Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (28): 4585-4592.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.28.025
Effectiveness of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for frozen shoulder: a Meta-analysis
Zhu Chang-e1, Wei Rong1, Zhang Sai-ji1, Chen Wen-hua2, Yu Bo2
- 1Department of Anesthesia, Children’s Hospital of Shanghai, Shanghai 200062, China; 2Department of Rehabilitation, Shanghai General Hospital, Shanghai 200080, China
-
Revised:2017-04-29Online:2017-10-08Published:2017-11-10 -
Contact:Chen Wen-hua, M.D., Professor, Department of Rehabilitation, Shanghai General Hospital, Shanghai 200080, China -
About author:Zhu Chang-e, Master, Physician, Department of Anesthesia, Children’s Hospital of Shanghai, Shanghai 200062, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhu Chang-e, Wei Rong, Zhang Sai-ji, Chen Wen-hua, Yu Bo. Effectiveness of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for frozen shoulder: a Meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(28): 4585-4592.
share this article

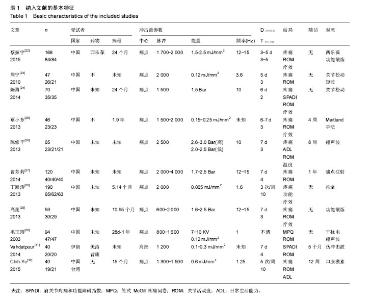
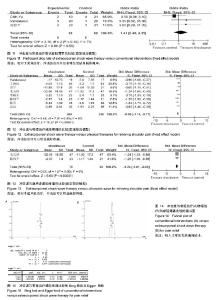
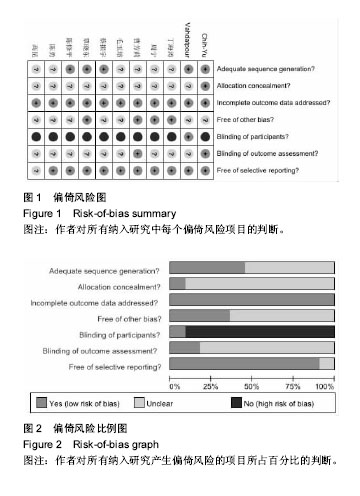
2.3 纳入研究的方法学质量评价 采用Cochrane协作网中RCT的偏倚风险评价标准进行方法学质量评价[18],共有11个RCT被进行质量评价[22-32],所纳入的研究中,蔡振宇- 2015[22],陈修平-2013[26],Chih-Yu-2015[32],Vahdatpour- 2014[31],覃小东-2013[25]详细描述了随机序列产生的方法,作者判断为“是”,其他研究只提及随机,未描述随机的方法,作者判断为“不清楚”。只有Vahdatpour-2014[31]的对照组为伪组,可以做到受试盲法,所以判断为“是”,其他研究者对照组为推拿、局部封闭、超声波、短波等,作者认为无法做到受试者盲法,因此判断为“否”,结果见图1,2。"
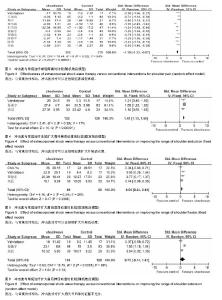
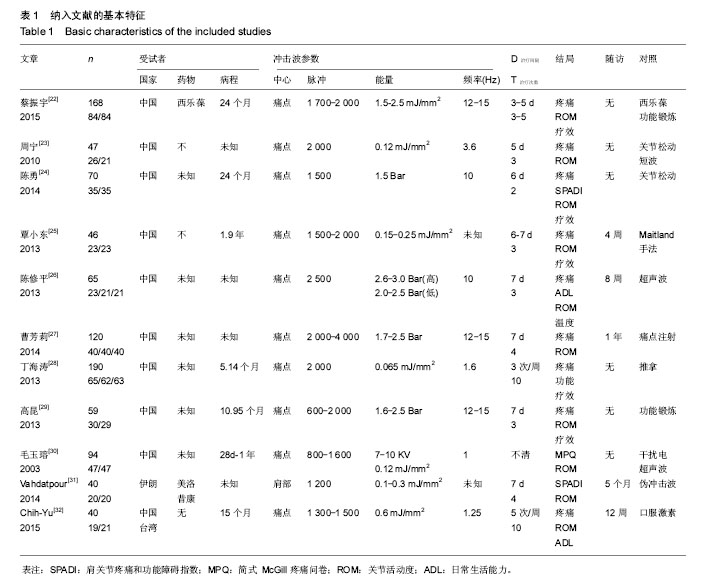
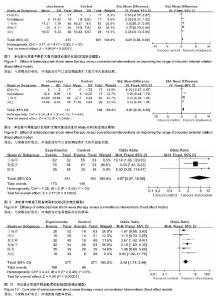
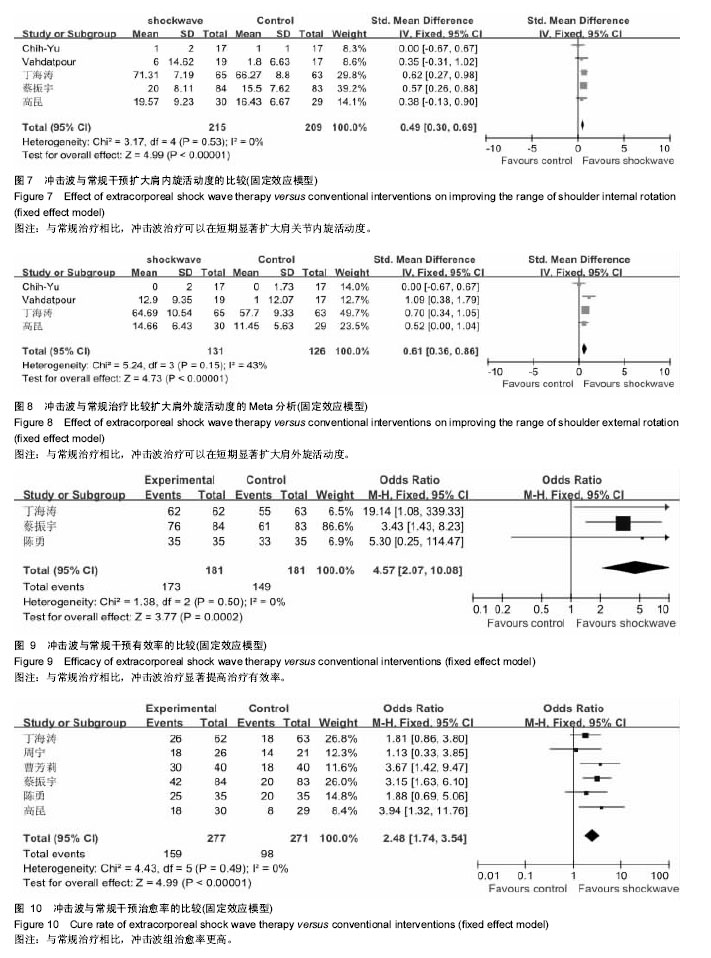
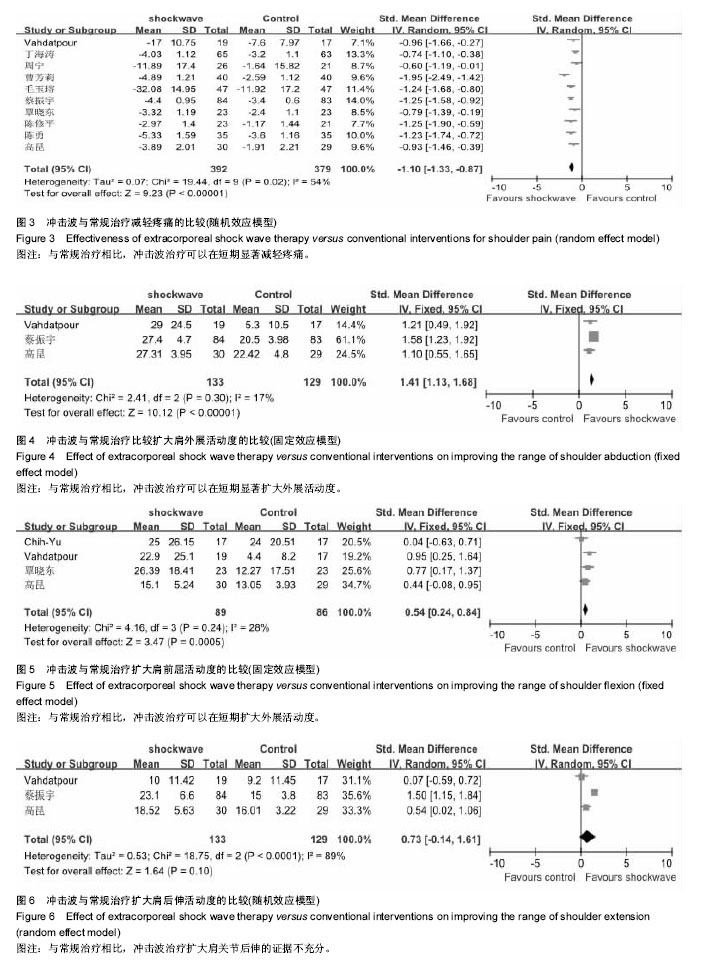
2.4 Meta分析结果 2.4.1 冲击波与常规治疗减轻疼痛症状的比较 作者提取到10个RCT中相关的数据[22-31],经χ2检验,各组研究间有统计学异质性(P=0.02,I2=54%),采用随机效应模型进行Meta分析。如图3结果显示,与常规治疗相比,包括药物治疗(口服西乐葆、痛点注射),物理疗法(物理因子治疗、关节松动、推拿、功能锻炼)以及安慰剂对照,冲击波治疗可以在短期减轻疼痛,组间差异有显著性意义[SMD= -1.1,95% CI为(-1.33至-0.87),P < 0.05]。 2.4.2 冲击波与常规治疗扩大肩关节活动度的比较 外展:作者提取到3个RCT中相关的数据[22,29,31],经χ2检验,各组研究间具有统计学同质性(I2=17%,P=0.3),采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析。如图4结果显示,与常规治疗相比,冲击波治疗可以在短期扩大外展活动度,组间差异有显著性意义[SMD=1.41,95% CI(1.13-1.68),P < 0.05]。 前屈:作者提取到4个RCT中相关的数据[25-32],经χ2检验,各组研究间具有统计学同质性(I2=28%,P=0.24),采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析。如图5结果显示,与常规治疗相比,冲击波治疗可以在短期扩大肩关节前屈活动度,组间差异有显著性意义[SMD=0.54,95%CI (0.24- 0.84),P < 0.05]。 后伸:作者提取到3个RCT中相关的数据[22,29,31],经χ2检验,各组研究间统计学异质性大(I2=89%,P < 0.000 1),采用随机效应模型进行Meta分析。如图6结果显示,与常规治疗相比,冲击波治疗扩大肩关节后伸的证据不充分[SMD=0.73,95%CI(-0.14-1.61),P=0.1]。 内旋:作者提取到5个RCT中相关的数据[22,28-29,31-32],经χ2检验,各组研究间具有统计学同质性(I2=0%,P=0.53),采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析。如图7结果显示,与常规治疗相比,冲击波治疗可以在短期扩大肩关节内旋活动度,组间差异有显著性意义[SMD=0.49,95%CI (0.3-0.69),P < 0.05]。 外旋:作者提取到4个RCT中相关的数据[28-29,31-32],经χ2检验,各组研究间具有统计学同质性(I2=43%,P= 0.15),采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析。如图8结果显示,与常规治疗相比,冲击波治疗可以在短期扩大肩外旋活动度,组间差异有显著性意义[SMD=0.61,95%CI(0.36- 0.86),P < 0.05]。 2.4.3 冲击波与常规干预有效率的比较 作者提取到3项RCT中相关的数据[22,24,28],经χ2检验,各组研究间具有统计学同质性(I2=0%,P=0.5),采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析。 如图9结果显示,与常规治疗相比,冲击波治疗提高治疗有效率,组间差异有显著性意义[SMD=4.57,95%CI (2.07-10.08),P < 0.05]。 2.4.4 冲击波与常规治愈率的比较 作者提取到6项RCT中相关的数据[22-24,27-29],经χ2检验,各组研究间具有统计学同质性(I2=0%,P=0.49),采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析。如图10结果显示,与常规治疗相比,冲击波组治愈率更高,组间比较差异有显著性意义[SMD=2.48,95%CI (1.74-3.54),P < 0.05]。 2.4.5 冲击波与常规治疗受试者脱落率的比较 3项研究中有受试者脱落,经χ2检验,各组研究间具有统计学同质性(I2=7%,P=0.34),采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析。如图11结果显示,组间脱落率差异无显著性意义[OR=1.41,95%CI (0.46-4.35),P=0.55]。相对于常规治疗,冲击波治疗并没有增加受试者脱落概率。 2.5 亚组分析 2.5.1 冲击波与物理治疗减轻疼痛的比较 由图4可以看出,将药物对照和非药物对照纳入后,各组研究间有统计学异质性(P=0.02,I2=54%),排除两项药物对照研究(口服西乐葆、痛点注射),各组研究间无统计学异质性(P=0.49,I2=0%),采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析。如图12所示,冲击波治疗可以明显减轻疼痛[SMD=-0.95,95%CI (-1.14至-0.07),P < 0.05]。 2.5.2 冲击波与超声波减轻疼痛的比较 两项研究中对照组为超声波治疗,研究间无统计学异质性(P=0.49, I,采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析。如图13所示,相对于超声波治疗,冲击波可以明显减轻疼痛[SMD= -1.24,95%CI(-1.61至-0.88),P < 0.05]。2=0%) 2.6 发表偏倚 漏斗图对侧分布,发表偏倚小(见图14)。Berg检验,P =0.474,Egger检验,P=0.976,纳入文章的发表偏倚较小(见图15)。"
| [1] 中华医学会.临床诊疗指南物理医学与康复分册[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2005:68-69.[2] 王玉龙,高晓平,张秀花,等. 康复功能评定学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2013:328-329.[3] 黄晓琳,燕铁斌,王宁华,等.康复医学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2013:215-216.[4] Padua R, Bondi R, Ceccarelli E, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for chronic calcifying tendinitis of the shoulder. J Orthop Traumatol.2002;2(3):147-150.[5] Gerdesmeyer L,Mittermayr R,Fuerst M,et al.Current evidence of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in chronic Achilles tendinopathy. Int J Surg.2015;24(Pt B): 154-159.[6] Huisstede BM, Gebremariam L,van der Sande R,et al.Evidence for effectiveness of Extracorporal Shock-Wave Therapy (ESWT) to treat calcific and non-calcific rotator cuff tendinosis--a systematic review. Man Ther, 2011;16(5): 419-433.[7] Harniman E, Carette S, Kennedy C, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for calcific and noncalcific tendonitis of the rotator cuff: a systematic review. J Hand Ther.2004;(2), 17: 132-151.[8] Schmitt J, Haake M, Tosch A, et al. Low-energy extracorporeal shock-wave treatment (ESWT) for tendinitis of the supraspinatus. A prospective, randomised study. J Bone Joint Surg Br.2001;83(6): 873-876.[9] Gross MW, Sattler A, Haake M, et al. The effectiveness of radiation treatment in comparison with extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) in supraspinatus tendon syndrome. Strahlenther Onkol.2002;178(6): 314-320.[10] Spacca G, Necozione S, Cacchio A. Radial shock wave therapy for lateral epicondylitis: a prospective randomised controlled single-blind study. Eura Medicophys.2005;41(1): 17-25.[11] Ilieva EM, Minchev RM, Petrova NS. Radial shock wave therapy in patients with lateral epicondylitis. Folia Med (Plovdiv).2012; 54(3): 35-41.[12] Reza Mafi, Sandip Hindocha, Wasim S Khan. Recent Surgical and Medical Advances in the Treatment of Dupuytren's Disease - A Systematic Review of the Literature.Open Orthop J.2012;6: 77-82.[13] Knobloch K, Vogt PM. High-energy focussed extracorporeal shockwave therapy reduces pain in plantar fibromatosis (Ledderhose's disease). BMC Res Notes. 2012;5: 542.[14] Alkhawashki HM. Shock wave therapy of fracture nonunion. Injury.2015;46: 2248-2252.[15] Bannuru RR,Flavin NE,Vaysbrot E,et al.High-energy extracorporeal shock-wave therapy for treating chronic calcific tendinitis of the shoulder: a systematic review. Ann Intern Med.2014;160(8): 542-549.[16] 杨克虎.系统评价指导手册[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2010: 149-163.[17] 刘鸣.系统评价、Meta-分析设计与实施方法[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2011.69-127.[18] Roach KE, Budiman-Mak E, Songsiridej N, et al. Development of a shoulder pain and disability index. Arthritis Care Res.1991;4(4):143-149.[19] 谭冠先.疼痛诊疗学[M] .北京:人民卫生出版社,2005: 7-9.[20] 国家中医药管理局.中医病证诊断疗效标准[M]. 南京:南京大学出版社,1994: 200.[21] 陈雯,阳芸.运动疗法结合推拿治疗对疼痛性肩关节挛缩症患者肩关节功能的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2012,34(1):76-77.[22] 蔡振宇,林山.体外冲击波治疗疼痛性肩关节挛缩症临床效果观察[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2015,7(3):157-161.[23] 周宁,邵彬,陈勇,等.体外冲击波与关节松动术加短波透热治疗疼痛性肩关节挛缩症的效果比较研究[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志, 2010,32(1):38-40.[24] 陈勇,彭轩,汤智伟,等.关节松动术结合体外冲击波治疗疼痛性肩关节挛缩症的疗效观察[J].中国康复,2014,29(3):192-194.[25] 覃小东,曹贤畅,符俏,等.放散状体外冲击波结合Maitland手法治疗疼痛性肩关节挛缩症的疗效观察[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志, 2013,35(7):571-572.[26] 陈修平,夏长所,杨志杰,等.放散式体外冲击波与超声波治疗疼痛性肩关节挛缩症的比较[J].中华实验外科杂志,2013,30(3):636-639.[27] 曹芳莉,郭晓丽,王伍超,等.体外冲击波联合痛点注射治疗疼痛性肩关节挛缩症的临床评价[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2014, 20(10): 722-724.[28] 丁海涛,唐学章,贾云芳,等.冲击波联合推拿治疗疼痛性肩关节挛缩症的临床疗效观察[J].中国康复医学杂志,2013,28(5):468-470.[29] 高昆,朱喜春,岳立辉,等.体外冲击波配合功能锻炼治疗疼痛性肩关节挛缩症的疗效观察[J].中国骨伤,2013,26(5):401-403.[30] 毛玉瑢,黄东锋,丁建新,等.体外冲击波疗法治疗肩关节周围炎的即时效果分析[J].中国临床康复,2003,7(23):3216-3217.[31] Vahdatpour B, Taheri P, Zade AZ, et al. Efficacy of extracorporeal shockwave therapy in frozen shoulder. Int J Prev Med.2014;5(7): 875-881.[32] Chen CY, Hu CC, Weng PW, et al. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy improves short-term functional outcomes of shoulder adhesive capsulitis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2014;23(12): 1843-1851. |
| [1] | Jing Jinpeng, Zhang Yue, Liu Xiaomin, Liu Yi. Traditional Chinese medicine injection for promoting blood circulation in prevention of deep vein thrombosis after orthopedic surgery: network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1467-1476. |
| [2] | Kan Houming, Fan Lijun, Chen Xuetai, Shen Wen. Application of platelet-rich plasma in neuropathic pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1286-1292. |
| [3] | Liu Gang, Ma Chao, Wang Le, Zeng Jie, Jiao Yong, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Hu Chuanyu, Xu Lin, Mu Xiaohong. Ankle-foot orthoses improve motor function of children with cerebral palsy: a Meta-analysis based on 12 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1299-1304. |
| [4] | Zhou Jianguo, Liu Shiwei, Yuan Changhong, Bi Shengrong, Yang Guoping, Hu Weiquan, Liu Hui, Qian Rui. Total knee arthroplasty with posterior cruciate ligament retaining prosthesis in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis with knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 892-897. |
| [5] | Lu Qinxue, Xu Ning, Yang Yinglan, Han Qianqian, Duanmu Xianyu, Guo Yuwei, Han Qing. Femoroacetabular impingement: strength trainings for nerve-muscle, peripheral muscle and core muscle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 786-791. |
| [6] | Liu Yiyi, Qiu Junqiang, Yi Longyan, Zhou Cailiang. Effect of resistance training on interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein in middle-age and elderly people: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 804-812. |
| [7] | Wang Nan, Qian Yuzhang, Xie Lin. Network Meta-analysis of different acupuncture methods for the treatment of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 813-820. |
| [8] | He Junjun, Huang Zeling, Hong Zhenqiang. Interventional effect of Yanghe Decoction on synovial inflammation in a rabbit model of early knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 694-699. |
| [9] | Wei Zhoudan, Li Wenjin, Zhu Li, Wang Yu, Zhao Jiaoyang, Chen Yanan, Guo Dong, Hao Min. Platelet-rich fibrin as a material for alveolar ridge preservation significantly reduces the resorption of alveolar bone height and width after tooth extraction: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 643-648. |
| [10] | Ou Liang, Kong Dezhong, Xu Daoqing, Ni Jing, Fu Xingqian, Huang Weichen. Comparative clinical efficacy of polymethyl methacrylate and self-solidifying calcium phosphate cement in vertebroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 649-656. |
| [11] | Cao Sheng, Kong Lingwei, Xu Kun, Sun Zhijie. Evaluation value of cervical sagittal plane sequence parameters on pain, cervical function and clinical efficacy in patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 419-424. |
| [12] | Yang Ruijia, Jiang Lingkai, Dong Zhengquan, Wang Yunfei, Ma Zhou, Cong Linlin, Guo Yanjing, Gao Yangyang, Li Pengcui. Open reduction and internal fixation versus circular external fixation for tibial plateau fractures: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 480-486. |
| [13] | Zhong Yuanming, He Bingkun, Wu Zhuotan, Wu Sixian, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng. Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of Jack kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 487-492. |
| [14] | Zhao Shuying, Guo Guangling, Liu Chenchen, Zhang Chao, Dong Sirui, Gong Qinqin, Ji Luwei. Stem cell transplantation in the treatment of premature ovarian failure: a meta-analysis based on 13 animal studies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 4084-4092. |
| [15] | Shi Yao, Han Shufeng, Yuan Yitong, Du Ruochen, Jing Zhijie, Zhao Bichun, Zhang Ruxin, Zhang Yujuan, Wang Chunfang. Efficacy and safety of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of spinal cord injury: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 4093-4100. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||