Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (12): 1959-1968.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3795
A meta-analysis of clinical efficacy of preoperative use of three-dimensional printing in the treatment of tibial plateau fractures
Li Yang, Min Shengwei, Xie Feng, Zhang Mingyong
- Department of Orthopedics, Tianyou Hospital Affiliated to Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430064, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2020-06-15Revised:2020-06-19Accepted:2020-07-20Online:2021-04-28Published:2020-12-26 -
Contact:Zhang Mingyong, Chief physician, Master, Department of Orthopedics, Tianyou Hospital Affiliated to Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430064, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Li Yang, Master candidate, Physician, Department of Orthopedics, Tianyou Hospital Affiliated to Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430064, Hubei Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Yang, Min Shengwei, Xie Feng, Zhang Mingyong. A meta-analysis of clinical efficacy of preoperative use of three-dimensional printing in the treatment of tibial plateau fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1959-1968.
share this article
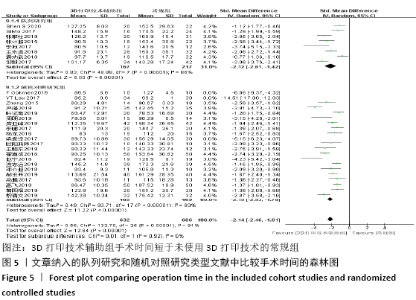
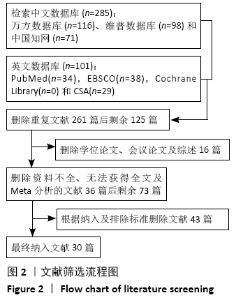
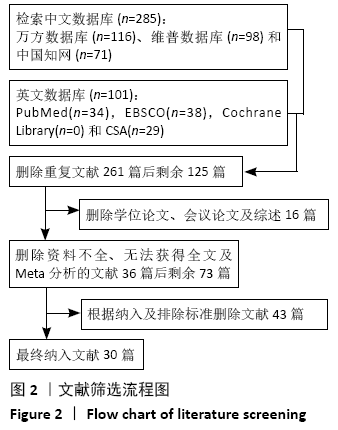
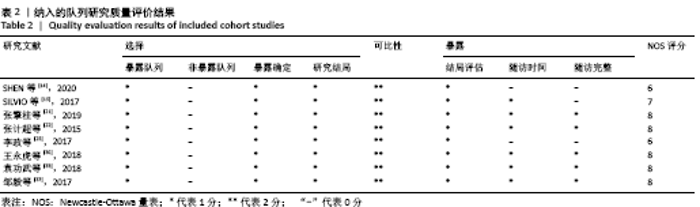
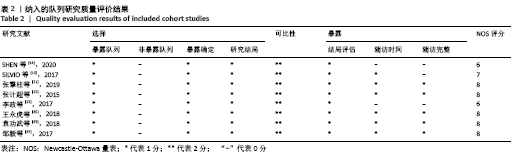
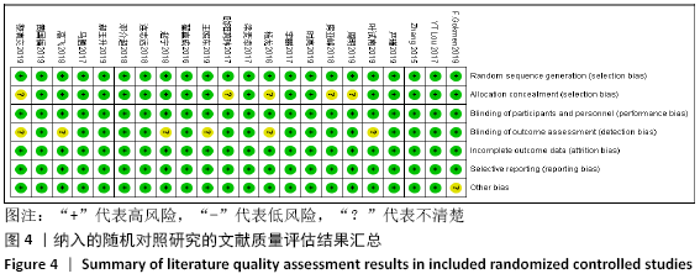
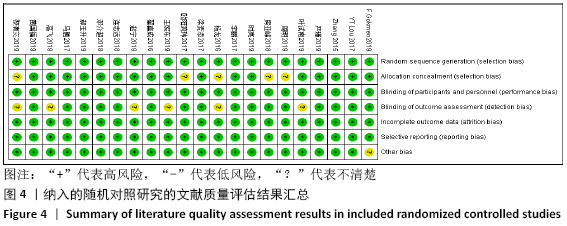
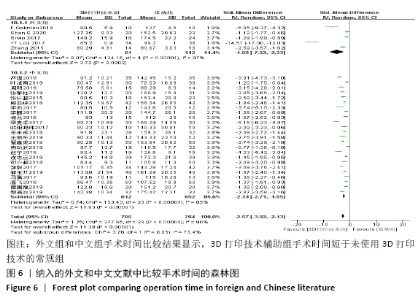
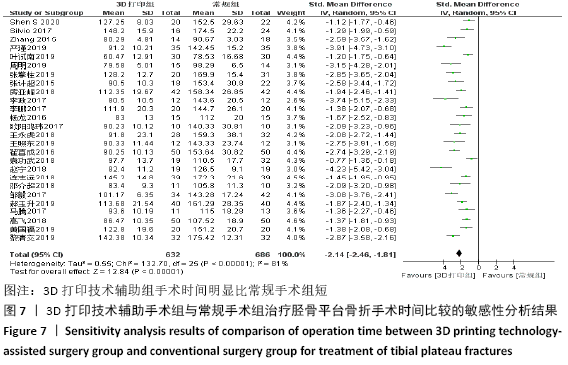
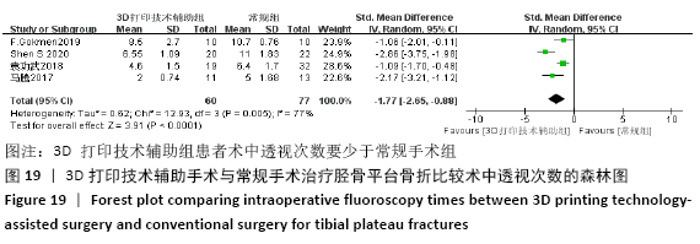
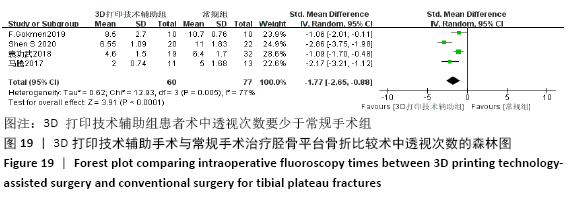
2.4 Meta分析结果 2.4.1 各组手术时间比较 纳入29篇文献 (3D打印技术辅助组706例,常规组764例)比较了两种方式在手术过程中所用的时间[13-23,25-42],各研究组间进行分析,有明显异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=90%)。进行亚组分析后,有8篇队列研究[14-15,21-22,25,30,33,37]、21篇随机对照研究[13,16-20,23,26-29,31-32,34-36,38-42],结果显示3D打印技术辅助组手术时间短于未使用3D打印技术的常规组(SMD= -2.12,95%CI:-2.81至-1.42,I2=86%,P < 0.000 01;SMD=-2.15,95%CI:-2.53至-1.78,I2=80%,P < 0.000 01),见图5。 "

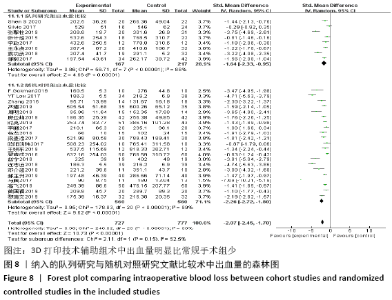
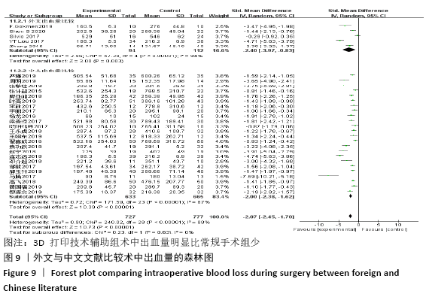
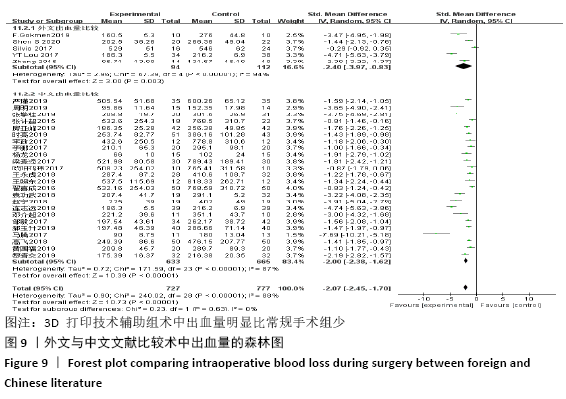
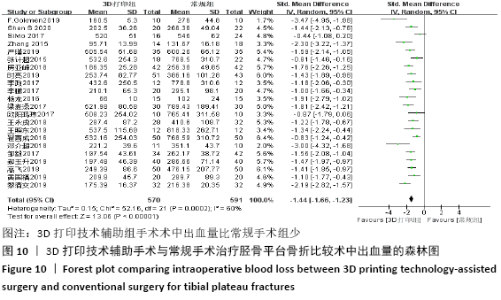
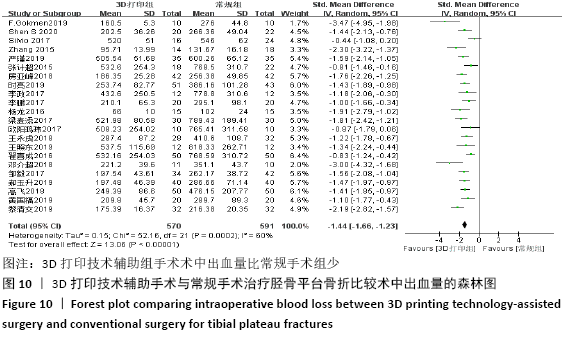
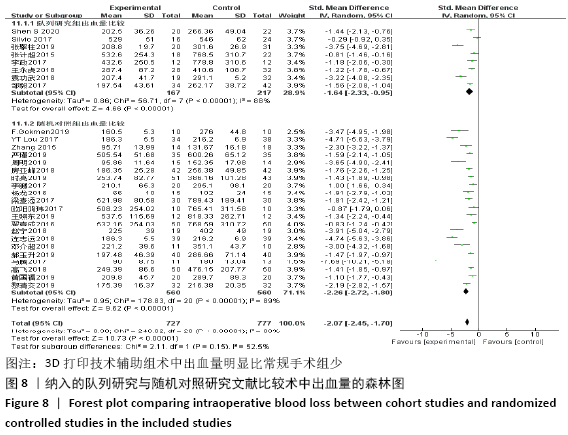
2.4.2 术中出血量分析 纳入29篇文献 (3D打印技术辅助组727例,常规组777例)比较了两种手术方式手术过程中的出血量[13-18,20-42],各研究组间进行分析,有明显异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=88%)。进行亚组分析后,有8篇队列研究[14-15,21-22,25,30,33,37]、21篇随机对照研究[13,16-18,20,23-24,26-29,31-32,34-36,38-42],结果显示3D打印技术辅助组术中出血量少于未使用3D打印技术的常规组(SMD=-1.64,95%CI:-2.33至-0.95,I2=88%,P < 0.000 01;SMD=-2.26,95%CI:-2.72至-1.80,I2=89%,P < 0.000 01),见图8。其中有24篇中文文献[18-23,25-42],5篇外文文献[13-17],显示3D打印技术辅助组术中出血量少于未使用3D打印技术的常规组(SMD=-2.00,95%CI:-2.38至-1.62,I2=87%,P < 0.000 01;SMD= -2.40,95%CI:-3.97至-0.83,I2=94%,P=0.003),见图9。 "
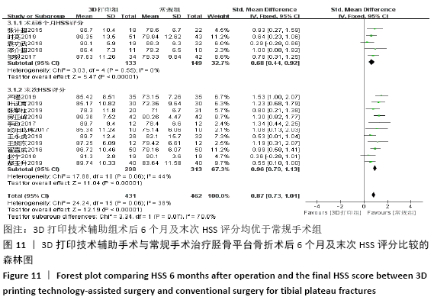
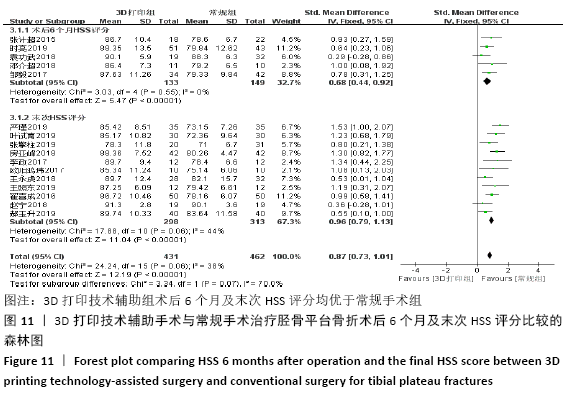
2.4.3 各组术后6个月及末次HSS评分比较 术后6个月HSS评分比较纳入5篇文献 (3打印组共133例,常规组149例)比较了两种手术方式患者术后HSS评分[22,24,33,36-37],各研究组间进行分析,无明显异质性(P=0.55,I2=0%),故采用固定效应模型,结果显示3D打印技术辅助组术后6个月评分优于常规组(SMD=0.68,95%CI:0.44-0.92,P < 0.000 01)。末次HSS评分纳入13篇文 献(3D打印技术辅助组352例,常规组373例)比较了两种手术方式患者术后末次HSS评分[14,16,18-19,21,23,25,29-32,34,38],各研究组间进行分析,两组有明显异质性,分别为(P < 0.000 01,I2=91%),进行敏感性分析发现去除2篇文献后[14,16],异质性由91%下降为44%,故采用固定效应模型分析,两组患者术后末次HSS评分差异有显著性意义(SMD=0.96,95%CI:0.79-1.13,P < 0.000 01),见图11。 "
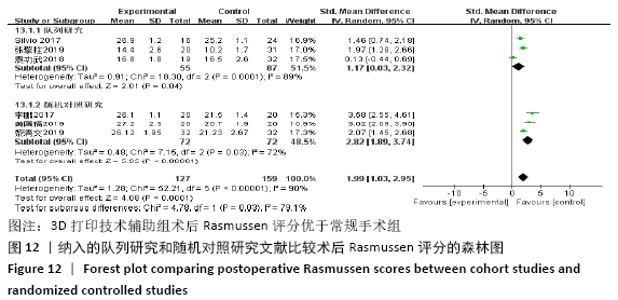
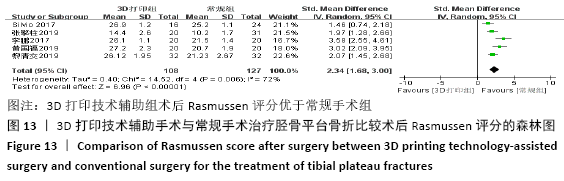
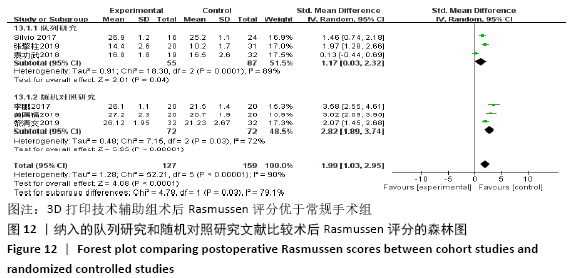
2.4.4 各组术后Rasmussen评分比较 纳入6篇文献 (3D打印技术辅助组127例,常规组159例)比较了两种手术方式患者术后Rasmussen评 分[15,21,26,32,41-42],各研究组间进行分析,有明显异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=90%),进行亚组分析,3篇队列研究[15,21,33]、3篇随机对照研究文献[26,41-42],显示3D打印技术辅助组术后Rasmussen评分优于未使用3D打印技术的常规组(SMD=1.17,95%CI:0.03-2.32,I2=89%,P=0.04;SMD=2.82,95%CI:1.89-3.74,I2=72%,P < 0.000 01),见图12。"

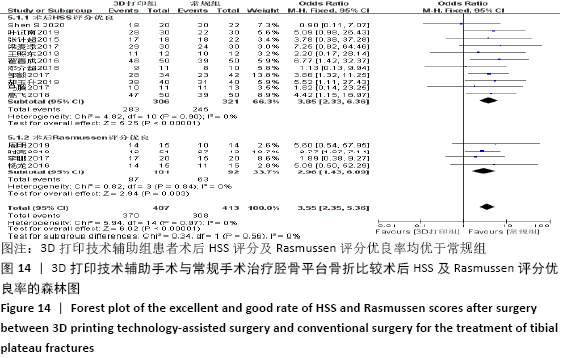
2.4.5 各组术后HSS评分及Rasmussen评分优良率比较 术后HSS评分优良率比较纳入的文献有11篇(3D打印技术辅助组306例,常规组321例)[14,19,22,28,31-32,36-40],术后Rasmussen评分优良率比较纳入的文献有4篇(3D打印技术辅助组101例,常规组92例)[20,24,26-27],比较了该两种方式术后HSS评分及Rasmussen评分的优良率,各研究组间进行分析,无明显异质性(P=0.90,I2=0%;P=0.84,I2=0%),故采用固定效应模型分析,结果显示3D打印技术辅助组患者术后HSS评分及Rasmussen评分优良率均优于常规组,两组术后HSS评分及Rasmussen评分优良率差异有显著性意义(OR=3.85,95%CI:2.33-6.36,P < 0.000 01;OR=2.96,95%CI:1.43-6.09,P=0.003),见图14。 "
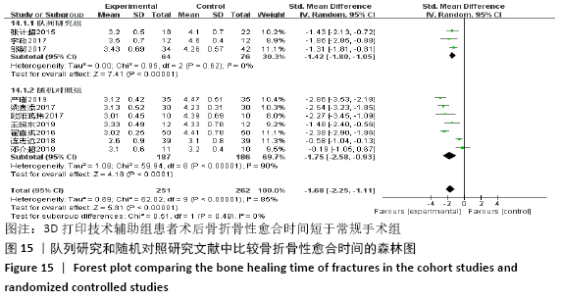
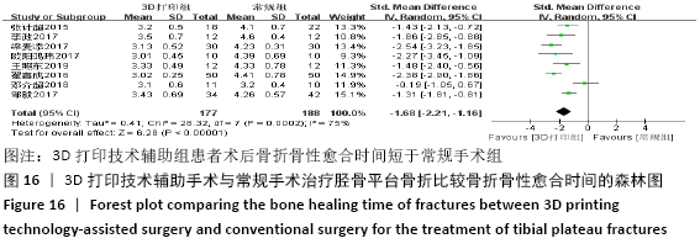
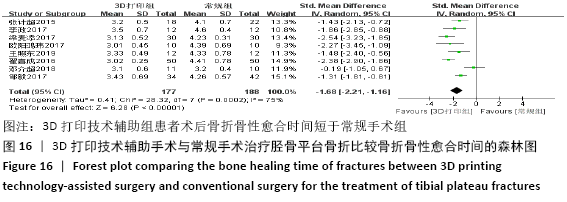
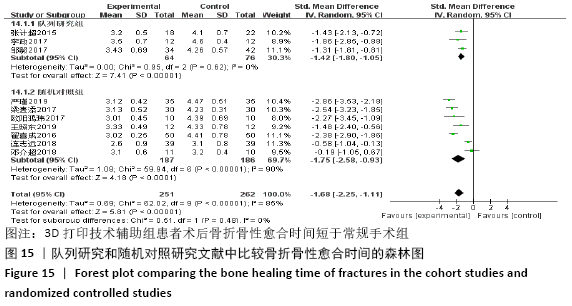
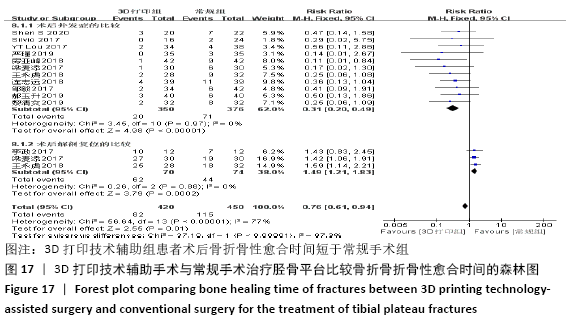
2.4.6 各组术后骨折骨性愈合时间比较分析 纳入10篇文献 (3D打印技术辅助组251例,常规组262例)比较了两种手术方式术后患者骨折骨性愈合时间[18,22,25,28-29,31-32,35-37],各研究组间进行分析,有明显异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2 =85%),进行亚组分析后,有3篇队列研究[22,25,37]、7篇随机对照研究类型的文献[18,28-29,31-32,35-36],显示3D打印技术辅助组患者术后患者骨折愈合时间要短于常规组(SMD=-1.42,95%CI:-1.80至-1.05,I2=0%,P < 0.000 01;SMD=-1.75,95%CI: -2.58至-0.93,I2=90%,P < 0.000 1)。见图15。 "
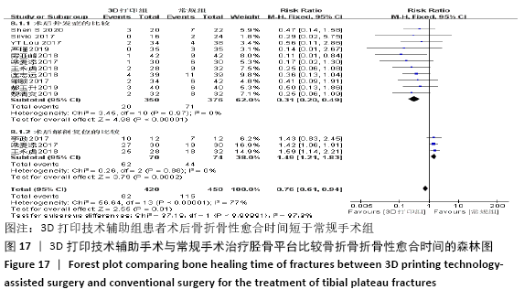
2.4.7 各组术后并发症发生率及解剖复位率的比较分析 术后并发症发生率比较纳入的文献有11篇(3D打印技术辅助组350例,常规组376例)[14-16,18,23,28,30,35,37-38,42],术后解剖复位率比较纳入的文献有3 篇(3D打印技术辅助组70例,常规组74例)[25,28,30],比较了该2种方式术后并发症发生率及解剖复位率,各研究组间进行分析,无明显异质性(P=0.97,I2=0%;P=0.88,I2=0%),故采用固定效应模型分析,结果显示3D打印技术辅助组患者术后并发症发生率要少于常规组,3D打印技术辅助组术后达到解剖复位率要优于常规组,两组术后并发症发生率及解剖复位率差异有显著性意义(RR=0.31,95%CI:0.20-0.49,P < 0.000 01;RR=1.49,95%CI:1.21-1.83,P=0.000 2),见图17。 "
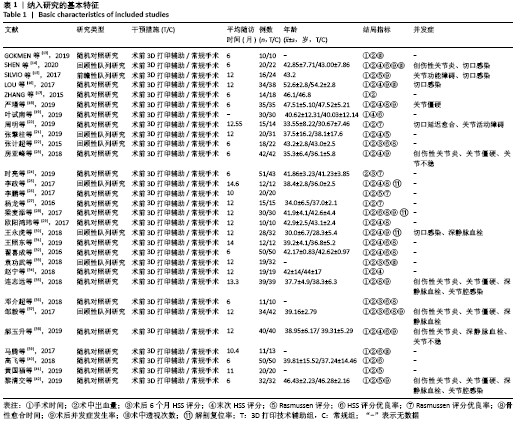
| [1] 张英泽.临床创伤骨科流行病学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2009. [2] 张莹莹,田京.数字骨科学在胫骨平台骨折的应用[J].实用骨科杂志,2014,7(11):183-184. [3] TAYLOR J, LANGENBACH A, MARCELLIN-LITTLE DJ. Risk factors for fibular fracture after TPLO. Vet Surg. 2011;40(6):687-693. [4] 王国旗,张里程,唐佩福.胫骨平台骨折的治疗策略与进展[J].中华骨科杂志,2016,36(18): 1202-1207. [5] PAPAGELOPOULOS PJ, PARTSINEVELOS AA, THEMISTOCLEOUS GS, et al. Complications after tibia plateau fracture surgery. Injury. 2006;37(6): 475-484. [6] VASANAD GH, ANTIN SM, AKKIMARADI RC, et al. Surgicalmanagement of tibial plateau fractures-a clinical study. Clin Diagn Res. 2013;7:3128-3130. [7] WASSERSTEIN D, HENRY P, PATERSON JM, et al. Risk of total knee arthop-lasty after operatively treated tibial plateau fracture: a matched population based cohort study.Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96:144-150. [8] CH T, ATHANASIOV A, WULLSCHLEGER M, et al. Current concepts in tibial plateau fractures. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2009;76:363-373. [9] 黄华军,张国栋,欧阳汉斌,等.基于3D打印技术的复杂胫骨平台骨折内固定手术数字化设计[J].南方医科大学学报,2015,35(2):218-222. [10] VON TENGG-KOBLIGK H, WEBER TF, RENGIER F, et al. Imaging modalities for the thoracic aorta. J Cardiovasc Surg. 2008;49(4):429-447. [11] 章莹,夏远军,万磊,等计算机三维仿真技术与常规手术治疗胫骨平台骨折的疗效对比分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2010,25(8):686-688. [12] RASMUSSEN PS. Tibial Condylar fracturesimpairment of knee joint stability as an indication for surgical treatment. J Bone Joint Surg (Am). 1973;55(7):1331-1350. [13] GOKMEN F, OZER MA, OZTURK AM, et al. Success in anatomic reduction of tibial pleau fractures: 3D patient special model. Int J Exp Clin Anat. 2019; 13(2):123-127. [14] SHEN S, WANG P, LI X, et al. Pre-operative simulation using a three-dimensional printing model for surgical treatment of old and complex tibial plateau fractures. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):6044. [15] GIANNETTI S, BIZZOTTO N, STANCATI A, et al. Minimally invasive fixation in tibial plateau fractures using an pre-operative and intra-operative real size 3D printing. Injury. 2017;48(3): 784-788. [16] LOU YT, CAI LY, WANG CG, et al. Comparison of traditional surgery and surgery assisted by three dimensional printing technology in the treatment of tibial plateau fractures. Int Orthop. 2017;41(9):1875-1880. [17] ZHANG H, LI Z, XU Q, et al. Analysis for clinical effect of virtual windowing and poking reduction treatment for Schatzker III tibial plateau fracture based on 3D CT data. Biome Res Int. 2015;12(2):1-2. [18] 严瑾,陈懿,沈敏,等.3D打印技术辅助手术治疗复杂胫骨平台骨折的效果观察[J].临床医学工程,2019,26(6):745-746. [19] 叶试南,阮平,郑帮明,等.3D打印技术对胫骨平台骨折关节面复位的应用价值及术后CT结果研究[J].中国现代医生,2019,57(21):21-23. [20] 周明,丁文斌,刘全,等.3D打印技术在复杂胫骨平台骨折手术中的应用研究[J].骨科, 2019, 10(1):31-36. [21] 张擎柱,张义,付世杰,等.3D打印技术在复杂胫骨平台骨折手术中的应用[J].临床骨科杂志, 2019,22(2):229-231. [22] 张计超,宁宇,王向前,等.3D打印技术在复杂胫骨平台骨折中的应用[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2015,12(6):26-28. [23] 房亚峰,魏戎,武军龙,等.基于3D打印技术治疗复杂胫骨平台骨折的研究[J].世界最新医学信息文献,2018,18(76):159-160. [24] 时亮,段亮,董向辉,等.3D打印联合数字化设计在复杂胫骨平台骨折内固定治疗中的应用[J].中国医学装备,2019,16(10):10-13. [25] 李政,卢启贵,黄东红,等.3D打印技术结合虚拟手术与传统手术在治疗复杂胫骨平台骨折的应用疗效比较[J].中国伤残医学,2017,25(10): 35-38. [26] 李鹏,彭文标,李鉴轶,等.数字化设计结合3D打印技术辅助手术治疗复杂型胫骨平台骨折[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2017,35(2):151-155. [27] 杨龙,王建吉,孙琦,等.胫骨平台骨折植入物内固定修复中3D打印技术的辅助应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(13):1904-1910. [28] 梁麦添,冯仕华,陈定启,等.复杂胫骨平台骨折治疗中3D打印技术的应用探析[J].数理医药学杂志,2017,30(11):1688-1690. [29] 欧阳鸿玮,赵雪丹,蔡平,等.传统手术与应用3D打印技术后手术治疗复杂胫骨平台骨折的疗效比较[J].中国卫生标准管理,2017,8(16):60-61. [30] 王永虎,史福东,谢伟.3D打印技术在Schatzker Ⅵ型胫骨平台骨折钢板内固定中的作用研究[J].创伤外科杂志,2018,20(12):926-929. [31] 王照东,官建中,吴敏,等.3D打印技术在复杂胫骨平台骨折手术中的应用[J].淮海医学,2019, 37(1):20-22. [32] 翟喜成.复杂胫骨平台骨折采用3D打印技术的分析[J].中国继续医学教育,2016,8(29):140-141. [33] 袁功武,聂宇,刘曦明,等.3D打印技术辅助治疗与传统手术方法治疗复杂胫骨平台骨折的对比研究[J].创伤外科杂志,2018,20(5):10-14. [34] 赵宁,陈劲,钟华,等.3D打印技术辅助治疗复杂胫骨平台骨折的疗效分析[J].中国临床新医学,2018,11(5):17-21. [35] 连志远,马少波,李建,等.传统手术与应用3D打印技术手术对胫骨平台骨折的疗效比较[J].湖南师范大学学报(医学版),2018,15(6):76-79. [36] 邓介超,丛云海,朱治国,等.3D打印在治疗复杂胫骨平台骨折制定术前计划中的应用价值[J].临床和试验医学杂志,2018,17(21):2336-2339. [37] 邹毅,叶茂,何玲莉,等.3D打印用于胫骨平台骨折辅助治疗的临床效果分析[J].实用临床医药杂志,2017,21(11):138-140. [38] 郝玉升,刘巍,王臣,等.3D打印技术在复杂胫骨平台骨折临床诊治中的应用[J].临床和试验医学杂志,2019,18(1):108-111. [39] 马腾,魏代好,秦悦,等.常规影像学结合3D打印技术在复杂胫骨平台骨折治疗中的应用[J].宁夏医科大学学报,2017,39(12):1452-1454. [40] 高飞.3D打印技术在复杂胫骨平台骨折诊治中的应用价值[J].临床医学研究与实践, 2018, 17:64-65. [41] 黄国福,苏福锦,何忠,等.3D打印技术结合数字化设计辅助手术治疗复杂胫骨平台骨折20例临床分析[J].广西医科大学学报, 2019, 36(10):1660-1664. [42] 黎清交,张观辉,朱绍琼,等.3D 打印技术辅助治疗与传统手术治疗复杂胫骨平台骨折患者的临床效果[J].医疗装备,2019,32(23):92-93. [43] HUANG H, HSIEH MF, ZHANG G, et al. Improved accuracy of 3D-printed navigational template during complicated tibial plateau fracture surgery. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med. 2015;38:109-117. [44] VASANAD GH, ANTIN SM, AKKIMARADI RC, et al. Surgical management of tibial plateau fractures-a clinical study. Clin Diagn Res. 2013;7:3128-3130. [45] WASSERSTEIN D, HENRY P, PATERSON JM, et al. Risk of total knee arthroplasty after operatively treated tibial plateau fracture:a matched-population-based cohort study. Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96:144-150. [46] 邱卫华,孔祥雪,李鉴轶,等.3D打印技术指导胫骨平台Schatzker IV、V型骨折复位的初步应用[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2016,34(6):697-699. [47] 王欣文,张垄,朱养均,等.3D打印技术在复杂胫骨平台骨折治疗中的临床应用[J].实用骨科杂志,2015,(10):887-890. [48] 刘泽,赵建勇.3D打印技术在骨科临床应用中的研究现状[J].河北医药,2017(2):288-293. [49] 温阳阳,李文龙,范亚楠,等.骨科3D打印技术的应用研究与前景展望[J].中国医药导报, 2017(6):41-44. [50] 王燎,戴魁戎.骨科个体化治疗与3D打印技术[J].医用生物力学,2014,29(3):193-199. [51] 邵佳申,常恒瑞,郑占乐,等.3D打印辅助手术治疗胫骨平台骨折疗效的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(23):3767-3772. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [3] | Lu Dezhi, Mei Zhao, Li Xianglei, Wang Caiping, Sun Xin, Wang Xiaowen, Wang Jinwu. Digital design and effect evaluation of three-dimensional printing scoliosis orthosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1329-1334. |
| [4] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [5] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [6] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [7] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [8] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [9] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [10] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [11] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [12] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [13] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [14] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [15] | Zhang Shangpu, Ju Xiaodong, Song Hengyi, Dong Zhi, Wang Chen, Sun Guodong. Arthroscopic suture bridge technique with suture anchor in the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1417-1422. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||