Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (14): 2199-2204.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3145
Previous Articles Next Articles
Correlation between inflammatory factors in synovial cells and microRNA-145/mitogen-activated protein kinase 4 molecular axis
Zhu Lixuan, Cui Yue, Luo Jing
- Department of Pain, The First People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650032, Yunnan Province, China
-
Received:2019-03-14Revised:2019-03-22Accepted:2020-09-10Online:2021-05-18Published:2020-12-30 -
Contact:Luo Jing, Associate chief physician, Department of Pain, The First People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650032, Yunnan Province, China -
About author:Zhu Lixuan, Associate chief physician, Department of Pain, The First People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650032, Yunnan Province, China -
Supported by:Health Science and Technology Project of Yunnan Province of China, No. 2018NS0243 (to LJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhu Lixuan, Cui Yue, Luo Jing. Correlation between inflammatory factors in synovial cells and microRNA-145/mitogen-activated protein kinase 4 molecular axis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2199-2204.
share this article
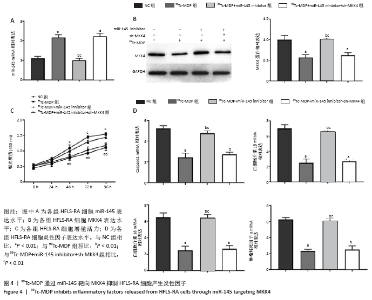
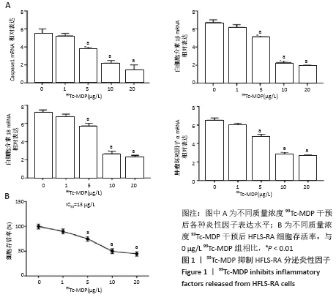
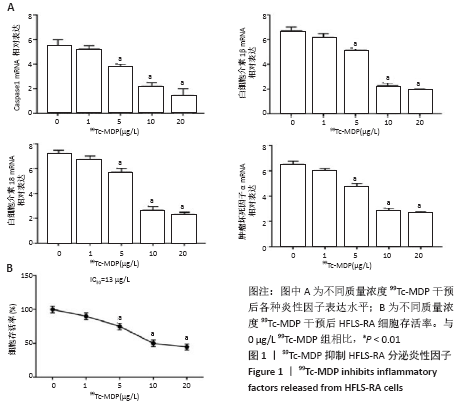
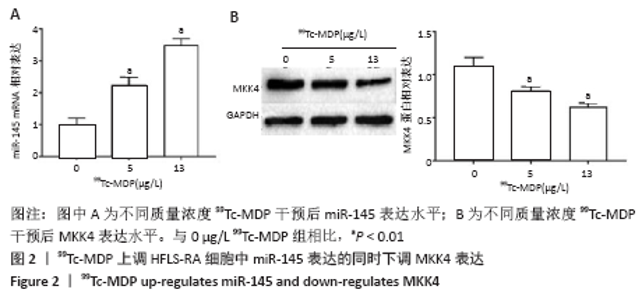
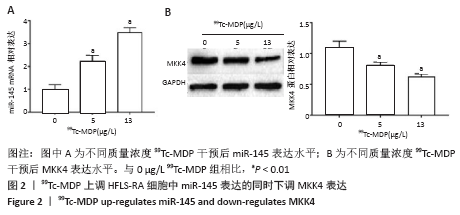
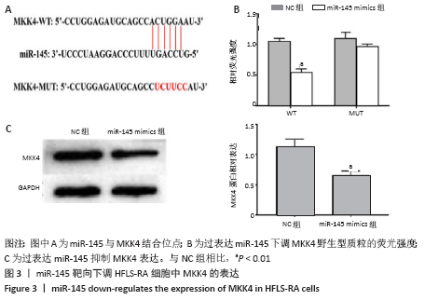
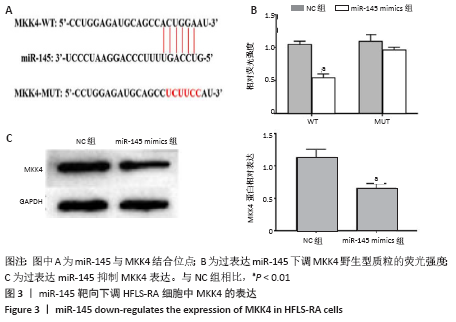
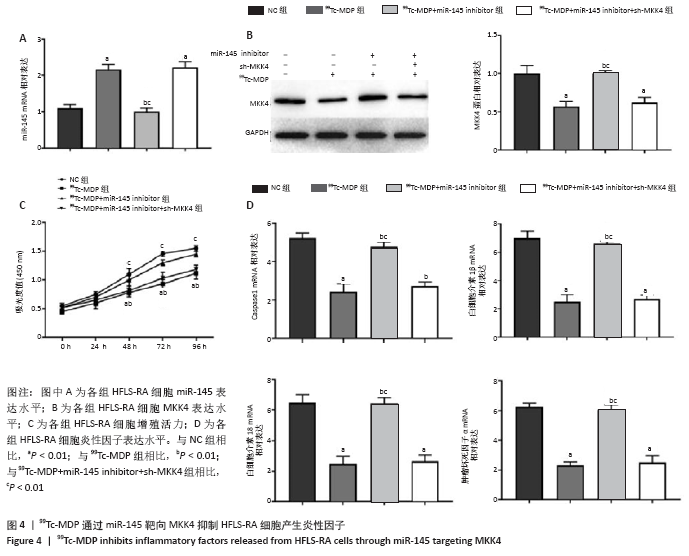
2.4 99Tc-MDP通过miR-145靶向MKK4抑制HFLS-RA细胞产生炎性因子 qRT-PCR实验结果显示,HFLS-RA细胞培养基中加入13 μg/L 99Tc-MDP后miR-145表达显著高于NC组;加药的同时转染miR-145 inhibitor后,miR-145表达显著低于加药组;而加药的同时转染miR-145 inhibitor和sh-MKK4后,miR-145表达又显著高于加药并转染miR-145 inhibitor(P < 0.01),见图4A。 Western blot实验结果显示,99Tc-MDP组MKK4表达明显低于NC组;99Tc-MDP+miR-145 inhibitor组MKK4表达明显高于99Tc-MDP组;而99Tc-MDP+miR-145 inhibitor+sh-MKK4组MKK4表达又明显低于99Tc-MDP+miR-145 inhibitor组(P < 0.01),见图4B。 CCK-8实验结果显示,99Tc-MDP组HFLS-RA细胞增殖活力显著低于NC组;99Tc-MDP+miR-145 inhibitor组HFLS-RA细胞增殖活力显著高于99Tc-MDP组;而99Tc-MDP +miR-145 inhibitor+sh-MKK4组HFLS-RA细胞增殖活力显著低于99Tc-MDP+miR-145 inhibitor组(P < 0.01),见图4C。 qRT-PCR实验结果显示,炎性分子caspase 1、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素18和肿瘤坏死因子α表达:99Tc-MDP组显著低于NC组;99Tc-MDP+miR-145 inhibitor组显著高于99Tc-MDP组;99Tc-MDP +miR-145 inhibitor+sh-MKK4组显著低于99Tc-MDP + miR-145 inhibitor组(P < 0.01),见图4D。99Tc-MDP通过miR-145靶向MKK4抑制HFLS-RA细胞分泌炎性因子caspase 1、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素18和肿瘤坏死因子α。 "
| [1] PUN YL, MOSKOWITZ RW, LIE S, et al. Clinical correlations of osteoarthritis associated with a single-base mutation (arginine519 to cysteine) in type II procollagen gene. A newly defined pathogenesis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994;37(2):264-269. [2] ROEMER FW, KWOH CK, HANNON MJ, et al. Partial meniscectomy is associated with increased risk of incident radiographic osteoarthritis and worsening cartilage damage in the following year. Eur Radiol. 2017;27(1):404-413. [3] LAI K, JIN C, TU S, et al. Intravitreal injection of (99)Tc-MDP inhibits the development of laser-induced choroidal neovascularization in rhesus monkeys. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2014;252(7):1049-1057. [4] ZHAO Y, WANG L, LIU Y, et al. Technetium-99 conjugated with methylene diphosphonate ameliorates ovariectomy-induced osteoporotic phenotype without causing osteonecrosis in the jaw. Calcif Tissue Int. 2012;91(6):400-408. [5] LAI K, XU L, JIN C, et al. Technetium-99 conjugated with methylene diphosphonate (99Tc-MDP) inhibits experimental choroidal neovascularization in vivo and VEGF-induced cell migration and tube formation in vitro. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52(8):5702-5712. [6] CHEN J, LAN Y, HE Y, et al. 99Tc-MDP-induced human osteoblast proliferation, differentiation and expression of osteoprotegerin. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(2):1801-1809. [7] WANG GD, ZHAO XW, ZHANG YG, et al. Effects of miR-145 on the inhibition of chondrocyte proliferation and fibrosis by targeting TNFRSF11B in human osteoarthritis. Mol Med Rep. 2017;15(1):75-80. [8] NISHITANI K, ITO H, HIRAMITSU T, et al. PGE2 inhibits MMP expression by suppressing MKK4-JNK MAP kinase-c-JUN pathway via EP4 in human articular chondrocytes. J Cell Biochem. 2010;109(2):425-433. [9] HU G, ZHAO X, WANG C, et al. MicroRNA-145 attenuates TNF-α-driven cartilage matrix degradation in osteoarthritis via direct suppression of MKK4. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8(10):e3140. [10] MIYAKI S, ASAHARA H. Macro view of microRNA function in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012;8(9):543-552. [11] ZHANG W, MOSKOWITZ RW, NUKI G, et al. OARSI recommendations for the management of hip and knee osteoarthritis, part I: critical appraisal of existing treatment guidelines and systematic review of current research evidence. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007;15(9):981-1000. [12] CROSS M, SMITH E, HOY D, et al. The global burden of hip and knee osteoarthritis: estimates from the global burden of disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(7):1323-1330. [13] HUNTER DJ. Pharmacologic therapy for osteoarthritis--the era of disease modification. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(1):13-22. [14] LORIES RJ, LUYTEN FP. The bone-cartilage unit in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(1):43-49. [15] MU R, LIANG J, SUN L, et al. A randomized multicenter clinical trial of 99 Tc-methylene diphosphonate in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Rheum Dis. 2018;21(1):161-169. [16] WU Q, NI Y, YANG Q, et al. 99Tc-MDP treatment for the therapy of rheumatoid arthritis, choroidal neovascularisation and Graves’ ophthalmopathy. Biomed Rep. 2016;4(4):400-402. [17] SU D, SHEN M, GU B, et al. (99) Tc-methylene diphosphonate improves rheumatoid arthritis disease activity by increasing the frequency of peripheral γδ T cells and CD4(+) CD25(+) Foxp3(+) Tregs. Int J Rheum Dis. 2016;19(6):586-593. [18] WANG L, GU Q, XU Y, et al. Effects of Yunke (technetium-99 conjugated with methylene diphosphonate; (99)Tc-MDP) and/or colloidal chromic phosphate phosphonium-32, alone and in combination, in rats with adjuvant arthritis. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2008;35(1):23-28. [19] HU J, WANG Z, PAN Y, et al. MiR-26a and miR-26b mediate osteoarthritis progression by targeting FUT4 via NF-κB signaling pathway. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2018;94:79-88. [20] NTOUMOU E, TZETIS M, BRAOUDAKI M, et al. Serum microRNA array analysis identifies miR-140-3p, miR-33b-3p and miR-671-3p as potential osteoarthritis biomarkers involved in metabolic processes. Clin Epigenetics. 2017;9:127. [21] CHEN L, LI Q, WANG J, et al. MiR-29b-3p promotes chondrocyte apoptosis and facilitates the occurrence and development of osteoarthritis by targeting PGRN. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(12): 3347-3359. [22] HONG BK, YOU S, YOO SA, et al. MicroRNA-143 and -145 modulate the phenotype of synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis. Exp Mol Med. 2017;49(8):e363. [23] DÉRIJARD B, RAINGEAUD J, BARRETT T, et al. Independent human MAP-kinase signal transduction pathways defined by MEK and MKK isoforms. Science. 1995;267(5198):682-685. [24] HAN J, LEE JD, JIANG Y, et al. Characterization of the structure and function of a novel MAP kinase kinase (MKK6). J Biol Chem. 1996;271(6):2886-2891. [25] BRANCHO D, TANAKA N, JAESCHKE A, et al. Mechanism of p38 MAP kinase activation in vivo. Genes Dev. 2003;17(16):1969-1978. [26] MANTENA SK, KATIYAR SK. Grape seed proanthocyanidins inhibit UV-radiation-induced oxidative stress and activation of MAPK and NF-kappaB signaling in human epidermal keratinocytes. Free Radic Biol Med. 2006;40(9):1603-1614. [27] LAI L, SONG Y, LIU Y, et al. MicroRNA-92a negatively regulates Toll-like receptor (TLR)-triggered inflammatory response in macrophages by targeting MKK4 kinase. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(11):7956-7967. [28] ZHANG L, ZHOU M, WANG Y, et al. miR-92a inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis: role of the MKK4-JNK pathway. Apoptosis. 2014;19(6):975-983. |
| [1] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [2] | Peng Zhihao, Feng Zongquan, Zou Yonggen, Niu Guoqing, Wu Feng. Relationship of lower limb force line and the progression of lateral compartment arthritis after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with mobile bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1368-1374. |
| [3] | Gu Xia, Zhao Min, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Relationship between hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha and hypoxia signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1284-1289. |
| [4] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [5] | Liu Xiangxiang, Huang Yunmei, Chen Wenlie, Lin Ruhui, Lu Xiaodong, Li Zuanfang, Xu Yaye, Huang Meiya, Li Xihai. Ultrastructural changes of the white zone cells of the meniscus in a rat model of early osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1237-1242. |
| [6] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [7] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [8] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [9] | Yang Yang, Yao Yu, Shen Xiaotian, Liu Jiajia, Xue Jianhua. Expression and significance of interleukin-21 in intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 690-694. |
| [10] | Ma Binxiang, He Wanqing, Zhou Guangchao, Guan Yonglin. Triptolide improves motor dysfunction in rats following spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 701-706. |
| [11] | Cao Xuhan, Bai Zixing, Sun Chengyi, Yang Yanjun, Sun Weidong. Mechanism of “Ruxiang-Moyao” herbal pair in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 746-753. |
| [12] | Li Yonghua, Feng Qiang, Tan Renting, Huang Shifu, Qiu Jinlong, Yin Heng. Molecular mechanism of Eucommia ulmoides active ingredients treating synovitis of knee osteoarthritis: an analysis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 765-771. |
| [13] | Song Shan, Hu Fangyuan, Qiao Jun, Wang Jia, Zhang Shengxiao, Li Xiaofeng. An insight into biomarkers of osteoarthritis synovium based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 785-790. |
| [14] | Liu Bo, Chen Xianghe, Yang Kang, Yu Huilin, Lu Pengcheng. Mechanism of DNA methylation in exercise intervention for osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 791-797. |
| [15] | Deng Zhenhan, Huang Yong, Xiao Lulu, Chen Yulin, Zhu Weimin, Lu Wei, Wang Daping. Role and application of bone morphogenetic proteins in articular cartilage regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 798-806. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||