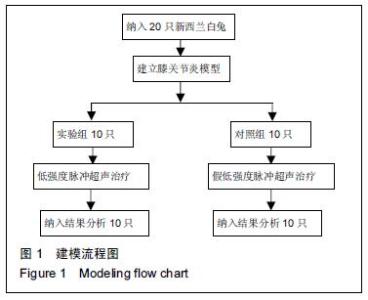
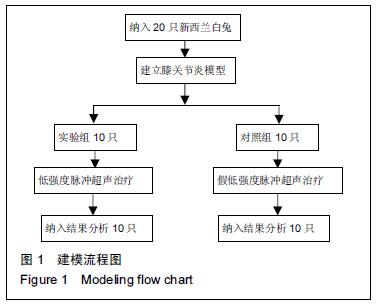
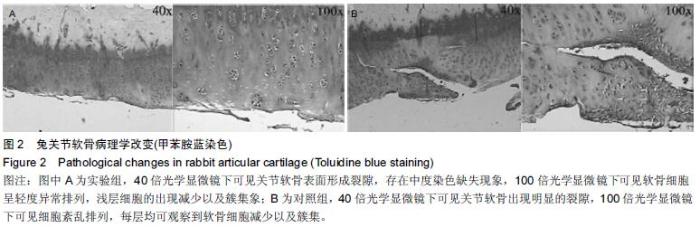
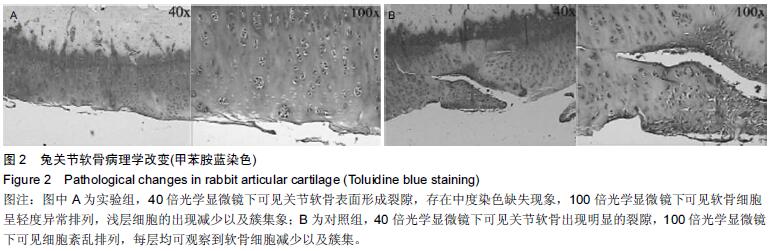
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (18): 2596-2602.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.18.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of low intensity pulsed ultrasound on the expression of type II collagen and matrix metalloproteinase-13 in chondrocytes of a rabbit model of knee arthritis
Wu Jian-ping1, Wang Zhi-gang2, Wang Li-ming3
- 1Special Inspection Branch, Binzhou People’s Hospital, Binzhou 256610, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Anesthesiology, Binzhou People’s Hospital, Binzhou 256610, Shandong Province, China; 3Department of Hand and Foot Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou 256610, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2016-02-24Online:2016-04-29Published:2016-04-29 -
Contact:Wu Jian-ping, Special Inspection Branch, Binzhou People’s Hospital, Binzhou 256610, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Wu Jian-ping, Master, Attending physician, Special Inspection Branch, Binzhou People’s Hospital, Binzhou 256610, Shandong Province, China
Cite this article
Wu Jian-ping, Wang Zhi-gang, Wang Li-ming. Effects of low intensity pulsed ultrasound on the expression of type II collagen and matrix metalloproteinase-13 in chondrocytes of a rabbit model of knee arthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(18): 2596-2602.
share this article
| [1] 柳学勇,冉春风,刘盼,等.低强度聚焦超声与普通超声治疗创伤性膝关节炎的疗效比较[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2011,33(12):927-929. [2] 夏鹏,李雪萍,林强,等.低强度脉冲超声对兔膝骨性关节炎软骨细胞整合素-局部粘着斑激酶-促分裂原活化蛋白激酶力化学转导通路相关蛋白表达的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2014,36(3):165-170. [3] 徐守宇,张丽梅,姚新苗,等.低强度脉冲超声对兔膝骨关节炎软骨细胞外基质的影响及机制[J].中国骨伤,2014, 27(9): 766-771. [4] 任莎莎,李雪萍,林强,等.低强度脉冲超声经PI3K/Akt通路调控兔膝骨性关节炎软骨细胞凋亡的作用机制研究[J].中国康复,2015,30(2):83-87. [5] 张雁军,柴利军,杜林海,等.玻璃酸钠联合低强度脉冲超声治疗膝骨性关节炎的临床疗效观察[J].临床合理用药杂志,2014,(31):77-78. [6] 潘晓华,何爽,谢小青,等.玻璃酸钠与超声导入Fastum凝胶联合治疗膝骨性关节炎合并滑膜炎[J].中国康复,2007, 22(2):110-111. [7] 张雁军,柴利军,杜林海,等.玻璃酸钠联合低强度脉冲超声治疗骨性关节炎疗效观察[J].临床合理用药杂志, 2014, 7(12A):28-29. [8] 周崑,周伟,贾小林,等.超声对实验性早期兔膝关节骨关节炎的作用[J].重庆医科大学学报,2008,33(1): 6-17. [9] 李涛.低强度脉冲超声、关节腔内注射玻璃酸钠及其两者联合治疗轻中度膝骨性关节炎的短期疗效分析[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2013. [10] 王小红.低强度脉冲超声对实验性兔骨性关节炎软骨损伤修复的影响[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2009. [11] 成吉华,赵丹,郭杨,等.低强度脉冲超声治疗骨关节炎的应用进展[J].临床超声医学杂志,2014,16(7):475-477. [12] Buchbender C, Sewerin P, Mattes-György K, et al. Utility of combined high-resolution bone SPECT and MRI for the identification of rheumatoid arthritis patients with high-risk for erosive progression. Eur J Radiol. 2013;82(2):374-379. [13] 王小红,王洪,杨述华,等.低强度脉冲式超声对实验性兔骨关节炎软骨损伤修复的影响[J].国际骨科学杂志,2009, 30(3):191-193. [14] Hwang SR, Seo DH, Al-Hilal TA, et al. Orally active desulfated low molecular weight heparin and deoxycholic acid conjugate, 6ODS-LHbD, suppresses neovascularization and bone destruction in arthritis. J Control Release. 2012;163(3):374-384. [15] 李涛.低强度脉冲超声治疗膝骨性关节炎的研究进展[J].国际检验医学杂志,2013,34(15):2000-2003. [16] 颜益红.超声波和运动疗法对兔膝骨关节炎软骨细胞凋亡BCL-2和MMP-13的影响[J].长沙:中南大学,2012. [17] Korstjens CM, vail der Rijt RH, Alhers GH, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound affects human articular chondrocytes in vitro. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2008;46(12):1263-1270. [18] Irrechukwu ON,Lin PC,Fritton K,et a1.Magnetic resonance studies of macromolecular content in engineered cartilage treated with low-intensity pulsedultrasound. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(3-4): 407-415. [19] 张丽梅,徐守宇.超声波对关节软骨影响的实验研究进展[J].风湿病与关节炎,2013,2(1):60-63. [20] 马勇,郭杨,屠娟,等.低强度脉冲超声介导威灵仙干预兔膝关节软骨细胞增殖及Ⅱ型胶原和转化生长因子β1的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,(38):6110-6115. [21] 贾小林,陈文直,周伟,等.低强度脉冲超声对关节软骨缺损修复影响的初步观察[J].中国超声医学杂志, 2003, 19(12): 889-891. [22] 郭杨,马勇,董睿,等.低强度脉冲超声对兔关节软骨细胞增殖及Ⅱ型胶原表达的影响[J].安徽医科大学学报, 2014, 49(12): 1739-1742. [23] 周嘉辉,吕红斌,胡建中,等.兔胫骨骨延长模型在低强度脉冲超声刺激条件下的骨再生与成熟[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(7):1141-1145. [24] 贾小林,陈文直,孙保勇,等.低强度脉冲超声对兔关节软骨损伤修复的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志, 2009, 31(5):305-307. [25] 肖惟雄,班兆阳,朱智敏,等.低强度脉冲超声在骨治疗中的生物学机制[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2013,40(4):557-560. [26] 钟守昌,黄丽霞,李长雷,等.低强度脉冲超声和低频电磁场联合治疗兔桡骨骨折中外骨痂和骨折线的影像评价[J].江汉大学学报(自然科学版),2014,(5):53-57. [27] 王小红,王洪,杨述华,等.低强度脉冲式超声对实验性兔骨关节炎软骨损伤修复的影响[J].国际骨科学杂志,2009, 30(3):191-193. [28] Naito K, Watari T, Muta T, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) increases the articular cartilage type II eoBagen in a rat osteoarthritis model. J Orhop Res. 2010;28(3):361-369. [29] Li X, Li J, Cheng K, et al. Effect oflow-intensity pulsed ultrasound on MMP-13 and MAPKs signaling pathway in rabbit knee osteoarthritis. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2011;61(2):427-434. [30] Koga T, Lee SY, Niikura T, et al. Effect of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on bone morphogenetic protein 7-induced osteogenic differentiation of human nonunion tissue-derived cells in vitro. J Ultrasound Med. 2013;32(6):915-922. [31] Ito A, Aoyama T, Yamaguchi S, et al. Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound Inhibits Messenger RNA Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinase-13 Induced by Interleukin-1β in Chondrocytes in an Intensity-Dependent Manner. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2012;38(10):1726-1733. [32] Lv YG, Zhao PC, Chen GB, et al. Effects of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on cell viability, proliferation and neural differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells-derived neural crest stem cells. Biotechnol Lett. 2013;35(12):2201-2212. [33] 高明霞,程凯,林强,等.低强度脉冲超声波对早中期兔膝骨性关节炎软骨细胞外基质及MAPKs信号通路的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志,2013,28(7):593-599. [34] Cheng K, Xia P, Lin Q, et al. Effects of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on integrin-FAK-PI3K/Akt mechanochemical transduction in rabbit osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2014;40(7): 1609-1618. [35] Hu J, Qu J, Xu D, et al. Combined application of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound and functional electrical stimulation accelerates bone-tendon junction healing in a rabbit model. J Orthop Res. 2014;32(2): 204-209. [36] 柯丹,刁庆春,李发琪,等.低强度脉冲超声对人皮肤成纤维细胞增殖及胶原蛋白合成的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2008,30(1):17-20. [37] Yang Z, Ren L, Deng F, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound induces osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament cells through activation of bone morphogenetic protein-smad signaling. J Ultrasound Med. 2014;33(5):865-873. [38] 李雪萍,励建安.低强度脉冲超声波促进骨性关节炎软骨修复的研究进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2010,25(12): 1204-1207. [39] 夏鹏.低强度脉冲超声波经整合素-FAK-MAPK力化学传导通路对兔膝骨性关节炎关节软骨细胞的作用研究[D].南京:南京医科大学,2014. [40] 周崑,周伟,陈文直,等.低强度脉冲超声对美蓝渗入正常兔膝关节软骨的作用[J].重庆医科大学学报,2012,37(2): 121-124. [41] Zieba J, Forlenza KN, Khatra JS, et al. TGFβ and BMP Dependent Cell Fate Changes Due to Loss of Filamin B Produces Disc Degeneration and Progressive Vertebral Fusions. PLoS Genet. 2016;12(3):e1005936. [42] Zhuang C, Xu NW, Gao GM, et al. Polysaccharide from Angelica sinensis protects chondrocytes from H2O2-induced apoptosis through its antioxidant effects in vitro. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;87:322-328. [43] Ding L, Wu J, Li D, Wang H, et al. Effects of CCN3 on rat cartilage endplate chondrocytes cultured under serum deprivation in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 2016;13(3): 2017-2022. [44] Yun S, Ku SK, Kwon YS. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and platelet-rich plasma synergistically ameliorate the surgical-induced osteoarthritis in Beagle dogs. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016;11(1):9. [45] Hemphill DD, McIlwraith CW, Slayden RA, et al. Adeno-associated virus gene therapy vector scAAVIGF-I for transduction of equine articular chondrocytes and RNA-seq analysis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015. [46] Lu H, Zeng C, Chen M, et al. Lentiviral vector-mediated over-expression of Sox9 protected chondrocytes from IL-1β induced degeneration and apoptosis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 . [47] Kudelko M, Chan CW, Sharma R, et al. Label-Free Quantitative Proteomics Reveals Survival Mechanisms Developed by Hypertrophic Chondrocytes under ER Stress. J Proteome Res. 2016;15(1):86-99. [48] Khazaeel K, Mazaheri Y, Hashemi Tabar M, et al. Effect of Enrofloxacin on Histochemistry, Immunohistochemistry and Molecular Changes in Lamb Articular Cartilage. Acta Med Iran. 2015;53(9): 555-561. [49] Kimura M, Ichimura S, Sasaki K, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis contributes to a skeletal dysplasia resembling platyspondylic lethal skeletal dysplasia, Torrance type, in a novel Col2a1 mutant mouse line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;468(1-2):86-91. [50] Che X, Chi L, Park CY, et al. A novel method to detect articular chondrocyte death during early stages of osteoarthritis using a non-invasive ApoPep-1 probe. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:309. [51] Correia SI, Silva-Correia J, Pereira H, et al. Posterior talar process as a suitable cell source for treatment of cartilage and osteochondral defects of the talus. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015. [52] Lin P, Weng X, Liu F, et al. Bushen Zhuangjin decoction inhibits TM-induced chondrocyte apoptosis mediated by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Int J Mol Med. 2015;36(6):1519-1528. Jia L, Chen J, Wang Y, et al. Focused Low-intensity Pulsed Ultrasound Affects Extracellular Matrix Degradation via Decreasing Chondrocyte Apoptosis and Inflammatory Mediators in a Surgically Induced Osteoarthritic Rabbit Model. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2016;42(1):208-219. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||