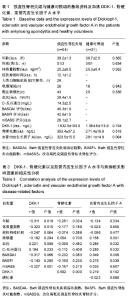
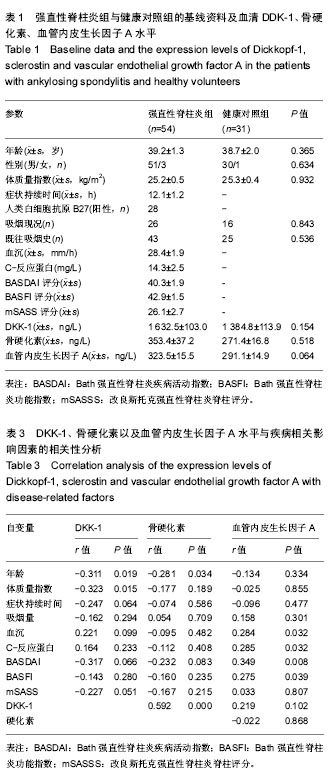
| [1] Solmaz D, Kozaci D, Sari I, et al. Oxidative stress and related factors in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Eur J Rheumatol. 2016;3(1):20-24.[2] Caglayan M, Sarac O, Kosekahya P, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of cornea in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Int Ophthalmol. 2016.[3] Nadkar MY, Warrier SR, Singh AO. Clinical profile of ankylosing spondylitis with special reference to hip involvement. J Assoc Physicians India. 2016;64(1):70.[4] Rudwaleit M, Landewe R, Sieper J. Ankylosing Spondylitis and Axial Spondyloarthritis. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(13): 1302-1303.[5] Yang C, Ding P, Wang Q, et al. Inhibition of Complement Retards Ankylosing Spondylitis Progression. Sci Rep. 2016;6:34643.[6] Ikegame M, Tabuchi Y, Furusawa Y, et al. Tensile stress stimulates the expression of osteogenic cytokines/growth factors and matricellular proteins in the mouse cranial suture at the site of osteoblast differentiation. Biomed Res. 2016; 37(2):117-126.[7] Karner CM, Esen E, Chen J, et al. Wnt Protein Signaling Reduces Nuclear Acetyl-CoA Levels to Suppress Gene Expression during Osteoblast Differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2016;291(25):13028-13039.[8] Ustun N, Tok F, Kalyoncu U, et al. Sclerostin and Dkk-1 in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Acta Reumatol Port. 2014;39(2):146-151.[9] Coskun BN, Oksuz MF, Ermurat S, et al. Neutrophil lymphocyte ratio can be a valuable marker in defining disease activity in patients who have started anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF) drugs for ankylosing spondylitis. Eur J Rheumatol. 2014;1(3):101-105.[10] Camirand A, Goltzman D, Gupta A, et al. The Role of Parathyroid Hormone-Related Protein (PTHrP) in Osteoblast Response to Microgravity: Mechanistic Implications for Osteoporosis Development. PLoS One. 2016;11(7):e160034.[11] Tayfur O, Kilic L, Karadag O, et al. Tuberculous bursitis of the greater trochanter mimicking ankylosing spondylitis. Eur J Rheumatol. 2015;2(1):31-32.[12] Sakellariou GT, Anastasilakis AD, Bisbinas I, et al. Circulating periostin levels in patients with AS: association with clinical and radiographic variables, inflammatory markers and molecules involved in bone formation. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015;54(5):908-914.[13] Mitulescu TC, Stavaru C, Voinea LM, et al. The role of Vitamin D in immuno-inflammatory responses in Ankylosing Spondylitis patients with and without Acute Anterior Uveitis. J Med Life. 2016;9(1):26-33.[14] Li DH, He CR, Liu FP, et al. Annexin A2, up-regulated by IL-6, promotes the ossification of ligament fibroblasts from ankylosing spondylitis patients. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;84:674-679.[15] Machado NP, Nogueira E, Oseki K, et al. Clinical characteristics and frequency of TLR4 polymorphisms in Brazilian patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Rev Bras Reumatol Engl Ed. 2016;56(5):432-440.[16] Hossan T, Nagarajan S, Baumgart SJ, et al. Histone Chaperone SSRP1 is Essential for Wnt Signaling Pathway Activity During Osteoblast Differentiation. Stem Cells. 2016; 34(5):1369-1376.[17] Fabiani C, Vitale A, Lopalco G, et al. Different roles of TNF inhibitors in acute anterior uveitis associated with ankylosing spondylitis: state of the art. Clin Rheumatol. 2016. |