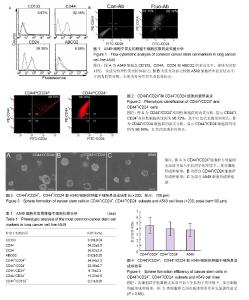
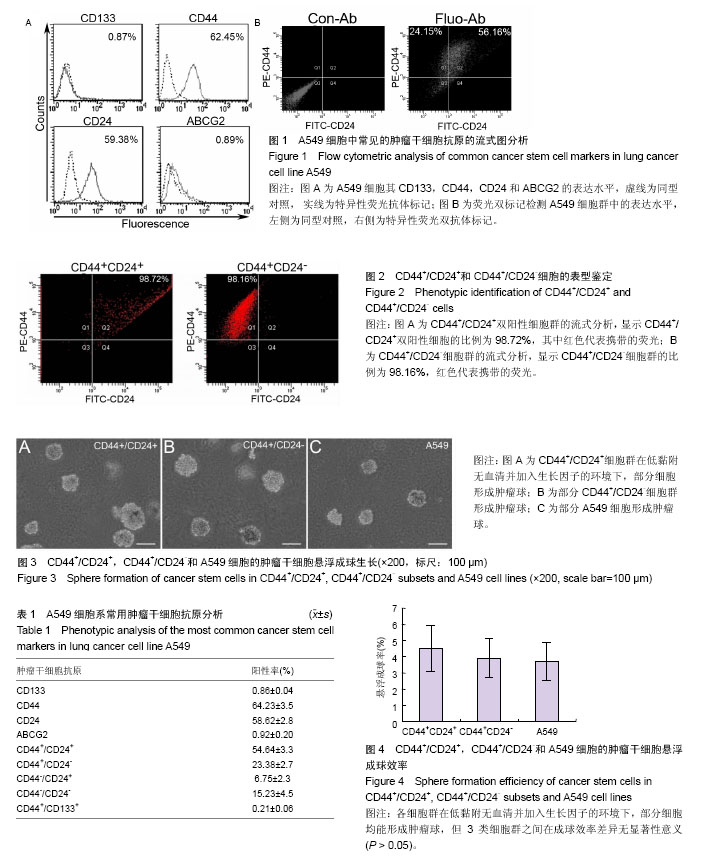
| [1] Travis WD, Brambilla E, and Geisinger KR. Histological grading in lung cancer: one system for all or separate systems for each histological type? Eur Respir J. 2016;47(3):720-723. [2] Shin J, Keam B, Kim M, et al. Prognostic Impact of Newly Proposed M Descriptors in TNM Classification of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2017;12(3): 520-528. [3] La Porta CA and Zapperi S. Complexity in cancer stem cells and tumor evolution: toward precision medicine. Semin Cancer Biol. 2017;44(6):3-9. [4] Jordan CT, Guzman ML and Noble M. Cancer stem cells. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(12):1253-1261. [5] Peitzsch C, Tyutyunnykova A, Pantel K. et al. Cancer stem cells: the root of tumor recurrence and metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 2017;44(6):10-24. [6] Codony-Servat J, Verlicchi A, and Rosell R. Cancer stem cells in small cell lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2016;5(1): 16-25.[7] Leon G, MacDonagh L, Finn SP, et al. Cancer stem cells in drug resistant lung cancer: targeting cell surface markers and signaling pathways. Pharmacol Ther. 2016;158:71-90. [8] Travis WD. Pathology of lung cancer. Clin Chest Med. 2011; 32(4):669-692.[9] Bertolini G, Roz L, Perego P, et al. Highly tumorigenic lung cancer CD133+ cells display stem-like features and are spared by cisplatin treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009; 106(38):16281-16286. [10] Eramo A, Lotti F, Sette G, et al. Identification and expansion of the tumorigenic lung cancer stem cell population. Cell Death Differ. 2008;15(3):504-514. [11] Sun FF, Hu YH, Xiong LP, et al. Enhanced expression of stem cell markers and drug resistance in sphere-forming non-small cell lung cancer cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(6):6287- 6300. [12] Roy S, Lu K, Nayak MK. et al. Activation of D2 Dopamine Receptors in CD133+ve Cancer Stem Cells in Non-small Cell Lung Carcinoma Inhibits Proliferation, Clonogenic Ability, and Invasiveness of These Cells. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(2):435-445. [13] Tu Z, Xie S, Xiong M. et al. CXCR4 is involved in CD133-induced EMT in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Oncol. 2017;50(2):505-514. [14] Chen YC, Hsu HS, Chen YW. et al. Oct-4 expression maintained cancer stem-like properties in lung cancer-derived CD133-positive cells. PLoS One. 2008;3(7):e2637. [15] Su J, Wu S, Wu H, et al. CD44 is functionally crucial for driving lung cancer stem cells metastasis through Wnt/beta-catenin-FoxM1-Twist signaling. Mol Carcinog. 2016; 55(12):1962-1973.[16] Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A, et al. Prospective identification of tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(7):3983-3988. [17] Leung EL, Fiscus RR, Tung JW. et al. Non-small cell lung cancer cells expressing CD44 are enriched for stem cell-like properties. PLoS One. 2010;5(11):e14062. [18] Hurt EM, Kawasaki BT, Klarmann GJ, et al. CD44+ CD24(-) prostate cells are early cancer progenitor/stem cells that provide a model for patients with poor prognosis. Br J Cancer. 2008;98(4):756-765. [19] Yeung TM, Gandhi SC, Wilding JL. et al. Cancer stem cells from colorectal cancer-derived cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(8):3722-3727. [20] Ding XW, Wu JH and Jiang CP. ABCG2: a potential marker of stem cells and novel target in stem cell and cancer therapy. Life Sci. 2010;86(17-18):631-637.[21] Ho MM, Ng AV, Lam S, et al. Side population in human lung cancer cell lines and tumors is enriched with stem-like cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2007;67(10):4827-4833. [22] Sung JM, Cho HJ, Yi H, et al. Characterization of a stem cell population in lung cancer A549 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;371(1):163-167. [23] Pastrana E, Silva-Vargas V and Doetsch F. Eyes wide open: a critical review of sphere-formation as an assay for stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2011;8(5):486-498. [24] Franken NA, Rodermond HM, Stap J, et al. Clonogenic assay of cells in vitro. Nat Protoc. 2006;1(5):2315-2319.[25] Naor D, Wallach-Dayan SB, Zahalka MA, et al. Involvement of CD44, a molecule with a thousand faces, in cancer dissemination. Semin Cancer Biol. 2008;18(4):260-267. [26] Kelly JJ, Stechishin O, Chojnacki A, et al. Proliferation of human glioblastoma stem cells occurs independently of exogenous mitogens. Stem Cells. 2009;27(8):1722-1733. [27] Kim J, Jung J, Lee SJ, et al. Cancer stem-like cells persist in established cell lines through autocrine activation of EGFR signaling. Oncol Lett. 2012;3(3):607-612.[28] Li G, Chen Z, Hu YD, et al. Autocrine factors sustain glioblastoma stem cell self-renewal. Oncol Rep. 2009;21(2): 419-424. |