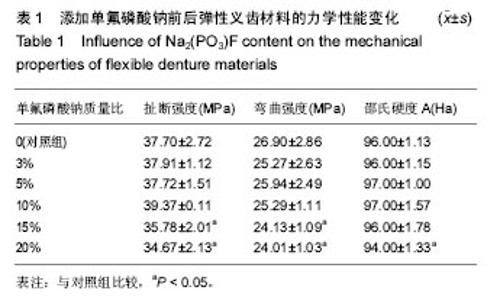
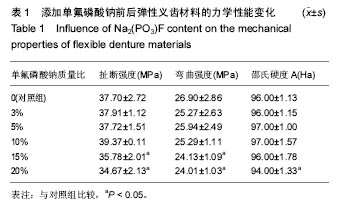
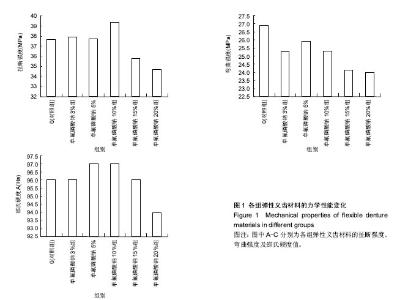
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (30): 4805-4810.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.30.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
A comparative study on the mechanical properties of flexible denture materials containing different fluoride concentrations
- 1The Second Affiliated Hospital of Guilin Medical University, Guilin 541001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2College of Materials Science and Engineering, Guilin University of Technology, Guilin 541004, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 3Guilin Stomatological Hospital, Guilin 541004, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2017-09-07Online:2017-10-28Published:2017-11-07 -
Contact:Tang Zhen-yu, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Guilin Medical University, Guilin 541001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Tang Zhen-yu, Master, Master’s supervisor, Chief physician, Professor, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Guilin Medical University, Guilin 541001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Research and Development Plan of Guangxi, No. 14124004-1-10; the Science and Technology Research Projects of Guangxi, No. 20140120-8-1, 2016012709
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tang Zhen-yu, Zhang Zhe, Zhang Wei-yi.
share this article
| [1]胡征,罗志红.3种义齿基托材料抛光后表面粗糙度的比较研究[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2014,23(3)):151-153.[2]Karakis D,Akay C,Oncul B,et al.Effectiveness of disinfectants on the adherence of Candida albicans to denture base resins with different surface textures.J Oral Sci.2016;58(3):431-437.[3]Mirizadeh A,Atai M,Ebrahimi S.Fabrication of denture base materials with antimicrobial properties. J Prosthet Dent. 2017; 26(3):35.[4]Shah J,Bulbule N,Kulkarni S,et al.Comparative evaluation of sorption, solubility and microhardness of heat cure polymethylmethacrylate denture base resin & flexible denture base resin.J Clin Diagn Res.2014;8(8):ZF01-04.[5]Hill EE,Rubel B,Smith JB,et al.Flexible removable partial dentures: a basic overview.Gen Dent. 2014;62(2):32-36.[6]赵献银.弹性义齿对基牙牙周牙体组织健康影响的研究[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2011,12(2):100.[7]胡征,罗志红.3 种义齿基托材料抛光后表面粗糙度的比较研究[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2014,23(3):151-153.[8]徐晶,张翔,陈小冬,等.不同磨光方法对弹性义齿基托表面粗糙度影响的实验研究[J].口腔医学研究,2012,28(7):689-693.[9]崔嘉玺,谭力芯,熊宇,等.应力中断式附着体义齿修复下颌双侧游离端缺失的生物力学分析[J].中国美容医学,2017,26(3):25-28.[10]孙静华,李仪红,侯本祥.龋病和牙周病主要致病菌分布的影响因素[J].北京口腔医学,2017,25(3):156-165.[11]李雅冬,李奕,彭方毅,等.重庆市老年人口腔健康现状及影响因素分析[J].重庆医学2016,45(31):4399-4401.[12]Bataineh M,Malinowski M,Duggal MS,et al.Comparison of the Newer Preventive Therapies on Remineralisation of Enamel in vitro.J Dent.2017.pii: S0300-5712(17)30209-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2017.08.013. [Epub ahead of print][13]Sivapriya E,Sridevi K,Periasamy R,et al.Remineralization ability of sodium fluoride on the microhardness of enamel, dentin, and dentinoenamel junction: An <i>in vitro</i> study. J Conserv Dent. 2017;20(2):100-104.[14]Muñoz-Millán P,Zaror C,Espinoza-Espinoza G,et al. Effectiveness of fluoride varnish in preventing early childhood caries in rural areas without access to fluoridated drinking water: A randomized control trial.Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2017.doi: 10.1111/cdoe.12330. [Epub ahead of print] [15]Aslanimehr M,Rezvani S,Mahmoudi A,et al.Comparison of Candida Albicans Adherence to Conventional Acrylic Denture Base Materials and Injection Molding Acrylic Materials.J Dent (Shiraz). 2017;18(1):61-64.[16]Rodríguez Acosta EJ,da Silva PM,Jacobina M,et al.Candida albicans adherence to denture base material: chemical disinfection and the effect of acquired salivary pellicle formation.J Prosthodont.2015;24(3):200-206.[17]Pignatelli I,Kumar A,Shah K,et al.Vertical scanning interferometry: A new method to quantify re-/de-mineralization dynamics of dental enamel.Dent Mater.2016;32(10):e251-261[18]Tiveron AR,Delbem AC,Gaban G,et al.In vitro enamel remineralization capacity of composite resins containing sodium trimetaphosphate and fluoride.Clin Oral Investig. 2015; 19(8):1899-1904.[19]Braun PA,Widmer-Racich K,Sevick C,et al.Effectiveness on Early Childhood Caries of an Oral Health Promotion Program for Medical Providers.Am J Public Health. 2017;107(S1): S97-S103.[20]Parkinson CR,Siddiqi M,Mason S,et al.In Situ Study to Confirm the Anticaries Potential of a Sodium Monofluorophosphate Dentifrice Containing Calcium Sodium Phosphosilicate.J Clin Dent. 2017;28(2):27-31.[21]Young S,Sufi F,Siddiqi M,et al.A Randomized Non-Inferiority Clinical Study to Evaluate the Efficacy of Two Dentifrices for Dentin Hypersensitivity.J Clin Dent.2016;27(4):97-104.[22]Parkinson CR,Siddiqi M,Mason S,et al.Anticaries Potential of a Sodium Monofluorophosphate Dentifrice Containing Calcium Sodium Phosphosilicate: Exploratory in situ Randomized Trial.Caries Res. 2017;51(2):170-178.[23]O'Mullane DM,Baez RJ,Jones S,et al.Fluoride and Oral Health.Community Dent Health. 2016;33(2):69-99.[24]Guissouma W,Hakami O,Al-Rajab AJ,et al.Risk assessment of fluoride exposure in drinking water of Tunisia. Chemosphere. 2017;177:102-108.[25]Takahashi T,Gonda T,Mizuno Y,et al.Reinforcement in removable prosthodontics: a literature review. J Oral Rehabil. 2017;44(2):133-143[26]Saisadan D,Manimaran P,Meenapriya PK.In vitro comparative evaluation of mechanical properties of temporary restorative materials used in fixed partial denture.J Pharm Bioallied Sci.2016;8(S 1):S105-S109.[27]Kapoor S,Prabhu N,Balakrishnan D.Comparison of the effect of different surface treatments on the bond strength of different cements with nickel chromium metal alloy: An in vitro study.J Clin Exp Dent. 2017;9(7):e912-e918.[28]Stawarczyk B,Silla M,Roos M,et al.Bonding Behaviour of Polyetherketoneketone to Methylmethacrylate- and Dimethacrylate-based Polymers.J Adhes Dent. 2017;8(28): 1-8.[29]Dias ARC,Barceleiro MO,Dias KRHC,et al.Influence of custom adaptation on the characteristics of fiber posts.Gen Dent.2017;65(5):e17-e22.[30]Sousa-Lima RX,Silva L,Chaves L,et al.Extensive Assessment of the Physical,Mechanical, and Adhesion Behavior of a Low-viscosity Bulk Fill Composite and a Traditional Resin Composite in Tooth Cavities.Oper Dent. 2017;42(5): E159-E166.[31]Tanimoto H,Akiba N,Nakamura T,et al.An objective estimation of the removability of three home reliners.Dent Mater J. 2017;36(3):309-318.[32]Mutluay MM,Tezvergil-Mutluay A.The influence of cyclic stress on surface properties of soft liners. Odontology. 2017;105(2):214-221.[33]Urban VM,Lima TF,Bueno MG,et al.Effect of the addition of antimicrobial agents on Shore A hardness and roughness of soft lining materials.J Prosthodont.2015;24(3):207-214.[34]唐震宇,张伟一,王海,等.含氟弹性义齿材料耐老化性能的研究[J].口腔医学研究,2013,29(4):305-307.[35]Archadian N,Kawano F,Ohguri T,et al.Flexural strength of rebased denture polymers.J Oral Rehabil. 2000;27(8): 690-696. [36]Sasaki H,Hamanaka I,Takahashi Y,et al.Effect of long-term water immersion or thermal shock on mechanical properties of high-impact acrylic denture base resins.Dent Mater J. 2016;35(2):204-209.[37]Sekinishi T,Inukai S,Murakami N,et al.Influence of denture tooth thickness on fracture mode of thin acrylic resin bases: An experimental and finite element analysis.J Prosthet Dent. 2015;114(1):122-129.[38]Kawaguchi T,Lassila LV,Sasaki H,et al.Effect of heat treatment of polymethyl methacrylate powder on mechanical properties of denturebase resin.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2014;39:73-78.[39]Hamanaka I,Iwamoto M,Lassila L,et al.Influence of water sorption on mechanical properties of injection-molded thermoplastic denturebase resins.Acta Odontol Scand. 2014;72(8):859-865.[40]Kaplan P. Flexible partial denture variations. The use of circumferential, combination, and continuous clasp designs. Dent Today. 2012;31(10):138-141.[41]Singh JP, Dhiman RK, Bedi RP, et al. Flexible denture base material: A viable alternative to conventional acrylic denture base material. Contemp Clin Dent. 2011;2(4):313-317.[42]Polyzois G, Lagouvardos P, Kranjcic J, et al. Flexible Removable Partial Denture Prosthesis: A Survey of Dentists' Attitudes and Knowledge in Greece and Croatia. Acta Stomatol Croat. 2015;49(4):316-324.[43]Shah VR, Shah DN, Chauhan CJ, et al. Evaluation of flexural strength and color stability of different denture base materials includingflexible material after using different denture cleansers. J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2015;15(4):367-373. [44]Takahashi T, Gonda T, Mizuno Y, et al. Reinforcement in removable prosthodontics: a literature review. J Oral Rehabil. 2017;44(2):133-143.[45]Hill EE, Rubel B, Smith JB. Flexible removable partial dentures: a basic overview. Gen Dent. 2014;62(2):32-36.[46]Iwata Y. Assessment of clasp design and flexural properties of acrylic denture base materials for use in non-metal clasp dentures. J Prosthodont Res. 2016;60(2):114-122.[47]Zhou Z,Hu YD,Sui QS,et al.Application of valplast dentures in the temporary restoration of single missing anterior tooth.Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2011;33(3): 334-336. [48]Falland-Cheung L,Waddell JN,Chun Li K,et al.Investigation of the elastic modulus, tensile and flexural strength of five skull simulant materials for impact testing of a forensic skin/skull/brain model.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2017;68: 303-307. [49]Sasaki H,Hamanaka I,Takahashi Y,et al.Effect of long-term water immersion or thermal shock on mechanical properties of high-impact acrylic denture base resins.Dent Mater J. 2016;35(2):204-209. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [3] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [4] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [5] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [6] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [7] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [8] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [9] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [10] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [11] | Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi. Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| [12] | Guan Jian, Jia Yanfei, Zhang Baoxin , Zhao Guozhong. Application of 4D bioprinting in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 446-455. |
| [13] | Huang Bo, Chen Mingxue, Peng Liqing, Luo Xujiang, Li Huo, Wang Hao, Tian Qinyu, Lu Xiaobo, Liu Shuyun, Guo Quanyi . Fabrication and biocompatibility of injectable gelatin-methacryloyl/cartilage-derived matrix particles composite hydrogel scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2600-2606. |
| [14] | Liu Jiali, Suo Hairui, Yang Han, Wang Ling, Xu Mingen. Influence of lay-down angles on mechanical properties of three-dimensional printed polycaprolactone scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2612-2617. |
| [15] | Li Xuan, Sun Yimin, Li Longbiao, Wang Zhenming, Yang Jing, Wang Chenglin, Ye Ling. Manufacturing of nano-modified polycaprolactone microspheres and its biological effects in dental pulp cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1530-1536. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||