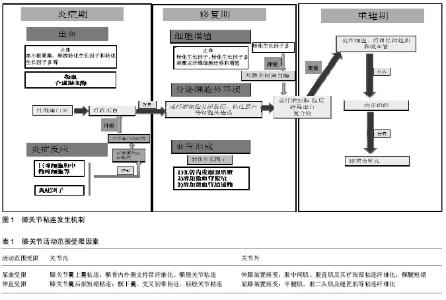
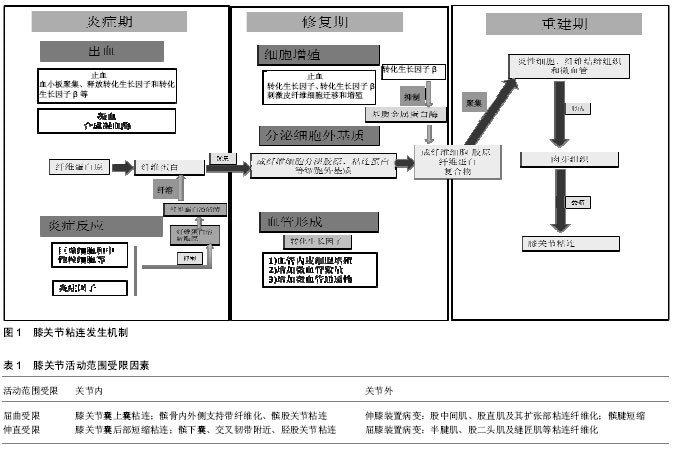
| [1] Bieger R, Kappe T, Fraitzl CR, et al.The aetiology of total knee arthroplasty failure influences the improvement in knee function. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;133(2):237-241.[2] Faust I, Traut P, Nolting F, et al. Human xylosyltransferases--mediators of arthrofibrosis? New pathomechanistic insights into arthrofibrotic remodeling after knee replacement therapy. Sci Rep. 2015;5:12537.[3] Mamarelis G, Sunil-Kumar KH, Khanduja V. Timing of manipulation under anaesthesia for stiffness after total knee arthroplasty. Ann Transl Med. 2015;3(20):316.[4] Zhao S, Sun Y, Li X, et al. Reduction of intraarticular adhesion of knee by local application of rapamycin in rabbits via inhibition of fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016; 19;11:45.[5] Eckenrode BJ, Sennett BJ. Arthrofibrosis of the knee following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2011;41(1):32.[6] Schiavone Panni A, Cerciello S, Vasso M, et al. Stiffness in total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Traumatol. 2009;10(3): 111-118.[7] Abdul N, Dixon D, Walker A, et al. Fibrosis is a common outcome following total knee arthroplasty. Sci Rep. 2015;5: 16469.[8] Xu H, Ying J. A mini-invasive procedure for treating arthrofibrosis of the knee. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2016;13(16):30009-30008.[9] Mercer PF, Chambers RC. Coagulation and coagulation signalling in fibrosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1832(7): 1018-1027.[10] Lieber RL, Ward SR. Cellular mechanisms of tissue fibrosis. 4.Structural and functional consequences of skeletal muscle fibrosis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013; 305(3):C241-252. [11] Shukla H, Nair SR, ThKIAker D. Role of telerehabilitation in patients following total knee arthroplasty: Evidence from a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. J Telemed Telecare. 2016; pii: 1357633X16628996.[12] Ipach I, Mittag F, Lahrmann J, et al. Arthrofibrosis after TKA - Influence factors on the absolute flexion and gain in flexion after manipulation under anaesthesia. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011;12:184.[13] Issa K, Banerjee S, Kester MA, et al. The effect of timing of manipulation under anesthesia to improve range of motion and functional outcomes following total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(16):1349-1357. [14] Pariente GM, Lombardi AV Jr, Berend KR, et al. Manipulation with prolonged epidural analgesia for treatment of TKA complicated by arthrofibrosis. Surg Technol Int. 2006; 5: 221-224.[15] Tjoumakaris FP, Tucker BC, Post Z, et al. Arthroscopic lysis of adhesions for the stiff total knee: results after failed manipulation. Orthopedics. 2014;37(5):e482-487.[16] Kim YM, Joo YB. Prognostic factors of arthroscopic adhesiolysis for arthrofibrosis of the knee. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2013;25(4):202-206.[17] Pujol N, Boisrenoult P, Beaufils P. Post-traumatic knee stiffness: surgical techniques. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015;101(1 Suppl): 179-186.[18] Pederzini LA, Milandri L, Tosi M, et al. Preliminary clinical experience with hyaluronan anti-adhesion gel in arthroscopic arthrolysis for posttraumatic elbow stiffness. J Orthop Traumatol. 2013;14(2):109-114.[19] Kundu Z, Sangwan S, Guliani G, et al. Thompson's quadricepsplasty for stiff knee. Indian J Orthop. 2007;41(4): 390-394.[20] Hahn SB, Choi YR, Kang HJ, et al. Prognostic factors and long-term outcomes following a modified Thompson's quadricepsplasty for severely stiff knees. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(2):217-221.[21] Oliveira VG, D'Elia LF, Tirico LE, et al. Judet quadricepsplasty in the treatment of posttraumatic knee rigidity: long-term outcomes of 45 cases. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012;72(2):E77-80.[22] Lee DH, Kim TH, Jung SJ, et al. Modified judet quadricepsplasty and Ilizarov frame application for stiff knee after femur fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2010;24(11):709-715.[23] Al-Zahid S, Davies AP. Closed suction drains, reinfusion drains or no drains in primary total knee replacement?. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2012;94(5):347-350.[24] Faldini C, Traina F, De Fine M, et al. Post-operative limb position can influence blood loss and range of motion after total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23(3):852-859.[25] Sun Y, Liang Y, Hu J, et al. Reduction of intraarticular adhesion by topical application of colchicine following knee surgery in rabbits. Sci Rep. 2014;4:6405.[26] BKIA?rhan S, Ünver B, Karatosun V. Effects of two different continuous passive motion protocols on the functional activities of total knee arthroplasty inpatients. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2015;49(5):497-502.[27] Joshi RN, White PB, Murray-Weir M, et al. Prospective Randomized Trial of the Efficacy of Continuous Passive Motion Post Total Knee Arthroplasty: Experience of the Hospital for Special Surgery. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(12):2364-2369.[28] Hill AD, Palmer MJ, Tanner SL, et al. Use of Continuous Passive Motion in the Postoperative Treatment of Intra-Articular Knee Fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014; 96(14): 118.[29] Tamer TM. Hyaluronan and synovial joint: function, distribution and healing. Interdiscip Toxicol. 2013;6(3):111-125.[30] Wang M, Liu C, Xiao W. Intra-articular injection of hyaluronic acid for the reduction in joint adhesion formation in a rabbit model of knee injury. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22(7):1536-1540.[31] Kanazawa K, Hagiwara Y, Tsuchiya M, et al. Preventing effects of joint contracture by high molecular weight hyaluronan injections in a rat immobilized knee model. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(4):3426-3440.[32] Ren C, Zhao D, Zhu L. Use of N,O-carboxymethyl chitosan to prevent postsurgical adhesions in a rabbit double uterine horn model: a randomized controlled design. Sci China Life Sci. 2016;59(5):504-509.[33] Carvalho M, Costa LM, Pereira JE, et al. The role of hybrid chitosan membranes on scarring process following lumbar surgery: post-laminectomy experimental model. Neurol Res. 2015;37(1):23-29.[34] Cho H, Walker A, Williams J, Hasty KA. Study of osteoarthritis treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs: cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor and steroids. Biomed Res Int.2015; 015:595273.[35] Sandoval MA, Hernandez-Vaquero D. Preventing peridural fibrosis with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(3):451-455.[36] Breitbach M, Rack D, Dietzel M, et al. Efficacy of a Dexamethasone Implant for the Treatment of Refractory Cystoid Macular Oedema in Non-Infectious Uveitis. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2016;233(5):601-605[37] Tian F, Dou C, Qi S, et al. Preventive effect of dexamethasone gelatin sponge on the lumbosacral epidural adhesion. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(4):5478-5484.[38] Reed KL, Stucchi AF, Becker JM. Pharmacologic inhibition of adhesion formation and peritoneal tissue-type plasminogen activator activity. Semin Reprod Med. 2008;26(4):331-340[39] Attard JA, MacLean AR. Adhesive small bowel obstruction: epidemiology, biology and prevention. Can J Surg. 2007; 50(4):291-300.[40] Arung W, Meurisse M, Detry O. Pathophysiology and prevention of postoperative peritoneal adhesions. World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17(41):4545-4553. [41] Jiang SJ, Ye LY, Meng FH. Comparison of intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin and mitomycin C administration for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: Ameta-analysis and systematic review. Oncol Lett. 2016;11(4):2751-2756.[42] Yazdani S, Rezai S, PKIAravan M, et al. Mitomycin-C Application Before versus After Scleral Flap Dissection in Trabeculectomy; a Randomized Clinical Trial. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2015;10(4):391-399.[43] Kocaoglu B, KIAgun U, Nalbantoglu U, et al. Adhesion reduction after knee surgery in a rat model by mitomycin C. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19(1):94-98.[44] Yan L, Sun Y, Wang J, et al. The effect of mitomycin C in reducing intraarticular adhesion after knee surgery in rabbits. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010;643(1):1-5.[45] Wang J, Yan L, Sun Y, et al. A comparative study of the preventive effects of mitomycin C and chitosan on intraarticular adhesion after knee surgery in rabbits. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2012;62(1):101-105.[46] Rabb CH. Failed back syndrome and epidural fibrosis. Spine J. 2010;10(5):454-455.[47] Cheng J, Qi J, Li XT, et al. ATRA and Genistein synergistically inhibit the metastatic potential of human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(3): 4220-4227.[48] Wu L, Chaudhary SC, Atigadda VR, et al. Retinoid X Receptor Agonists Upregulate Genes Responsible for the Biosynthesis of All-Trans-Retinoic Acid in Human Epidermis. PLoS One. 2016;11(4):e0153556.[49] Zhang C, Kong X, Ning G, et al. All-trans retinoic acid prevents epidural fibrosis through NF-κB signaling pathway in post-laminectomy rats. Neuropharmacology. 2014; 79: 275-281.[50] Dong Z, Tai W, Yang Y, et al. The role of all-trans retinoic acid in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Exp Lung Res. 2012;38(2):82-89.[51] Wang Y, Zhang C, Cheng H, et al. All-trans retinoic Acid reduces joint adhesion formation: an experimental study in rats. Med Sci Monit. 2015; 21:1598-1603.[52] Sexton TR, Wallace EL, Macaulay TE, et al. The effect of rosuvastatin on thromboinflammation in the setting of acute coronary syndrome. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2015;39(2): 186-195.[53] Semenova AE, Sergienko IV, Masenko VP, et al. Effect of rosuvastatin therapy and myocardial revascularization on angiogenesis in coronary artery disease patients. Kardiologiia. 2007;47(11):4-8. Russian.[54] hang CC, Wang SS, Hsieh HG, et al. Rosuvastatin improves hepatopulmonary syndrome through inhibition of inflammatory angiogenesis of lung. Clin Sci (Lond). 2015; 129(6):449-460. [55] Wu H, Germanov AV, Goryaeva GL, et al. The Topical Application of Rosuvastatin in Preventing Knee Intra-Articular Adhesion in Rats. Med Sci Monit. 2016; 22:1403-1409.[56] Nam HK, Lee SJ, Kim MH, et al. Rosuvastatin attenuates inflammation, apoptosis and fibrosis in a rat model of cyclosporine-induced nephropathy. Am J Nephrol. 2013; 37(1):7-15. [57] Park JH, Yoo C, Kim YY. Effect of Lovastatin on Wound-Healing Modulation After Glaucoma Filtration Surgery in a Rabbit Model. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016;57(4): 1871-1877[58] Gürer B, Kahveci R, Gökçe EC, et al. Evaluation of topical application and systemic administration of rosuvastatin in preventing epidural fibrosis in rats. Spine J. 2015;15(3): 522-529.[59] Zhang C, Feng S, Hu N, et al. Letter to the editor regarding: Evaluation of topical application and systemic administration of rosuvastatin in preventing epidural fibrosis in rats" by Bora Gürer et al. Spine J. 2015;15(5):1165-1166. |