Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (4): 633-640.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.04.024
Previous Articles Next Articles
Metabolomics characteristics in a rat model of myocardial infarction based on bibiometrics analyses
Wu Xin-cheng1, Zheng Jing-hui2, Ma Xiao-cong1, Zhuo Xiao-yuan1, Zhang Xin-chun1
- 1Graduate School of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Cardiovasology, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2016-11-30Online:2017-02-08Published:2017-03-13 -
Contact:Corresponding author: Zheng Jing-hui, M.D., Associate professor, Department of Cardiovasology, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Wu Xin-cheng, Studying for master’s degree, Graduate School of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81360535; the Science and Technology Development Program of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, No. 1598012-55; a grant from the Education Commission of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region-the Engineering of Training Excellent Young Scholars in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, No. [2013]16
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Xin-cheng1, Zheng Jing-hui2, Ma Xiao-cong1, Zhuo Xiao-yuan1, Zhang Xin-chun1. Metabolomics characteristics in a rat model of myocardial infarction based on bibiometrics analyses[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(4): 633-640.
share this article
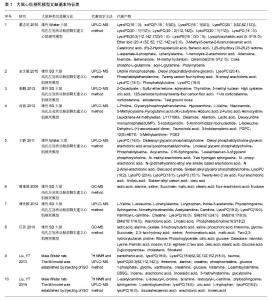
篇,PubMed 2篇,中国知网4篇,万方数据库7篇,维普数据库2篇,排出重复收录文献和相同数据文献,最后有10项研究被纳入[1-10],其中中文文献8篇,英文文献2篇。纳入研究文献特征表1。 2.2 代谢产物的确定 纳入的10项研究从大鼠血清角度对产物进了分析。汇总各研究的代谢产物,收集至少重复2次的代谢产物,总共26个,重复5次的有1个:LysoPC(18:0);重复3次的有6个:alanine、aminomalonic acid、lactic acid、linoleic acid、LysoPC(16:0)、LysoPC(18:2);重复2次的有19个:creatine、four arachidonic acid、glucose、glycine、L-isoleucineL-palmitoylcarnitine、L-phenylalanine、L-proline、LysoPC(20:1(11Z))、LysoPC(18:1)、LysoPC(20:4)、malic acid、oleic acid、oleoyl phosphatidylcholine glycerol、sphinganine、stearic acid、succinate、threonine、uric acid、valine。"
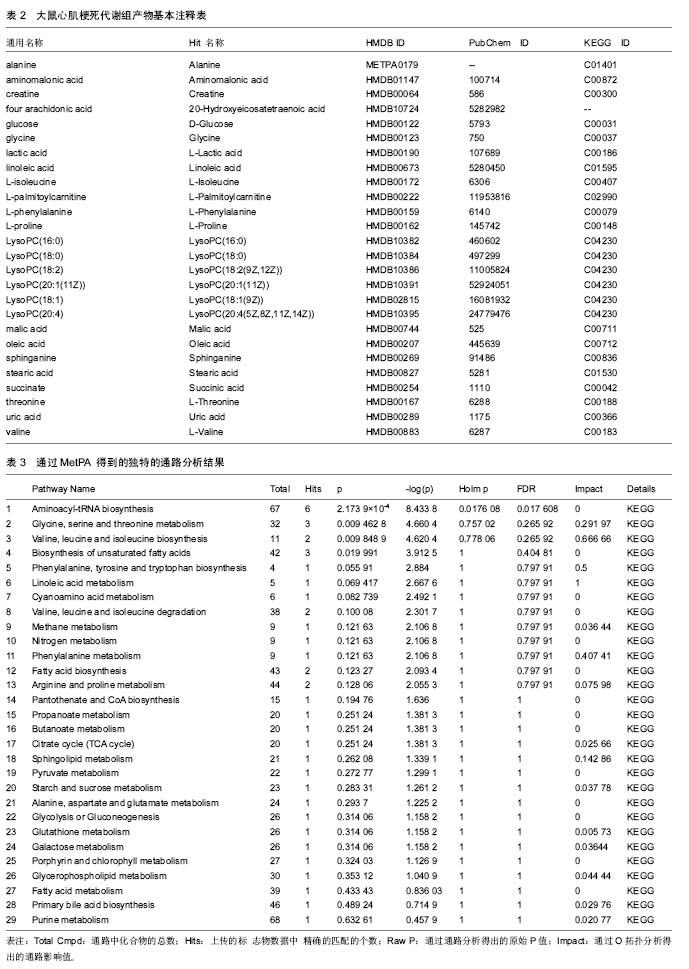
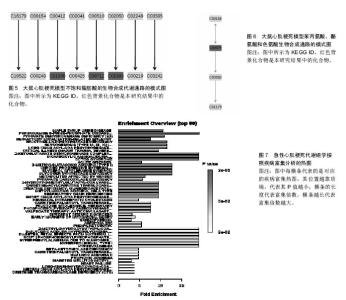
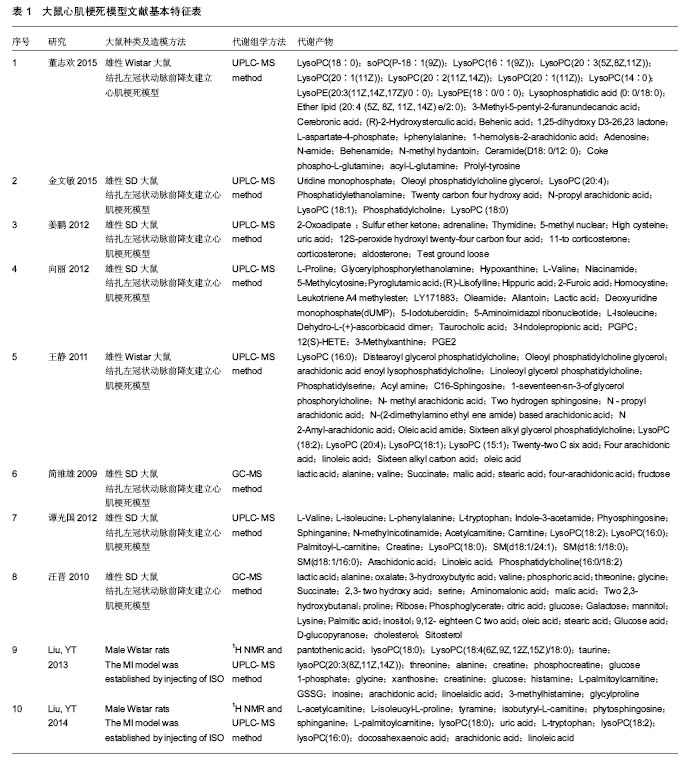
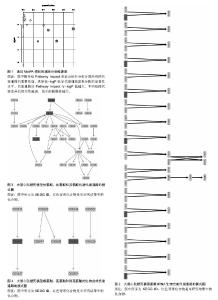
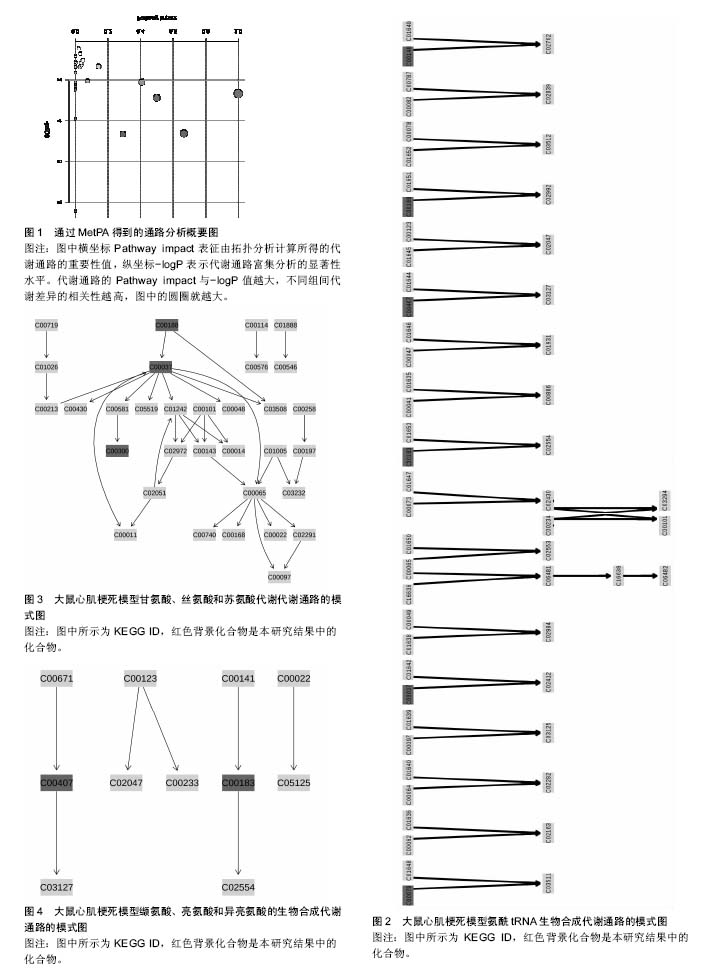
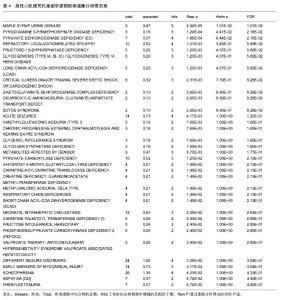
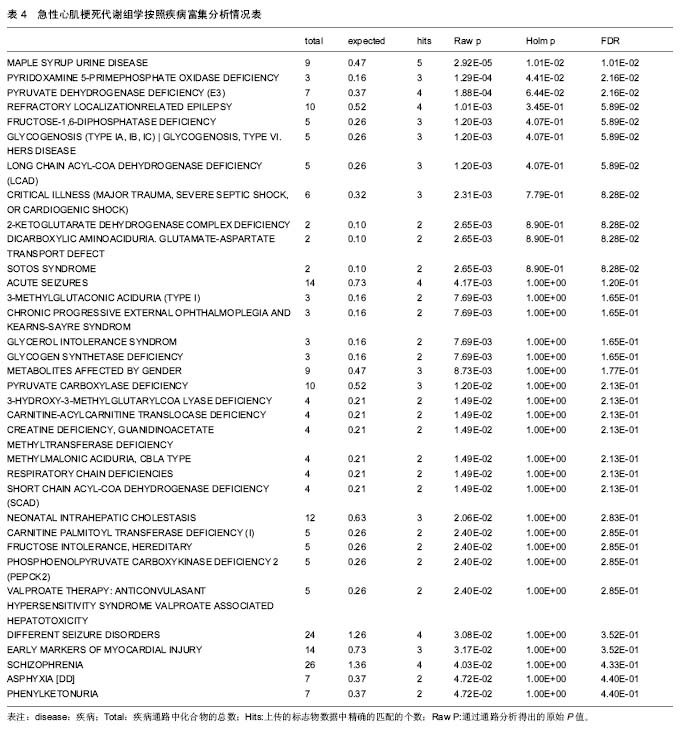
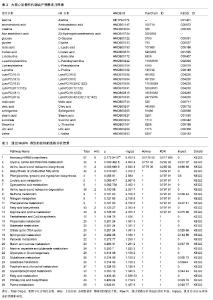
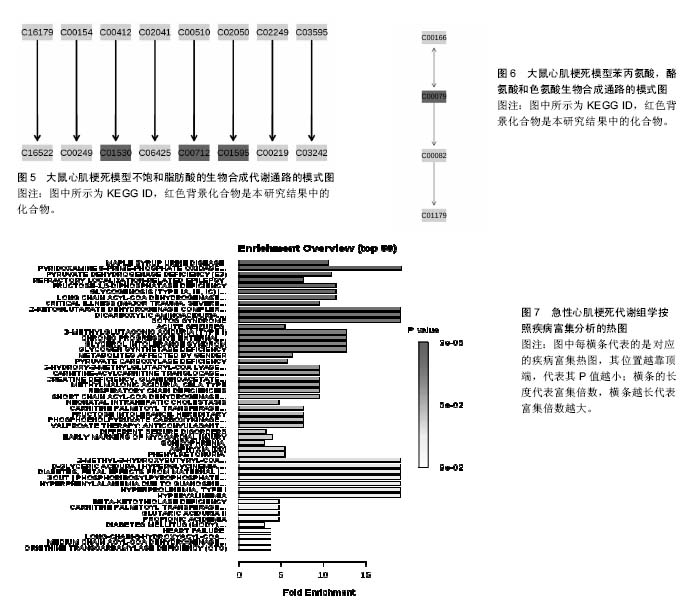
2.3 代谢组产物通路检索路匹配情况 对研究中重复出现的26种代谢产物在HMDB、PubChem和KEGG中检索,相应的ID号及基本情况注释见表2。 2.4 代谢产物路径分析 用MetPA分析的生物代谢通路显示,26个代谢产物主要参与了29条代谢路径(表3、图1)。 通过通路拓扑分析计算其影响值,选出了影响值最高的5条代谢通路作为大鼠心肌梗死过程代谢通路,前4条P < 0.05,另外1条P=0.055 91,分别是:氨酰tRNA生物合成(Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis)、甘氨酸、丝氨酸和苏氨酸代谢(Glycine,serine and threonine metabolism)、缬氨酸、亮氨酸和异亮氨酸的生物合成(Valine, leucine and isoleucine biosynthesis)、不饱和脂肪酸的生物合成(Biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids)、苯丙氨酸,酪氨酸和色氨酸生物合成(Phenylalanine,yrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis) (图2-6)。 2.5 代谢产物富集分析 研究收集的26个代谢产物按疾病分类富集,出现了124个富集集(表4、图7),其中有34个富集集P值小于0.05,与本研究收集的代谢产物关系最为密切的5种疾病为槭糖尿病(maple syrup urine disease)、吡多胺-5-磷酸氧化酶缺乏症(pyridoxamine-"
| [1] 向丽.麝香保心丸及组分配伍代谢组学研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2009.[2] 谭光国.中药四逆汤化学物质组和代谢组学研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2012.[3] 姜鹏.麝香保心丸代谢组学和代谢动力学研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2012.[4] 金文敏,穆殿平.芪参益气滴丸用于大鼠急性心肌梗死的代谢组学研究[J].天津药学,2015,27(6):9-13.[5] 王静.复方中药芪参益气滴丸化学物质基础与作用机理研究[D].天津:南开大学,2011:1-127.[6] 简维雄,黄献平,陈清华,等.基于气相色谱-质谱的大鼠心血瘀阻证血浆代谢组学研究[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2009,27(4): 796-798.[7] 汪晋,张玉峰,邵青,等.三七总皂苷对急性心肌缺血大鼠血清代谢物组的影响研究[J].中国中药杂志,2010,35(23):3199-3202.[8] Liu YT,Jia HM,Chang X,et al.The metabolic disturbances of isoproterenol induced myocardial infarction in rats based on a tissue targeted metabonomics.Mol. BioSyst.2013;9(11): 2823-2834.[9] Liu YT,Jia HM,Chang X,et al. Metabolic pathways involved in Xin-Ke-Shu protecting against myocardial infarction in rats using ultra high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry .J Pharm Biomed Anal.2013;5 (90): 35-44.[10] 董志欢,李彤,张磊,等.大鼠急性心肌梗死后期血清代谢轮廓研究[J].天津医药,2015,43(10):1166-1170.[11] 吴德坤,郑景辉,王铁华,等.大鼠急性心肌梗死血瘀证心肌组织代谢组学的生物信息学分析[J].辽宁中医杂志,2016,43(3): 630-632.[12] 李伟霞.当归-川芎药对功效物质与配伍作用机理研究[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2014.[13] 郑景辉,陈建军,简维雄,等.冠心病心血瘀阻证患者血浆代谢组学的通路分析[J]. 时珍国医国药,2015,26(2): 485–487.[14] 张玲.基于LC-Q/TOF-MS生当归及其不同炮制品挥发油干预LPS炎症大鼠的代谢组学研究[D].甘肃: 甘肃农业大学,2015. |
| [1] | Li Shengkai, Li Tao, Wei Chao, Shi Ming. Comparison of biomechanical properties of calcium phosphate/polymethyl methacrylate composite bone cement and polymethyl methacrylate bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2581-2586. |
| [2] | Yang Xue, Wang Baoqun, Jiang Xiaowen, Zou Shengcan, Ming Jinfa, Lin Shasha. Preparation and properties of biodegradable plant polysaccharide hemostatic microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2607-2611. |
| [3] | Liu Jiali, Suo Hairui, Yang Han, Wang Ling, Xu Mingen. Influence of lay-down angles on mechanical properties of three-dimensional printed polycaprolactone scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2612-2617. |
| [4] | Liu Xiaojun, Xu Yuyin, Liu Kangbo, Zhou Jing, Han Ying, Xiong Yue, Tian Yuan. Preparation and properties of carboxymethylated cotton linters hemostatic gauze [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2593-2599. |
| [5] | Huang Bo, Chen Mingxue, Peng Liqing, Luo Xujiang, Li Huo, Wang Hao, Tian Qinyu, Lu Xiaobo, Liu Shuyun, Guo Quanyi . Fabrication and biocompatibility of injectable gelatin-methacryloyl/cartilage-derived matrix particles composite hydrogel scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2600-2606. |
| [6] | Luo Di, Liang Xuezhen, Liu Jinbao, Li Jiacheng, Yan Bozhao, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Difference in osteogenesis- and angiogenesis-related protein expression in femoral head samples from patients with femoral head necrosis of different etiologies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1641-1647. |
| [7] | Zhu Chunhui, Zhang Yi, Song Huanghe, Liang Wenwei. Protective effect of astaxanthin on tert-butyl hydrogen peroxide-induced chondrocyte damage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1648-1655. |
| [8] | Zhao Tianyu, Jin Song, Zhang Di, Liu Xiaoxiao, Ma Jiang, Wang Ju. Baduanjin training for patellar tendinopathy in a randomized controlled trial: improving pain, muscle flexibility and lower limb balance stability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1662-1668. |
| [9] | Zhang Lei, Xiu Chunmei, Ni Li, Chen Jianquan. Identification and expression analysis of mouse nucleus pulposus specific markers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1669-1674. |
| [10] | Yu Dong, Liu Kan, Shi Zongting, Yang Xiaoxia, Liu Hengping, Zhang Qingfeng. Pathological changes of the cervical intervertebral discs and rules of migration and apoptosis in endplate chondrocytes in a rabbit model of dynamic disequilibrium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1675-1679. |
| [11] | Tian Zhuang, Wang Diaodiao, Zhang Chu, Li Hanchen, Zhou Jian, Yao Qi. The mechanism by which bone morphogenetic protein 2 indirectly regulates sclerostin expression in osteocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1686-1691. |
| [12] | Li Jingyu, Su Yingying, Bai Ding. Morphological characteristics of subchondral bone in a mouse model of early osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1692-1698. |
| [13] | Bao Hongyu Lü Dongmei, He Yun, Xia Delin, Chen Junliang. Incidence of osteonecrosis in rats with jaw versus femoral defects following zoledronic acid injection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1699-1704. |
| [14] | Tan Qian, Li Bocun, Li Jing, Li Jia, Xiang Hongchun, Cai Guowei. Acupuncture combined with moxibustion regulates the expression of circadian clock protein in the synovium of rats with osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1714-1719. |
| [15] | Fei Jing, Tao Meihui, Li Leiji. Electroacupuncture promotes facial nerve regeneration in a rat model of facial nerve crush [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1728-1733. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||