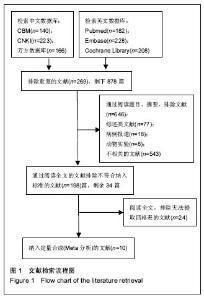
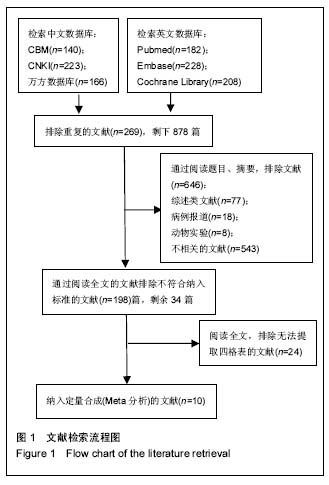
| [1] 卓超, 钟南山. 骨关节外科相关感染国外指南述评[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2015,9(1):128-132.[2] 张鑫, 李慧娟, 周亮, 等. 骨科术后感染临床治疗分析[J]. 实用药物与临床, 2016,19(1):58-61.[3] 杨松, 张耀亭. PCT与感染相互关系的研究进展[J]. 临床肺科杂志, 2013,18(9):1666-1668.[4] 杨明, 李新军, 麻雅婷, 等. PCT在不同病原体感染诊断中的研究进展[J]. 临床检验杂志(电子版), 2015,4(4):1003-1007.[5] Foushee JA, Hope NH, Grace EE. Applying biomarkers to clinical practice: a guide for utilizing procalcitonin assays. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012;67(11):2560-2569.[6] 刘蓉华, 林文源. PCT检测在感染性疾病中的应用进展[J]. 医学综述, 2014,20(22):4106-4108.[7] 王簕, 娄爱菊, 郭元, 等. 血清降钙素原鉴别成人化脓性关节炎与非化脓性关节炎的价值[J]. 广东医学, 2014,35(23):3646-3649.[8] Fottner A, Birkenmaier C, von Schulze Pellengahr C, et al. Can serum procalcitonin help to differentiate between septic and nonseptic arthritis? Arthroscopy. 2008;24(2): 229-233.[9] Hügle T, Schuetz P, Mueller B, et al. Serum procalcitonin for discrimination between septic and non-septic arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2008;26(3):453.[10] Maharajan K, Patro DK, Menon J, et al. Serum Procalcitonin is a sensitive and specific marker in the diagnosis of septic arthritis and acute osteomyelitis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2013;8:19.[11] Martinot M, Sordet C, Soubrier M, et al. Diagnostic value of serum and synovial procalcitonin in acute arthritis: a prospective study of 42 patients. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2005;23(3):303-310.[12] Oppegaard O, Skodvin B, Halse AK, et al. CD64 as a potential biomarker in septic arthritis. BMC Infect Dis. 2013;13(1):278.[13] Talebi-Taher M, Shirani F, Nikanjam N, et al. Septic versus inflammatory arthritis: discriminating the ability of serum inflammatory markers. Rheumatol Int. 2013;33(2):319-324.[14] Yuan K, Li WD, Qiang Y, et al. Comparison of procalcitonin and C-reactive protein for the diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection before revision total hip arthroplasty. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2015;16(2):146-150. [15] 张立营,沈伟,高鹏,等. 开放性骨折感染患者CD64指数白细胞介素-6和降钙素原测定的临床价值[J]. 山西医药杂志, 2016, 45(9):1100-1102.[16] 解光越, 高惠丽, 高雯, 等. 血清降钙素原和C反应蛋白在骨折术后感染中的诊断价值[J]. 中国实验诊断学, 2014,18(10): 1713-1714.[17] Paosong S, Narongroeknawin P, Pakchotanon R, et al. Serum procalcitonin as a diagnostic aid in patients with acute bacterial septic arthritis. Int J Rheum Dis. 2015;18(3):352-359.[18] 秦杰,单仁飞,叶一冰,等. 血清降钙素原与C-反应蛋白水平检测对患者早期感染的诊断[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2015,25(2): 271-272.[19] 郭红明. 降钙素原对早期脓毒症诊断价值的研究[D]. 河北医科大学, 2014.[20] 郑金菊, 张少强. PCT与CRP及白细胞计数对细菌感染性疾病诊断价值[J]. 青岛大学医学院学报, 2015,59(2):191-193.[21] 戴万亨,张永涛. 诊断学[M]. 北京:中国中医药出版社, 2012: 282-283.[22] 邵卫勇,陈淑丹,于小妹,等. 9024例血沉报告结果分析与探讨[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志, 2013,23(16):3288-3289.[23] 李自军. 联合检测血沉、C-反应蛋白及降钙素原在关节置换术后感染的临床意义[J]. 中外医疗, 2016,35(14):13-16.[24] 郭旗,郑稼,金毅,等. 血沉、C反应蛋白及ECT联合诊断假体周围感染临床研究[J]. 中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2010,24(3): 255-257.[25] 任丽娟, 郑文亮, 艾根伟. 降钙素原与真菌血流感染的相关性研究[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2011,21(24):5122-5124.[26] 杜翠霞. 血清降钙素原和C反应蛋白水平在感染性疾病中的诊断价值[J]. 实用心脑肺血管病杂志, 2012,20(8):1366-1367.[27] 闫立伟, 王文波, 李昭旭, 等. 血清降钙素原在诊断膝关节置换术后早期感染的意义[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志, 2015,14(4): 317-319.[28] Schuetz P, Christ-Crain M, Müller B. Procalcitonin and other biomarkers to improve assessment and antibiotic stewardship in infections--hope for hype? Swiss Med Wkly.2009;139 (23-24):318-326.[29] Limper M, de Kruif MD, Duits AJ, et al. The diagnostic role of procalcitonin and other biomarkers in discriminating infectious from non-infectious fever. J Infect. 2010;60(6):409-416.[30] 降钙素原急诊临床应用专家共识组. 降钙素原(PCT)急诊临床应用的专家共识[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志, 2012,21(9):944-951.[31] 汤瑾, 许静, 王坚镪, 等. 降钙素原联合C反应蛋白检测在血流感染早期临床诊断的应用[J]. 检验医学, 2013,28(8):662-665.[32] 李满江, 王智勇, 张志强. 血清降钙素原在诊断关节置换术后早期感染的临床意义[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2015,8(6): 546-548.[33] 黄金河,谭颖,温贺龙,等. 降钙素原监测指导膝关节滑膜炎合理使用抗生素的临床研究[J]. 中国医学工程, 2016,42(8):41-43.[34] 张俊, 徐志伟, 李克. 诊断性试验Meta分析的效应指标评价[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2013,13(7):890-895.[35] 罗杰, 冷卫东. 系统评价/Meta分析理论与实践[G]. 2013. |