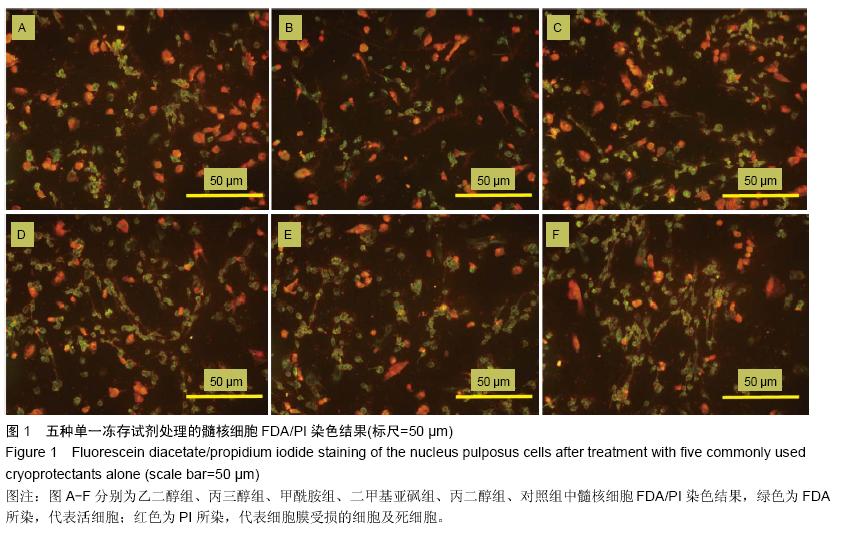
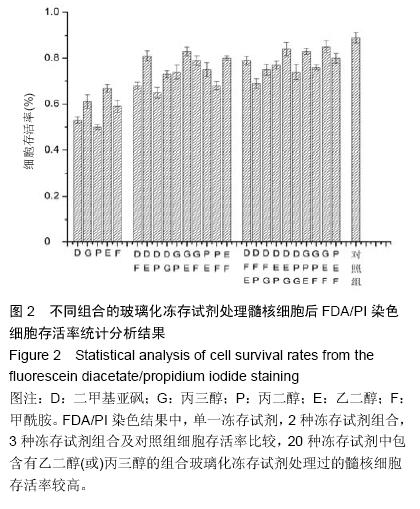
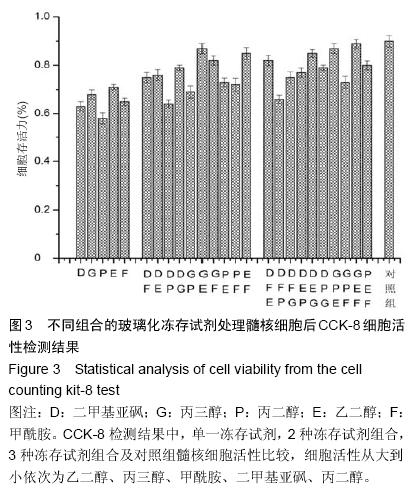
| [1] Tsai HH, Tsai CH, Wu WT, et al.Numerical investigation into thermal effects of pre-cooling zone in vitrification- based cryopreservation process. Cryobiology. 2015; 70(1): 32-37.[2] Pyne DG, Liu J, Abdelgawad M, et al.Digital microfluidic processing of mammalian embryos for vitrification. PLoS One.2014;9(9): e108128.[3] Jafarabadi M, Abdollahi M, Salehnia M. Assessment of vitrification outcome by xenotransplantation of ovarian cortex pieces in gamma-irradiated mice: morphological and molecular analyses of apoptosis. J Assist Reprod Genet.2015;32(2): 195-205.[4] Figueroa E, Merino O, Risopatrón J, et al.Effect of seminal plasma on Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) sperm vitrification. Theriogenology.2015; 83(2): 238-245.e2.[5] De Munck N, Petrussa L, Verheyen G, et al. Chromosomal meiotic segregation, embryonic developmental kinetics and DNA (hydroxy)methylation analysis consolidate the safety of human oocyte vitrification. Mol Hum Reprod. 2015;21(6): 535-544.[6] Mori C, Yabuuchi A, Ezoe K, et al.Hydroxypropyl cellulose as an option for supplementation of cryoprotectant solutions for embryo vitrification in human assisted reproductive technologies. Reprod Biomed Online.2015;30(6):613-621.[7] Maehara M, Sato M, Watanabe M, et al.Development of a novel vitrification method for chondrocyte sheets. BMC Biotechnol.2013;13: 58.[8] Brockbank KG, Chen Z, Greene ED, et al.Vitrification of heart valve tissues. Methods Mol Biol.2015;1257: 399-421.[9] Marco-Jiménez F, Garcia-Dominguez X, Jimenez-Trigos E, et al.Vitrification of kidney precursors as a new source for organ transplantation. Cryobiology.2015;70(3): 278-282.[10] Kim SH, Kuh SU, Kim KN, et al.Biologic response of degenerative living human nucleus pulposus cells to treatment with cytokines. Yonsei Med J.2015; 56(1): 277-286.[11] Silveira JW, Issy AC, Castania VA, et al.Protective effects of cannabidiol on lesion-induced intervertebral disc degeneration. PLoS One.2014;9(12):e113161.[12] Lam SK, Chan SC, Leung VY, et al.The role of cryopreservation in the biomechanical properties of the intervertebral disc. Eur Cell Mater.2011;22: 393-402.[13] Lee CK, Goel VK.Artificial disc prosthesis: design concepts and criteria. Spine J.2004;4(6 Suppl): 209s-218s.[14] Dong L, Tan MS, Yan QH, et al.Footprint mismatch of cervical disc prostheses with Chinese cervical anatomic dimensions. Chin Med J (Engl).2015;128(2): 197-202.[15] Luk KD, Ruan DK..Intervertebral disc transplantation: a biological approach to motion preservation. Eur Spine J.2008;17 Suppl 4:504-510.[16] Zander-Fox D, Lane M, Hamilton H. Slow freezing and vitrification of mouse morula and early blastocysts. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2013;30(8):1091-1098.[17] Brockbank KG, Chen ZZ, Song YC. Vitrification of porcine articular cartilage. Cryobiology. 2010; 60(2): 217-221.[18] Yang CY, Yeh YH, Lee PT,et al. Effect of cooling rate and cryoprotectant concentration on intracellular ice formation of small abalone(Haliotis diversicolor) eggs. Cryobiology. 2013;67(1):7-16.[19] Marques LS, Bos-Mikich A, Godoy LC, et al. Viability of zebrafish (Danio rerio) ovarian follicles after vitrification in a metal container. Cryobiology. 2015; 71(3):367-373.[20] Jomha NM, Weiss AD, Fraser Forbes J, et al. Cryoprotectant agent toxicity in porcine articular chondrocytes. Cryobiology.2010;61(3): 297-302.[21] Pegg DE. Principles of cryopreservation. Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1257:3-19.[22] Almansoori KA, Prasad V, Forbes JF, et al. Cryoprotective agent toxicity interactions in human articular chondrocytes. Cryobiology.2012;64(3): 185-191.[23] Fahy GM, Wowk B. Principles of cryopreservation by vitrification. Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1257:21-82.[24] Jin B, Mazur P. High survival of mouse oocytes/ embryos after vitrification without permeating cryoprotectants followed by ultra-rapid warming with an IR laser pulse. Sci Rep. 2015;5:9271. |