Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (30): 4852-4859.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.30.017
Previous Articles Next Articles
Therapeutic effect of adipose derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium thermosensitive hydrogel on skin scald
- 1Department of Burn & Plastic Surgery, 2Cyromedicine Lab, Qilu Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan 250012, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2017-05-12Online:2017-10-28Published:2017-11-07 -
Contact:Li Dong, M.D., Associate professor, Cyromedicine Lab, Qilu Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan 250012, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Liu Pei, M.D., Attending physician, Department of Burn & Plastic Surgery, Qilu Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan 250012, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:CMA-LOREAL China Hair Grant, No. H2015121409
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Pei, Hu Zhen-sheng, Ma Ling, Wang Huan-huan, Li Dong.
share this article
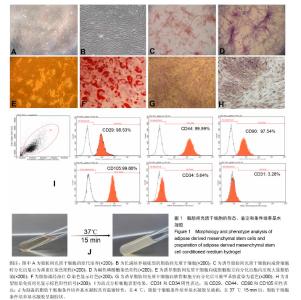
2.1 人脂肪间充质干细胞基本生物学特征 脂肪组织消化得到的单个核细胞培养2 d后就有少量成纤维状细胞贴壁(图1A),经过约10 d培养后这些细胞汇合成片,传代两三次后能获得长梭形的形态均一的细胞(图1B),平均倍增时间为55 h。 在适当的分化条件诱导下,所获得的贴壁细胞可以向成骨细胞、软骨细胞和脂肪细胞分化。向成骨细胞诱导分化后,细胞渐渐聚集生长,诱导14 d后大部分细胞出现钙化胞外基质,茜素红S染色阳性(图1C),碱性磷酸酶染色阳性(图1D);向脂肪细胞诱导分化1周后,细胞开始变得宽大,细胞内出现脂肪颗粒(图1E),14 d后> 75%的细胞内油红O染色阳性(图1F),软骨的成功诱导则以出现甲苯胺蓝胶原染色阳性(图1G)和Ⅱ型胶原免疫组化阳性结果(图1H)为准。 流式细胞仪检测结果显示,所获得的贴壁细胞CD31和CD34表达极低,CD29、CD44、CD90和CD105表达阳性(图1I)。这些结果证明所获得的贴壁细胞符合脂肪间充质干细胞的标准。"

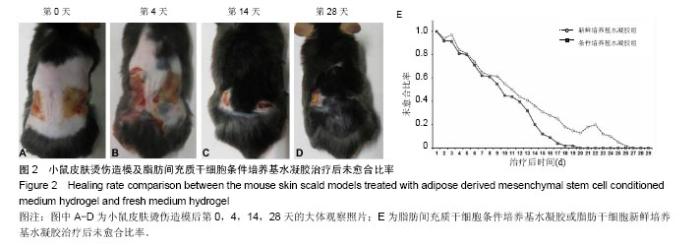
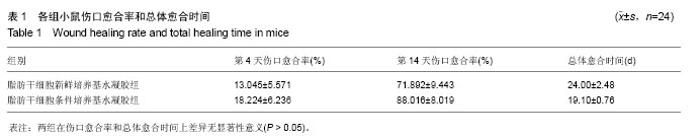
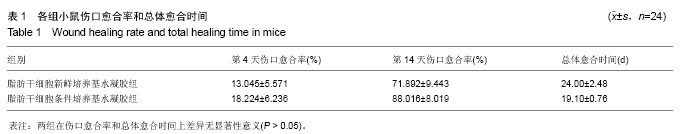
2.2 制备的脂肪干细胞条件培养基水凝胶的理化性质 在4-20 ℃条件下,脂肪干细胞条件培养基水凝胶为清亮透明的黏稠液体(图1J,pH=6.5),而当放入37 ℃ 15 min后,变为半固态凝胶状(图1J,pH=7.2)。表明脂肪干细胞条件培养基水凝胶可以在生理条件下凝胶化。 2.3 小鼠皮肤烫伤造模及病理学检测结果 构建C57BL/6小鼠烫伤模型后立即取小鼠烫伤区域皮肤行苏木精-伊红染色,结果示小鼠表皮、真皮及皮下脂肪和肌肉组织的结构完全破坏,符合严重的3度烫伤标准(图2A),各组造模小鼠的伤口面积均大致为3 cm2,在修复实验过程中,发现脂肪干细胞条件培养基水凝胶组创口(右侧)愈合时间明显短于脂肪干细胞新鲜培养基水凝胶组(左侧),且伤口恢复更为整洁,瘢痕增生较少(图2B-D)。第4,14天两组的伤口愈合速率和总体伤口愈合时间见表1,逐日统计结果见图2E,可见脂肪干细胞条件培养基水凝胶组的愈合快于脂肪干细胞新鲜培养基水凝胶组,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。"
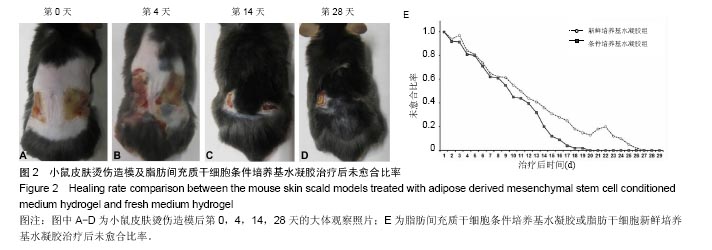
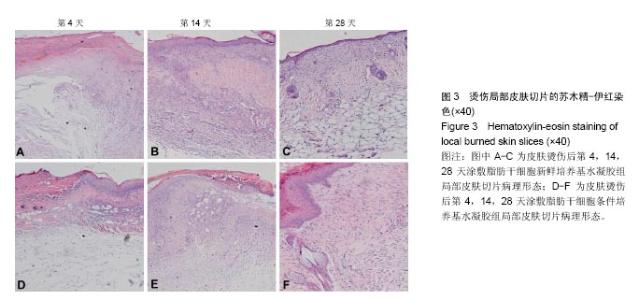
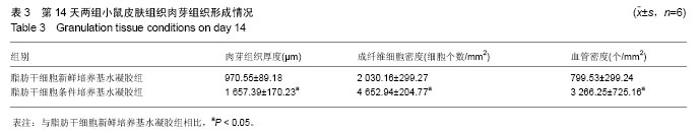
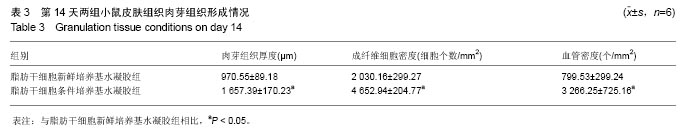
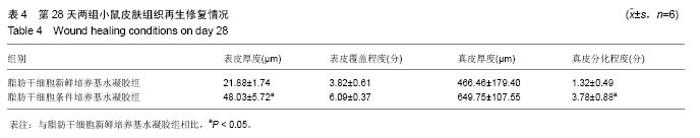
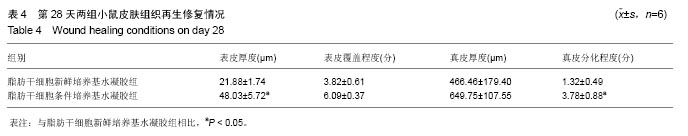
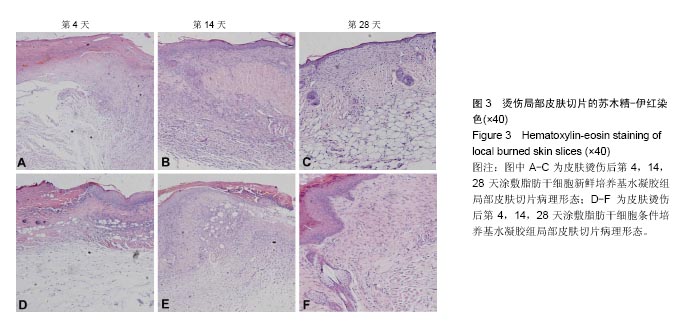
取局部皮肤组织行苏木精-伊红染色,与脂肪干细胞新鲜培养基水凝胶组相比,在相同时间点脂肪干细胞条件培养基水凝胶组创面表皮层和真皮层组织结构恢复得更好,组织完整,细胞排列更加有序(图3)。为了研究脂肪干细胞条件培养基水凝胶对急性期伤口炎症浸润和再上皮化的影响,测量第4天炎症浸润的相关指标,如炎症浸润深度和炎症浸润细胞密度,以及上皮舌的长度(图3A,D,表2);为了研究脂肪干细胞条件培养基水凝胶对烫伤愈合过程中血管新生和肉芽组织形成的影响,测量第14天相关参数,包括肉芽组织厚度、肉芽组织内成纤维细胞和新生血管的密度(图3B,E,表3);为了评估烫伤皮肤再生的总体结构修复情况,测量第28天有关损伤修复的指标,如表皮的厚度、真皮的厚度、表皮覆盖程度与真皮分化程度(图3C,F,表4)。"
| [1]Mandapalli PK, Labala S, Jose A, et al. Layer-by-Layer Thin Films for Co-Delivery of TGF-β siRNA and Epidermal Growth Factor to Improve Excisional Wound Healing. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech. 2017;18(3):809-820. [2]Nakamichi M, Akishima-Fukasawa Y, Fujisawa C, et al. Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor Induces Angiogenic Properties of Fibrocytes to Stimulate Vascular Formation during Wound Healing. Am J Pathol. 2016;186(12): 3203-3216.[3]Lord MS, Ellis AL, Farrugia BL, et al. Perlecan and vascular endothelial growth factor-encoding DNA-loaded chitosan scaffolds promote angiogenesis and wound healing. J Control Release. 2017;250:48-61.[4]丁韧,汤学明.创伤愈合的细胞生物学进展[J].创伤外科杂志, 2000,2(1):59.[5]王红梅,郭光华,曾小平,等.骨髓间充质干细胞靶向治疗大鼠烫伤创面愈合[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2010,32(1):69-72.[6]Lopez-Santalla M, Menta R, Mancheño-Corvo P, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells modulate experimental autoimmune arthritis by inducing an early regulatory innate cell signature. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2016;4(2):213-224.[7]De Jesus MM, Santiago JS, Trinidad CV, et al. Autologous Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells for the Treatment of Psoriasis Vulgaris and Psoriatic Arthritis: A Case Report. Cell Transplant. 2016;25(11):2063-2069.[8]Riester SM, Denbeigh JM, Lin Y, et al. Safety Studies for Use of Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells in a Rabbit Model for Osteoarthritis to Support a Phase I Clinical Trial. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(3):910-922.[9]Panés J, García-Olmo D, Van Assche G, et al. Expanded allogeneic adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (Cx601) for complex perianal fistulas in Crohn's disease: a phase 3 randomised, double-blind controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;388(10051):1281-1290.[10]Staff NP, Madigan NN, Morris J, et al. Safety of intrathecal autologous adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in patients with ALS. Neurology. 2016;87(21):2230-2234.[11]Chen YW, Scutaru TT, Ghetu N, et al. The Effects of Adipose-Derived Stem Cell-Differentiated Adipocytes on Skin Burn Wound Healing in Rats. J Burn Care Res. 2017; 38(1):1-10.[12]闫飞,王曌华,刘艳玲,等.脐带间充质干细胞促进烫伤创面愈合的作用机制[J].中国生物制品学杂志,2016,29(10): 1047-1051.[13]Fang F, Huang RL, Zheng Y, et al. Bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibit the proliferative and profibrotic phenotype of hypertrophic scar fibroblasts and keloid fibroblasts through paracrine signaling. J Dermatol Sci. 2016;83(2):95-105.[14]Qu Y, Zhang Q, Cai X, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-181-5p-modified adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells prevent liver fibrosis via autophagy activation. J Cell Mol Med. 2017 Apr 6. [Epub ahead of print][15]Hu L, Wang J, Zhou X, et al. Exosomes derived from human adipose mensenchymal stem cells accelerates cutaneous wound healing via optimizing the characteristics of fibroblasts. Sci Rep. 2016;6:32993.[16]Zhang J, La X, Fan L, et al. Immunosuppressive effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in rat burn models. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(5):5129-5136.[17]吴在德,吴肇汉. 外科学[M]. 7版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2008.[18]褚锋,刘建国,唐帆,等.小鼠Ⅲ度烧伤模型的复制及皮肤病理形态改变的动态观察[J].中国实验动物学报, 2009,17(3): 213-215.[19]Zhang K, Pei Y, Gan Z, et al. Local Administration of Thiamine Ameliorates Ongoing Pain in a Rat Model of Second-Degree Burn. J Burn Care Res. 2017 Feb 7. [Epub ahead of print][20]Lavertu M, Filion D, Buschmann MD. Heat-induced transfer of protons from chitosan to glycerol phosphate produces chitosan precipitation and gelation. Biomacromolecules. 2008;9(2):640-650.[21]Niranjan R, Koushik C, Saravanan S, et al. A novel injectable temperature-sensitive zinc doped chitosan/β-glycerophosphate hydrogel for bone tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2013;54:24-29.[22]Dhivya S, Saravanan S, Sastry TP, et al. Nanohydroxyapatite-reinforced chitosan composite hydrogel for bone tissue repair in vitro and in vivo. J Nanobiotechnology. 2015;13:40.[23]Cheng YH, Yang SH, Su WY, et al. Thermosensitive chitosan-gelatin-glycerol phosphate hydrogels as a cell carrier for nucleus pulposus regeneration: an in vitro study. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(2):695-703.[24]Kiyozumi T, Kanatani Y, Ishihara M, et al. Medium (DMEM/F12)-containing chitosan hydrogel as adhesive and dressing in autologous skin grafts and accelerator in the healing process. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2006;79(1):129-136.[25]Kiyozumi T, Kanatani Y, Ishihara M, et al. The effect of chitosan hydrogel containing DMEM/F12 medium on full-thickness skin defects after deep dermal burn. Burns. 2007;33(5):642-648.[26]Hu MS, Maan ZN, Wu JC, et al. Tissue engineering and regenerative repair in wound healing. Ann Biomed Eng. 2014;42(7):1494-1507.[27]Ud-Din S, Volk SW, Bayat A. Regenerative healing, scar-free healing and scar formation across the species: current concepts and future perspectives. Exp Dermatol. 2014;23(9):615-619.[28]Dahiya P. Burns as a model of SIRS. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009;14:4962-4967.[29]Silva L, Garcia L, Oliveira B, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome in burn patients: incidence and risk factor analysis. Ann Burns Fire Disasters. 2016;29(3): 178-182.[30]Kim A, Lang T, Xue M, et al. The Role of Th-17 Cells and γδ T-Cells in Modulating the Systemic Inflammatory Response to Severe Burn Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(4): E758.[31]Cao F, Liu T, Xu Y, et al. Culture and properties of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells: characteristics in vitro and immunosuppression in vivo. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(7):7694-7709.[32]Xishan Z, Baoxin H, Xinna Z, et al. Comparison of the effects of human adipose and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on T lymphocytes. Cell Biol Int. 2013;37(1): 11-18.[33]Maria AT, Maumus M, Le Quellec A, et al. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Autoimmune Disorders: State of the Art and Perspectives for Systemic Sclerosis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017;52(2):234-259.[34]Shalaby SM, Sabbah NA, Saber T, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells modulate the immune response in chronic experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis model. IUBMB Life. 2016;68(2):106-115. [35]Manferdini C, Maumus M, Gabusi E, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells exert antiinflammatory effects on chondrocytes and synoviocytes from osteoarthritis patients through prostaglandin E2. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(5): 1271-1281.[36]Liu S, Yuan M, Hou K, et al. Immune characterization of mesenchymal stem cells in human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly and derived cartilage cells. Cell Immunol. 2012;278(1-2): 35-44.[37]Soleymaninejadian E, Pramanik K, Samadian E. Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells: cytokines and factors. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2012;67(1): 1-8.[38]Masson F. Skin hydration and hyaluronic acid. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2010;137 Suppl 1:S23-25.[39]Deitch EA, Gelder F, McDonald JC. Prognostic significance of abnormal neutrophil chemotaxis after thermal injury. J Trauma. 1982;22(3):199-204.[40]Hacker S, Mittermayr R, Nickl S, et al. Paracrine Factors from Irradiated Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Improve Skin Regeneration and Angiogenesis in a Porcine Burn Model. Sci Rep. 2016;6:25168.[41]Ong HT, Redmond SL, Marano RJ, et al. Paracrine Activity from Adipose-Derived Stem Cells on In Vitro Wound Healing in Human Tympanic Membrane Keratinocytes. Stem Cells Dev. 2017;26(6):405-418.[42]Zhong Z, Gu H, Peng J, et al. GDNF secreted from adipose-derived stem cells stimulates VEGF-independent angiogenesis. Oncotarget. 2016;7(24):36829-36841. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [3] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [4] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [5] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [6] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [7] | Zhou Ying, Zhang Huan, Liao Song, Hu Fanqi, Yi Jing, Liu Yubin, Jin Jide. Immunomodulatory effects of deferoxamine and interferon gamma on human dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1012-1019. |
| [8] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [9] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [10] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [11] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [12] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [13] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [14] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [15] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||