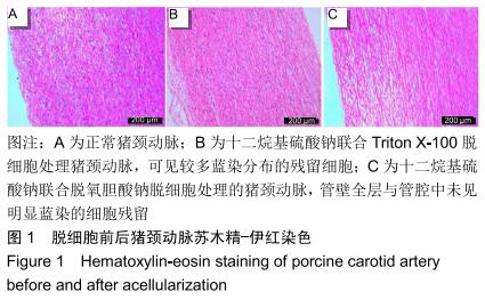
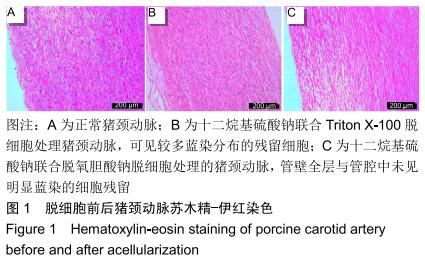
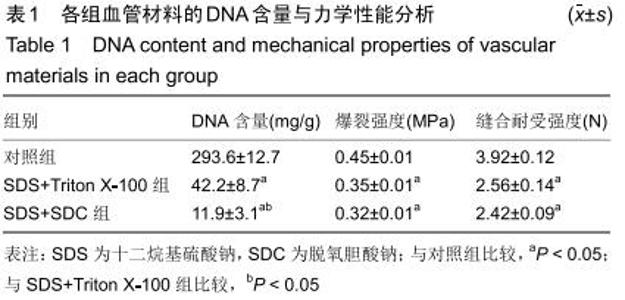
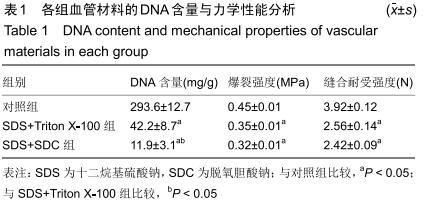
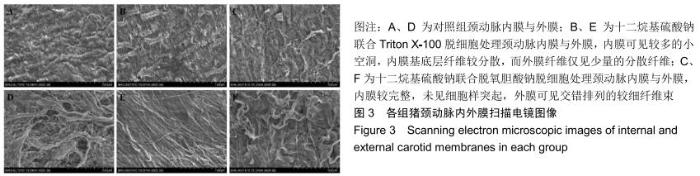
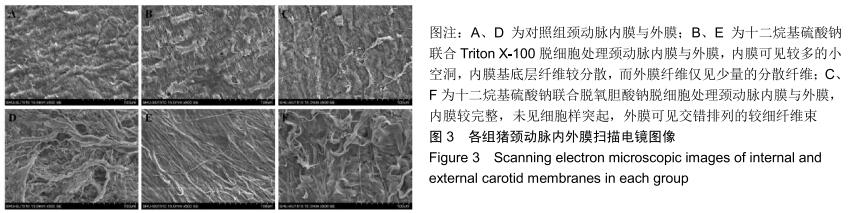
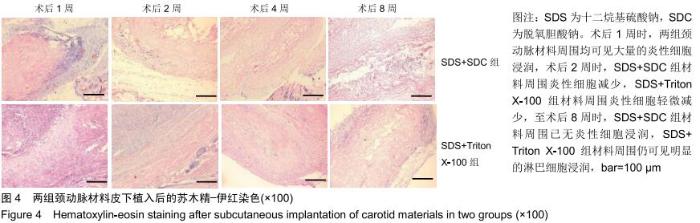
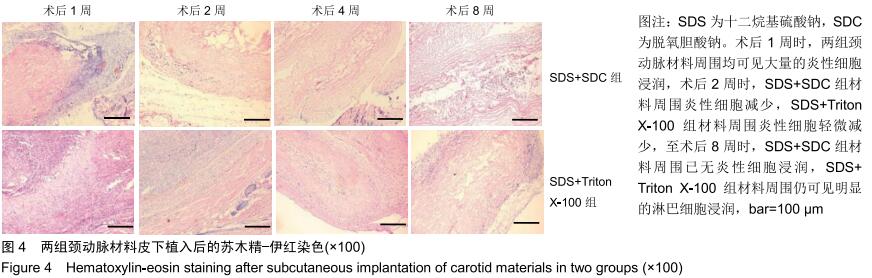
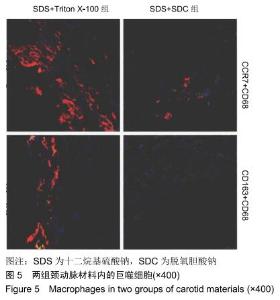
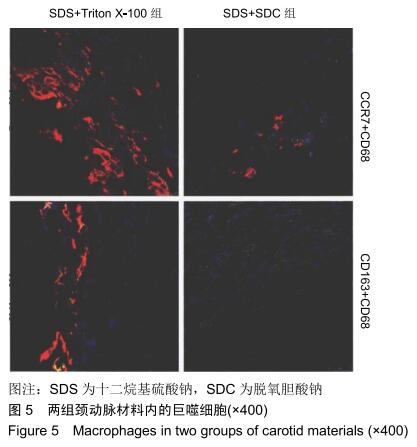
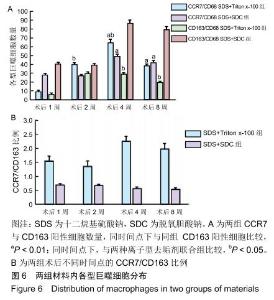
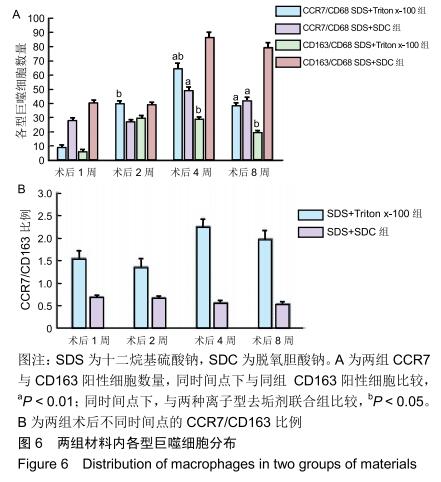
|
[1] 李冈栉,赵瑾洁,马蓉,等.下肢动脉旁路移植术与腔内血管成形术治疗老年人下肢动脉硬化闭塞症的安全性和有效性探讨[J].中国普通外科杂志,2019,28(6):756-761.
[2] WANG B, LIU W, HUO Y, et al. Application of femoral-femoral artery bypass grafting combined with transverse tibial bone transporting for lower extremity arteriosclerosis obliterans or combined with diabetic foot.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.2018;32(12):1576-1580.
[3] DESAI M, SEIFALIAN AM, HAMILTON G. Role of prosthetic conduits in coronary artery bypass grafting.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg.2011;40(2):394-398.
[4] BRACALE UM, GIRIBONO AM, SPINELLI D, et al. Long-term Results of Endovascular Treatment of TASC C and D Aortoiliac Occlusive Disease with Expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene Stent Graft.Ann Vasc Surg. 2019;56: 254-260.
[5] LU S, SUN X, ZHANG P, et al. Local hemodynamic disturbance accelerates early thrombosis of small-caliber expanded polytetrafluoroethylene grafts.Perfusion.2013;28(5): 440-448.
[6] DAI L, HE Z, JIANG Y, et al. One-step strategy for cartilage repair using acellular bone matrix scaffold based in situ tissue engineering technique in a preclinical minipig model.Am J Transl Res.2019;11(10):6650-6659.
[7] WANG F, SONG Q, DU L, et al. Development and Characterization of an Acellular Porcine Small Intestine Submucosa Scaffold for Use in Corneal Epithelium Tissue Engineering.Curr Eye Res.2020;45(2):134-143.
[8] AKBARZADEH A, KIANMANESH M, FENDERESKI K, et al. Decellularised whole ovine testis as a potential bio-scaffold for tissue engineering.Reprod Fertil Dev.2019. doi: 10.1071/RD19070. [Epub ahead of print]
[9] 邵营宽,严夏霖,饶志恒,等.大鼠胰腺去细胞天然支架生物相容性的鉴定[J].解剖学报,2014,45(4):561-568
[10] LAWSON JH, GLICKMAN MH, ILZECKI M, et al. Bioengineered human acellular vessels for dialysis access in patients with end-stage renal disease: two phase 2 single-arm trials.Lancet. 2016;387(10032):2026-2034.
[11] 许洁,金冰慧,赵应征.大鼠子宫去细胞支架及其细胞外基质凝胶的制备[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2018,35(2):237-243.
[12] 梁远锋,文章,刘尚敏,等.CHAPS联合十二烷基硫酸钠的除垢剂动脉脱细胞支架材料制备[J].岭南心血管病杂志, 2018,24(4): 450-455
[13] 蒲磊,吴剑,孟明耀,等.不同脱细胞方案制备主动脉细胞外基质支架的比较研究[Z].2014:28,1413-1421.
[14] 蒲磊,潘兴纳,张静,等.新方法可获得更佳的组织工程小直径血管细胞外基质支架[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,22(6):855-862.
[15] VISHWAKARMA SK, LAKKIREDDY C, BARDIA A,et al. Engineering bio-mimetic humanized neurological constructs using acellularized scaffolds of cryopreserved meningeal tissues.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;102:34-44.
[16] JOSZKO K, GZIK-ZROSKA B, KAWLEWSKA E, et al. Evaluation of the impact of decellularization and sterilization on tensile strength transgenic porcinedermal dressings.Acta Bioeng Biomech. 2019;21(3):87-97.
[17] LIU W, ZHANG SN, HU ZQ, et al. Study of Recellularized Human Acellular Arterial Matrix Repairs Porcine Biliary Segmental Defects.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;16(6): 653-665.
[18] 赵宇,于淼,柏树令.脱细胞技术及其在组织工程中的应用研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2013,27(8):950-954
[19] HAN LW, XU G, GUO MY, et al. Comparison of SB-SDS and other decellularization methods for the acellular nerve graft: Biological evaluation and nerve repair in vitro and in vivo. Synapse. 2020;74(5):e22143.
[20] GILBERT T, SELLARO T, BADYLAK S. Decellularization of tissues and organs.Biomaterials.2006;27(19):3675-3683.
[21] KNIGHT RL, WILCOX HE, KOROSSIS SA, et al. The use of acellular matrices for the tissue engineering of cardiac valves.Proc Inst Mech Eng H.2008;222(1):129-143.
[22] 王心,程宏斌,李媛,等.灌注法制备大鼠全胰腺脱细胞基质支架的实验研究[J].中华普通外科杂志,2016,31(12):1034-1037
[23] FAULK DM, CARRUTHERS CA, WARNER HJ, et al. The effect of detergents on the basement membrane complex of a biologic scaffold material.Acta Biomater. 2014;10(1): 183-193.
[24] APER T, SCHMIDT A, DUCHROW M, et al. Autologous blood vessels engineered from peripheral blood sample.Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg.2007;33(1):33-39.
[25] HAHN MS, MCHALE MK, WANG E, et al. Physiologic pulsatile fl ow bioreactor conditioning of poly(ethylene glycol)-based tissue engineered vascular grafts.Ann Biomed Eng.2007;35(2):190-200.
[26] LEE SJ, LIU J, OH SH, et al. Development of a composite vascular scaffolding system that withstands physiological vascular conditions.Biomaterials.2008;29(19):2891-2898.
[27] KEANE TJ, LONDONO R, TURNER NJ, et al. Consequences of ineffective decellularization of biologic scaffolds on the host response.Biomaterials.2012;33(6):1771-1781.
[28] WANG Z, CUI Y, WANG J, et al. The effect of thick fibers and large pores of electrospun poly(epsilon-caprolactone) vascular grafts on macrophage polarization and arterial regeneration.Biomaterials.2014;35(22):5700-5710.
|