Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (23): 3627-3635.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2661
Previous Articles Next Articles
Expression of connexin 43 in cartilage and chondrocyte of osteoarthritis and construction of shRNA lentiviral vector targeting connexin 43
Xue Junjie1, Li Jingyu2, Zhang Li1, Ren Chaochao1
- 1Department of Orthodontics, Beijing Stomatological Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100050, China; 2Department of Stomatology, Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100070, China
-
Received:2019-09-18Revised:2019-09-20Accepted:2019-10-26Online:2020-08-18Published:2020-04-25 -
Contact:Ren Chaochao, MD, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthodontics, Beijing Stomatological Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100050, China -
About author:Xue Junjie, MD, Attending physician, Department of Orthodontics, Beijing Stomatological Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100050, China -
Supported by:the Basic-Clinical Scientific Research Cooperation Foundation of Capital Medical University, No. 16JL32; Discipline Construction Special Project of Beijing Stomatological Hospital of Capital Medical University, No. 16-09-10
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xue Junjie, Li Jingyu, Zhang Li, Ren Chaochao. Expression of connexin 43 in cartilage and chondrocyte of osteoarthritis and construction of shRNA lentiviral vector targeting connexin 43[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(23): 3627-3635.
share this article
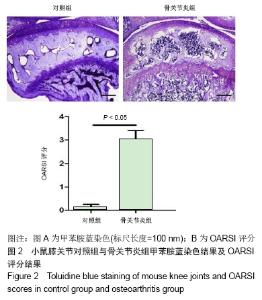
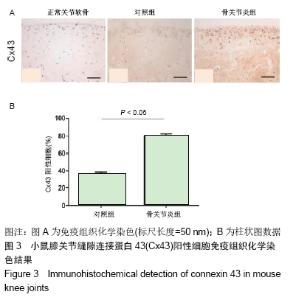
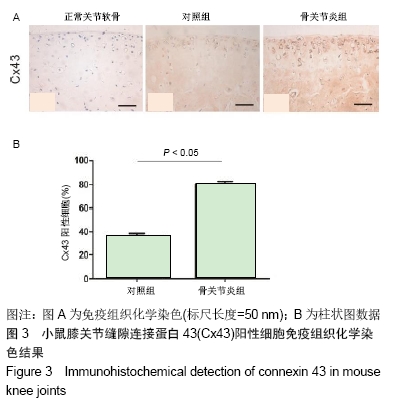
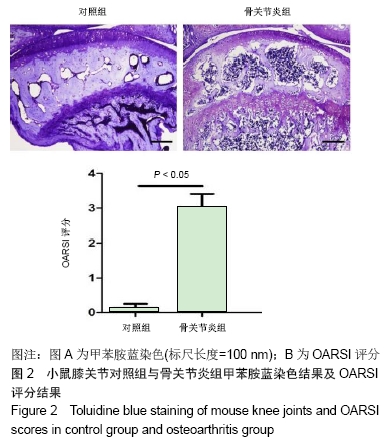
2.1 实验动物数量分析 实验选用C57BL/6小鼠6只,实验过程无脱失,全部进入结果分析。 2.2 骨关节炎动物模型中实验侧关节较对照侧关节有更高的OARSI评分 见图2。镜下可见手术诱导膝骨关节炎4周后,实验侧与对照侧相比,关节软骨层明显变薄,粘合线崎岖不平,局部出现裂隙。根据OARSI对小鼠骨关节炎模型建立后关节炎严重程度的评分体系[10],OARSI评分较高则证明骨关节炎较严重,反之则证明骨关节炎病变程度较轻。对甲苯胺蓝染色后的小鼠双侧关节组织切片进行评分及统计,结果发现对照侧与实验侧关节评分有明显差异,实验侧的评分明显高于对照侧,说明膝关节前交叉韧带切断术可以有效诱导小鼠膝骨关节炎,并出现明显的骨关节炎表型。 "
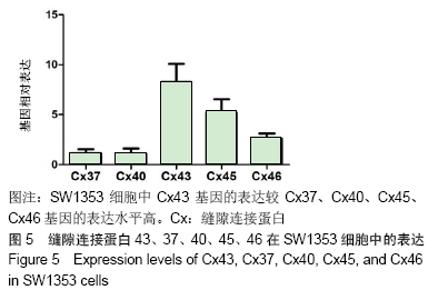
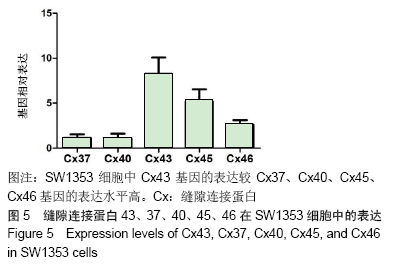
2.5 Cx43、Cx37、Cx40、Cx45、Cx46在SW1353细胞中的表达 使用RT-PCR检测软骨细胞SW1353细胞株中Cx43、Cx37、Cx40、Cx45、Cx46基因的表达水平,结果显示SW1353细胞中Cx43基因的表达水平较Cx37、Cx40、Cx45、Cx46基因的表达水平高。见图5。实验结果显示:在基因水平上,SW1353细胞中编码Cx43的Gja1基因的表达水平较编码Cx37、Cx40、Cx45、Cx46的基因表达水平高(P < 0.01)。结果表明:与连接蛋白家族的其他缝隙连接蛋白的基因表达水平对比,Cx43在SW1353细胞中的表达水平较高,验证了SW1353细胞中Cx43的表达在连接蛋白家族中具有主导地位。 "
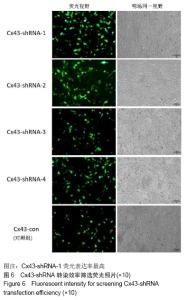
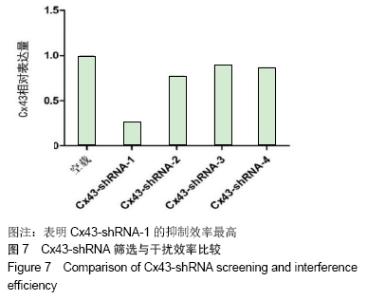
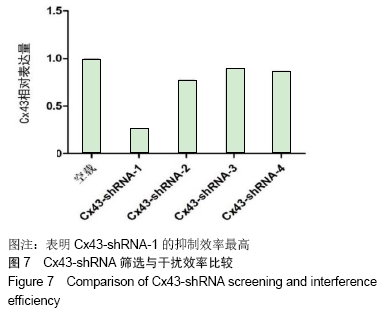
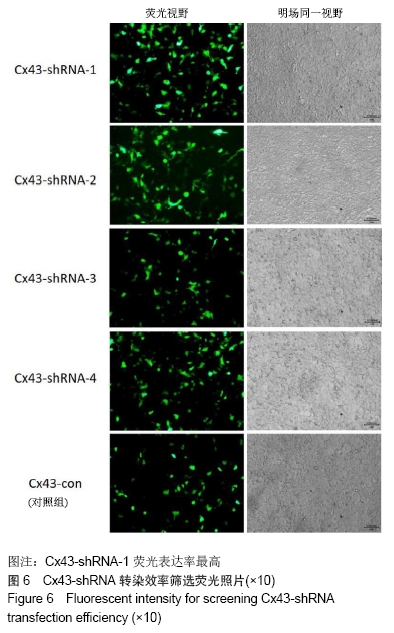
2.6 Cx43-shRNA慢病毒载体构建结果 慢病毒载体的测序鉴定结果显示:阳性克隆测序结果与目标序列完全一致,质粒构建成功。转染293T细胞36 h后,荧光显微镜下观察,质粒转染组各组均可见荧光蛋白表达,4个Cx43-shRNA慢病毒质粒Cx43-shRNA-1,Cx43-shRNA-2,Cx43-shRNA-3,Cx43-shRNA-4中,Cx43-shRNA-1荧光表达率最高,见图6。将转染36 h后的细胞进行裂解,获取RNA,反转录成cDNA,通过RT-PCR分析Cx43的相对表达量。相对于空载对照组Cx43-CON,其他组Cx43的表达量均明显下降,Cx43-shRNA-1组的Cx43表达量最低,表明Cx43-shRNA-1的抑制效率最高,其抑制率>75%,见图7。 "
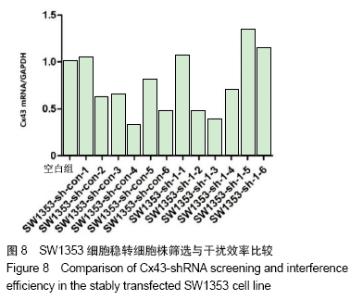
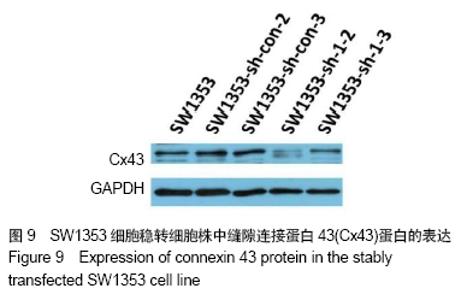
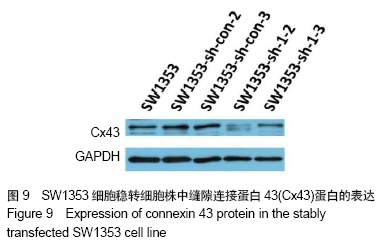
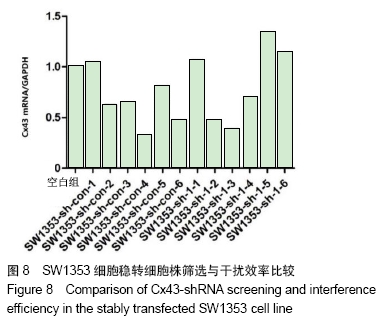
2.7 SW1353细胞稳转细胞株的筛选及鉴定结果 用转染后抑制效率最高Cx43-shRNA-1慢病毒质粒转染SW1353细胞。转染48 h后,未转染的SW1353作为空白组,对照组和实验组分别取自复苏后的6株SW1353细胞样本,并在转染前后做自身对照,对照组为:SW1353-sh-con-1,SW1353-sh-con-2,SW1353-sh-con-3,SW1353-sh-con-4,SW1353-sh-con-5,SW1353-sh-con-6,感染了Cx43-shRNA-1慢病毒载体的SW1353细胞作为实验组:SW1353-sh-1-1,SW1353-sh-1-2,SW1353-sh-1-3,SW1353-sh-1-4,SW1353-sh-1-5,SW1353-sh-1-6。对上述细胞进行裂解,获取RNA,反转录成cDNA,通过RT-PCR分析Cx43在各组细胞中的的相对表达量,见图8;SW1353细胞稳转细胞株中Cx43蛋白的表达见图9。根据结果筛选出良好的稳转株为后续研究做准备。 "
| [1] BORING MA, HOOTMAN JM, LIU Y, et al. Prevalence of Arthritis and Arthritis-Attributable Activity Limitation by Urban-Rural County Classification-United States, 2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017,66(20):527-532. [2] ENTESHARI-MOGHADDAM A, ISAZADEHFAR K, HABIBZADEH A, et al. Efficacy of Methotrexate on Pain Severity Reduction and Improvement of Quality of Life in Patients with Moderate to Severe Knee Osteoarthritis. Anesth Pain Med.2019;9(3):e89990. [3] IMANI F, PATEL VB. Therapeutic Challenges for Knee Osteoarthritis.Anesth Pain Med. 2019;9(3):e95377. [4] BATRA N, KAR R, JIANG JX. Gap junctions and hemichannels in signal transmission, function and development of bone. Biochim Biophys Acta.2012;1818(8):1909-1918. [5] LIU S, NIGER C, KOH EY, et al. Connexin43 Mediated Delivery of ADAMTS5 Targeting siRNAs from Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Synovial Fibroblasts.PLoS One.2015;10(6):e129999. [6] ZAPPITELLI T, AUBIN JE. The "connexin" between bone cells and skeletal functions.J Cell Biochem. 2014;115(10):1646-1658. [7] GRIMSTON SK, WATKINS MP, BRODT MD, et al. Enhanced periosteal and endocortical responses to axial tibial compression loading in conditional connexin43 deficient mice. PLoS One.2012;7(9):e44222. [8] WATKINS M, GRIMSTON SK, NORRIS JY, et al. Osteoblast connexin43 modulates skeletal architecture by regulating both arms of bone remodeling.Mol Biol Cell.2011;22(8): 1240-1251. [9] LORENZ J, GRASSEL S. Experimental osteoarthritis models in mice.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1194:401-419. [10] GLASSON SS, CHAMBERS MG, VAN DEN BERG WB, et al. The OARSI histopathology initiative - recommendations for histological assessments of osteoarthritis in the mouse. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2010;18 Suppl 3:S17-S23. [11] LOESER RF, GOLDRING SR, SCANZELLO CR, et al. Osteoarthritis: a disease of the joint as an organ. Arthritis Rheum.2012;64(6):1697-1707. [12] OLAH T, REINHARD J, GAO L, et al. Topographic modeling of early human osteoarthritis in sheep.Sci Transl Med.2019; 11(508). pii: eaax6775. [13] BECKER SK. Osteoarthritis, entheses, and long bone cross-sectional geometry in the Andes: Usage, history, and future directions.Int J Paleopathol. 2019 Aug 28. pii: S1879-9817(19)30023-3. [14] 张荣,张向东,赵明宇.膝骨关节炎发病机制及治疗进展[J].风湿病与关节炎,2019,8(5):68-72. [15] SERAKINCI N, SAVTEKIN G. Modeling Mesenchymal Stem Cells in TMJ Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis Therapy. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr.2017;27(3):205-210. [16] LIU Y, ZOU R, WANG Z, et al. Exosomal KLF3-AS1 from hMSCs promoted cartilage repair and chondrocyte proliferation in osteoarthritis.Biochem J.2018;475(22):3629-3638. [17] JEVOTOVSKY DS, ALFONSO AR, EINHORN TA, et al. Osteoarthritis and stem cell therapy in humans: a systematic review.Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2018;26(6):711-729. [18] 张平平,向川.骨髓间充质干细胞治疗骨关节炎:可能与未来[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(6):968-973. [19] DE MIGUEL MP, FUENTES-JULIAN S, BLAZQUEZ-MARTINEZ A, et al. Immunosuppressive properties of mesenchymal stem cells: advances and applications.Curr Mol Med.2012;12(5): 574-591. [20] MURPHY MB, MONCIVAIS K, CAPLAN AI. Mesenchymal stem cells: environmentally responsive therapeutics for regenerative medicine.Exp Mol Med.2013;45:e54. [21] LI KC, HU YC. Cartilage tissue engineering: recent advances and perspectives from gene regulation/therapy.Adv Healthc Mater.2015;4(7):948-968. [22] TARZEMANY R, JIANG G, LARJAVA H, et al. Expression and function of connexin 43 in human gingival wound healing and fibroblasts.PLoS One.2015;10(1):e115524. [23] TARZEMANY R, JIANG G, JIANG JX, et al.C onnexin 43 Hemichannels Regulate the Expression of Wound Healing- Associated Genes in Human Gingival Fibroblasts.Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):14157. [24] TARZEMANY R, JIANG G, JIANG JX, et al. Connexin 43 regulates the expression of wound healing-related genes in human gingival and skin fibroblasts.Exp Cell Res.2018;367(2): 150-161. [25] SCHWAB W, HOFER A, KASPER M. Immunohistochemical distribution of connexin 43 in the cartilage of rats and mice. Histochem J.1998;30(6):413-419. [26] ZHANG M, PRITCHARD MR, MIDDLETON FA, et al. Microarray analysis of perichondral and reserve growth plate zones identifies differential gene expressions and signal pathways. Bone.2008;43(3):511-520. [27] MAYAN MD, GAGO-FUENTES R, CARPINTERO-FERNANDEZ P, et al. Articular chondrocyte network mediated by gap junctions: role in metabolic cartilage homeostasis.Ann Rheum Dis.2015;74(1):275-284. [28] MIYAKI S, ASAHARA H. Macro view of microRNA function in osteoarthritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012,8(9):543-552. [29] KOLOMYTKIN OV, MARINO AA, WADDELL DD, et al. IL-1beta-induced production of metalloproteinases by synovial cells depends on gap junction conductance. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.2002;282(6):C1254-C1260. [30] KIM JH, JEON J, SHIN M, et al. Regulation of the catabolic cascade in osteoarthritis by the zinc-ZIP8-MTF1 axis.Cell. 2014;156(4):730-743. [31] GUPTA A, NIGER C, BUO AM, et al. Connexin43 enhances the expression of osteoarthritis-associated genes in synovial fibroblasts in culture.BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2014;15:425. [32] LI K, YAO J, SHI L, et al. Reciprocal regulation between proinflammatory cytokine-induced inducible NO synthase (iNOS) and connexin43 in bladder smooth muscle cells.J Biol Chem.2011;286(48):41552-41562. [33] CRONIN M, ANDERSON PN, COOK JE, et al. Blocking connexin43 expression reduces inflammation and improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2008;39(2):152-160. [34] DANESH-MEYER HV, HUANG R, NICHOLSON LF, et al. Connexin43 antisense oligodeoxynucleotide treatment down-regulates the inflammatory response in an in vitro interphase organotypic culture model of optic nerve ischaemia. J Clin Neurosci.2008;15(11):1253-1263. [35] TSUCHIDA S, ARAI Y, KISHIDA T, et al. Silencing the expression of connexin 43 decreases inflammation and joint destruction in experimental arthritis.J Orthop Res.2013;31(4):525-530. [36] HAACK K, COCKRELL AS, MA H, et al. Transactivator and structurally optimized inducible lentiviral vectors.Mol Ther. 2004;10(3):585-596. [37] MILONE MC, O'DOHERTY U. Clinical use of lentiviral vectors. Leukemia.2018;32(7):1529-1541. [38] ZHENG CX,WANG SM,BAI YH,et al.Lentiviral Vectors and Adeno-Associated Virus Vectors: Useful Tools for Gene Transfer in Pain Research.Anat Rec (Hoboken).2018;301(5): 825-836. [39] 景黎君,贾永林,鲁晶晶,等.MicroRNA-9-1慢病毒载体的构建及其对小鼠骨髓间质干细胞诱导分化为神经细胞的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2011,27(02):326-331. [40] 孟凡荣,陈琛,万海粟,等.慢病毒载体及其研究进展[J].中国肺癌杂志,2014,17(12):870-876. [41] 汤晗,聂建云,李文斌,等.慢病毒载体系统的发展及在肿瘤基因治疗中的应用[J].现代肿瘤医学,2017,25(10):1659-1662. |
| [1] | Peng Zhihao, Feng Zongquan, Zou Yonggen, Niu Guoqing, Wu Feng. Relationship of lower limb force line and the progression of lateral compartment arthritis after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with mobile bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1368-1374. |
| [2] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [3] | Liu Xiangxiang, Huang Yunmei, Chen Wenlie, Lin Ruhui, Lu Xiaodong, Li Zuanfang, Xu Yaye, Huang Meiya, Li Xihai. Ultrastructural changes of the white zone cells of the meniscus in a rat model of early osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1237-1242. |
| [4] | Liu Xin, Yan Feihua, Hong Kunhao. Delaying cartilage degeneration by regulating the expression of aquaporins in rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 668-673. |
| [5] | Ma Zetao, Zeng Hui, Wang Deli, Weng Jian, Feng Song. MicroRNA-138-5p regulates chondrocyte proliferation and autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 674-678. |
| [6] | Xie Chongxin, Zhang Lei. Comparison of knee degeneration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with or without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 735-740. |
| [7] | Cao Xuhan, Bai Zixing, Sun Chengyi, Yang Yanjun, Sun Weidong. Mechanism of “Ruxiang-Moyao” herbal pair in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 746-753. |
| [8] | Li Yonghua, Feng Qiang, Tan Renting, Huang Shifu, Qiu Jinlong, Yin Heng. Molecular mechanism of Eucommia ulmoides active ingredients treating synovitis of knee osteoarthritis: an analysis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 765-771. |
| [9] | Song Shan, Hu Fangyuan, Qiao Jun, Wang Jia, Zhang Shengxiao, Li Xiaofeng. An insight into biomarkers of osteoarthritis synovium based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 785-790. |
| [10] | Deng Zhenhan, Huang Yong, Xiao Lulu, Chen Yulin, Zhu Weimin, Lu Wei, Wang Daping. Role and application of bone morphogenetic proteins in articular cartilage regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 798-806. |
| [11] | Zheng Li, Li Dadi, Hu Weifan, Tang Jinlong, Zhao Fengchao. Risk assessment of contralateral knee arthroplasty after unilateral total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 374-379. |
| [12] | Lü Jiaxing, Bai Leipeng, Yang Zhaoxin, Miao Yuesong, Jin Yu, Li Zhehong, Sun Guangpu, Xu Ying, Zhang Qingzhu. Evaluation of internal fixation with proximal femoral nail antirotation in elderly knee osteoarthritis patients with femoral intertrochanteric fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 391-396. |
| [13] | Luo Anyu, Liu Hanlin, Xie Xiaofei, Huang Chen. Effect of antioxidant mixture on structural degeneration of an osteoarthritis rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3625-3629. |
| [14] | Gao Kun, Chen Dayu, Zhang Yong, Liu Weidong, Sun Shufen, Lai Wenqiang, Ma Dujun, Wu Yihong, Lin Zhanpeng, Jiang Yinglu, Yu Weiji. Achyranthes bidentata alcohol extract inhibits extracellular matrix degradation of the cartilage by regulating synovial fibroblast exosomes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3636-3640. |
| [15] | Liu Jinfu, Zeng Ping, Nong Jiao, Fan Siqi, Feng Chengqin, Huang Jiaxing. Integrative analysis of biomarkers and therapeutic targets in synovium of patients with osteoarthritis by multiple microarrays [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3690-3696. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||