| [1] Sandowski C,lubbeke A,Saudan M, et al.Treatment of reverse obligue and transverse intertrochanteric fractures with use of an intramedullary nail or a 95°screw-place, a prospectives, randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg(Am). 2002;84-(A):372-381.
[2] Chirodian N.Arch B, Parker MJ.Sliding hip screw fixation of tro-chanteric hip fractures :outcome of 1024 procedures. Injury. 2005;36(6):793-800.
[3] Kesmezacar H,Ayhan E,Unlu MC,et al. Predictors of mortality in elderly patients with an intertrochanteric or a femoral neck fracture.J Trauma. 2010;68(1):153-158.
[4] Kakar S,little D,Einhorn TA.Can we improve fixation and outcomes in the treatment Of femoral neck fracture femoral neck fracture ?The use of pharmaceuticals. J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23(b):413-421.
[5] Kadakia A,Langkamar VG.Cancellous screw fixation of undisplaced femoral neck fracrures in over 70 years. Injury Extra. 2007;38(4):146-147.
[6] Efstathopoals NE,Nikolaou VS,Lazarettors JT.Intrameduallary fixation of interochanterie hip fractures a comparison of two implant designs.Int Orthop. 2007;31(1):71-76.
[7] Parker MJ,White A,Boyle A.Fixation versus hemiarthro plasty for undisplaced intracapsular hip fractures. Injury. 2008;39(7): 791-795.
[8] Whatling GM,Nokes LD.Literatures review of current techniques for the insertion of distal screws into intramedully locking nails.Injury. 2006;37(2):109-119.
[9] Chang Q,Liu S,Guan C,et al. Bipolar hip artroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2011;26(8):1455-1459.
[10] 焦祥,关鹏飞,苏立新. PFNA治疗老年不稳定性股骨头粗隆间骨折的疗效分析[J]. 组织工程与重建外科杂志,2013,9(1):40-41.
[11] Dai Z,Li Y,Jiang D.Meta-analysis comparing arthroplasty with internal fixation for displaced femoral neck fracture in the elderty.J Surg Res. 2011;165(1):68-74.
[12] Zielinski SM,Meeuwis MA,Heetveld MJ,et al.Adherence to a femoral neck fracture treatment guideline.Int Orthop. 2013.
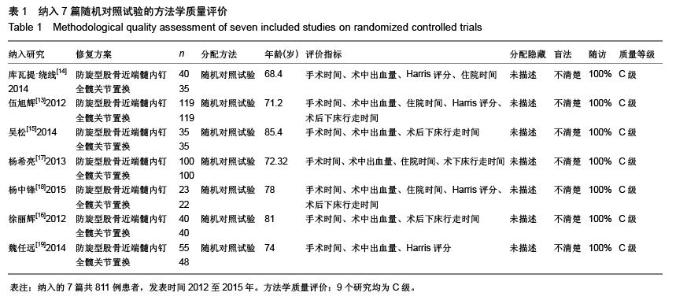
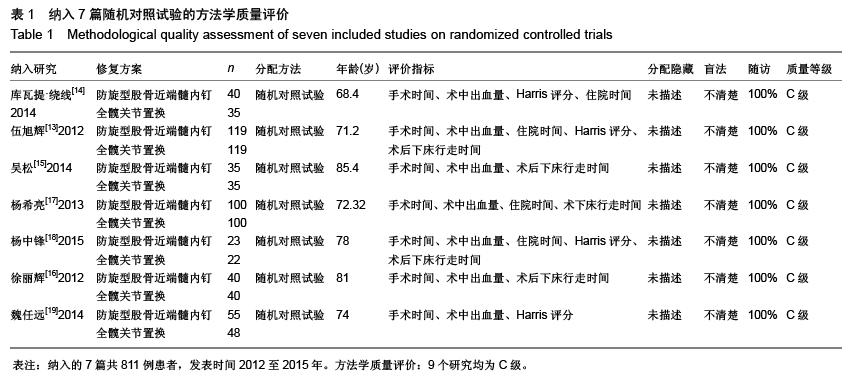
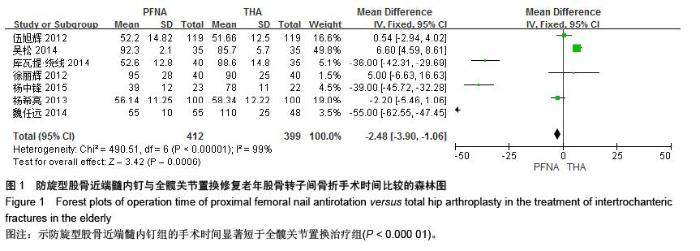
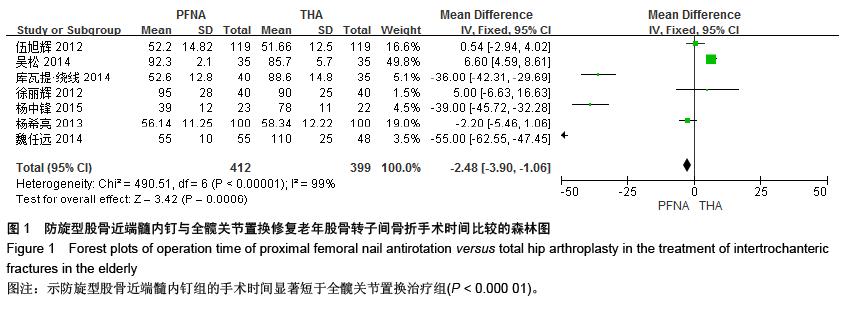
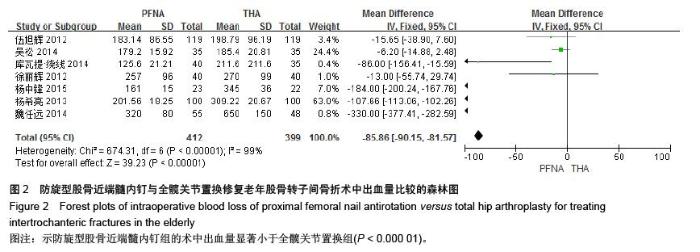
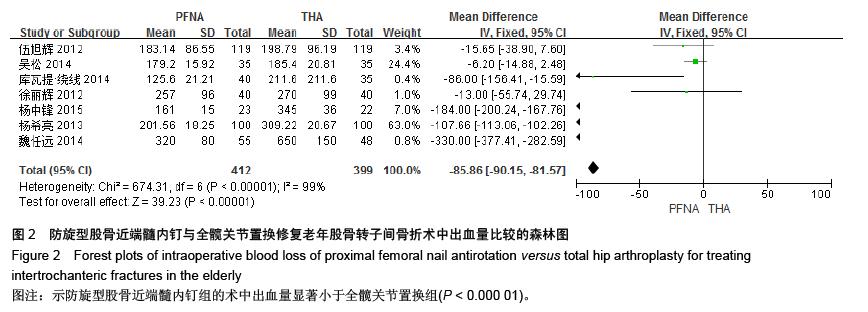
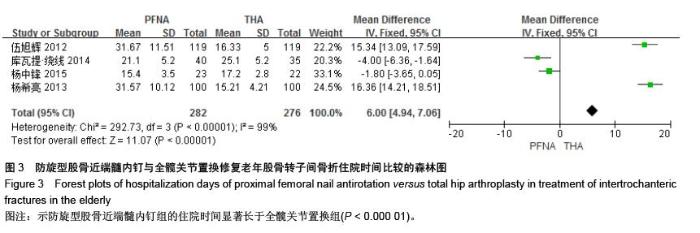
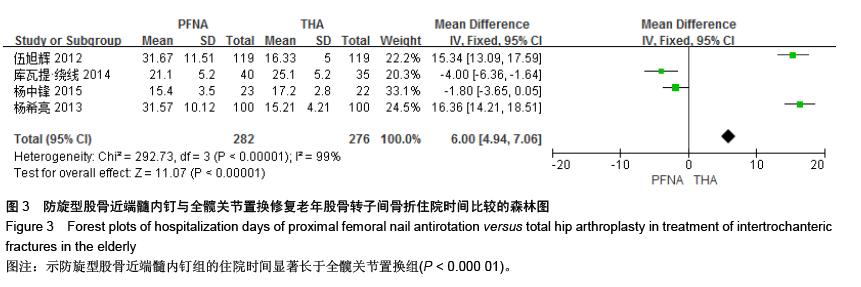
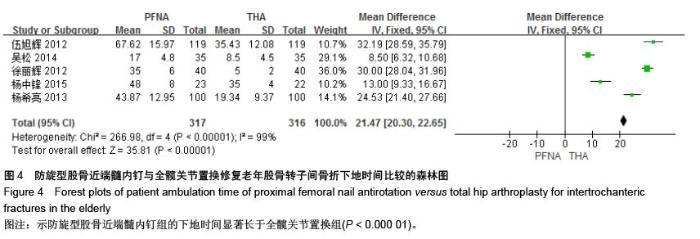
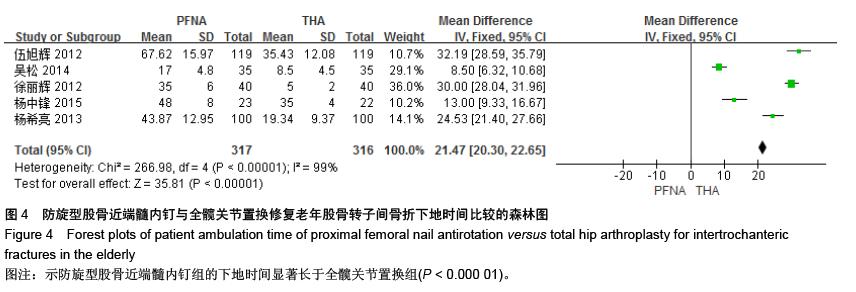
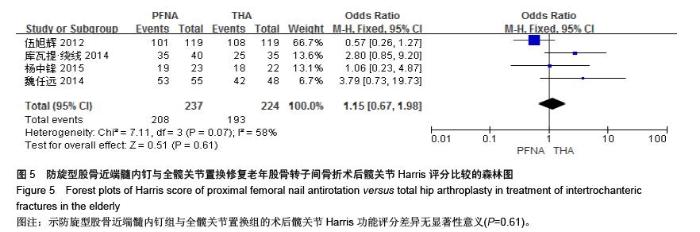
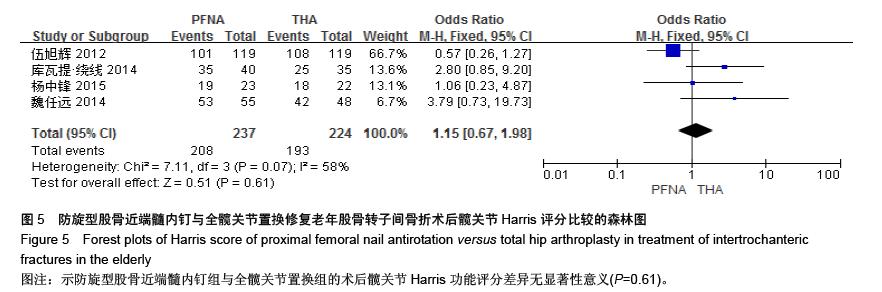
[13] 伍旭辉.PFNA和THA治疗老年性股骨粗隆间骨折的临床观察[J]. 中国医药导报,2012,9(36):85-89.
[14] 库瓦提•绕线,杜曼•吐鲁木.DHS、PFNA及人工髋关节置换不同植入物治疗老年人股骨粗隆间骨折的临床疗效[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志,2014,11(13):1815-1817.
[15] 吴松,邹玮君.不稳定型股骨粗隆间骨折行髋关节置换治疗的效果观察[J]. 当代医学,2014,3(20):40-41.
[16] 徐丽辉.股骨近端防旋髓内钉、动力髋螺钉及人工关节置换治疗高龄股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效对比[J],中国老年学杂志, 2012, 32(24):5596-5598.
[17] 杨希亮.髋关节置换和股骨近端髓内钉治疗粗隆间骨折的临床研究[J]. 中国医学创新,2013,8 (10):125-127.
[18] 杨中锋.老年股骨粗隆间骨折的外科治疗及其临床疗效观察[J]. 医学综述,2015,2(21):757-759.
[19] 魏任远,姜卓男.全髋关节置换与股骨近端髓内钉治疗高龄股骨粗隆间骨折的临床疗效对比研究[J]. 临床合理用药,2014,7(7):116-117.
[20] Alderson P, Green S, Higgins JPT, et al. Cochrane Reviews’ Handbook4.2.1//the Cochrane Library. UK: John Wiley &Sons, Ltd,2004.
[21] Smith AM, Mardones RM, Sperling JW, et al.Early complications Of operatively treated proximal humeralfractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007;16:14-24.
[22] Pu JS, Liu L, Wang GL, et al. Results of the proximal femoral nail anti-rotation(PFNA) inelderly Chinese patients. Int Orthop. 2009;33(5):1441-1444.
[23] Lee YK,Ha YC,Chang BK,et al.Cementless bipolar hemiarthroplasty using a hydroxyatite-coated long sterm for osteoorotic unstable interochanteric fractures. J Arthrpolasty. 2011;26(4):626-632.
[24] Lee YK, Ha YC, Park C, et al. Trends of Surgical Treatment in Femoral Neck Fracture.A Nation wide Study Based on Claim Registy. J Arthroplasty.2013;28(10):1839-1841. |