Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (28): 4577-4584.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.28.024
Previous Articles Next Articles
Scientific assessment of post-exercise oxidative stress and reasonable antioxidant supplement
Gao Zhao1, 2, Yang Xing-ping3, Zhang Yuan1, Lin Wen-tao4
- 1Institute of Tropical Medicine, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 2Guangdong Provincial Research Institute of Sport Science, Guangzhou 510663, Guangdong Province, China; 3the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China; 4Guangzhou Sport University, Guangzhou 510500, Guangdong Province, China
-
Revised:2017-04-23Online:2017-10-08Published:2017-11-10 -
Contact:Yang Xing-ping, Attending physician, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Gao Zhao, Master, Assistant researcher, Institute of Tropical Medicine, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; Guangdong Provincial Research Institute of Sport Science, Guangzhou 510663, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Sports Specific Research Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. GDSS2016155; the Medical Research Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. A2016600
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Gao Zhao, Yang Xing-ping, Zhang Yuan, Lin Wen-tao. Scientific assessment of post-exercise oxidative stress and reasonable antioxidant supplement[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(28): 4577-4584.
share this article
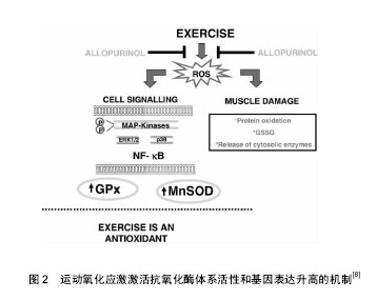
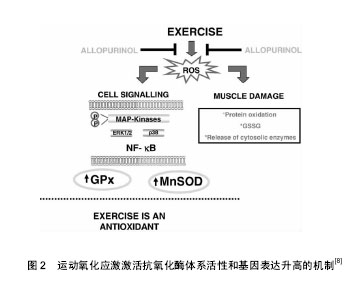
2.1 氧化应激与运动 氧化应激是指机体内产生的活性氧、活性氮等活性自由基超出机体抗氧化防御系统的清除能力,导致氧化系统及抗氧化系统的失衡引起机体的细胞结构和功能损伤[5]。人体在剧烈运动中会产生一系列化学性质活泼的含氧和含氮自由基及其衍生物、活性氧主要包括氧化氢(H2O2)、超氧自由基(O2•-)、羟自由基(•OH)及脂质过氧化自由基(LOO•)等;活性氮主要指NO与包括活性氧在内的化合物相互作用,衍生出的一氧化氮(•NO)、二氧化氮(•NO2)和过氧化亚硝酸盐 (•ONOO-)等具有高度氧化活性的自由基和硝基类化合物,而活性自由基在人体免疫应激[6]、基因转录、细胞信号传导(如IKK/NF-kB、CD40/CD40L)中均有重要介导作用[7],另外还在人体内氧化还原敏感蛋白激酶(如AMPK/Sirtl细胞信号通路通路诱导骨骼肌细胞凋亡)相关酶促反应的调控过程中发挥着重要作用,研究表明强度适中的规律运动可以提高机体的抗氧化损伤能力[8](见图2)。"
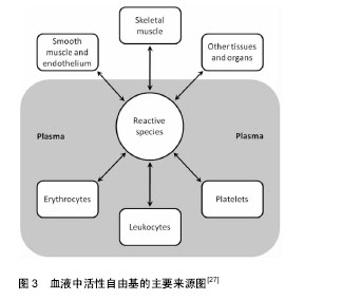
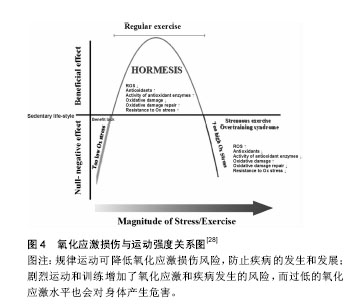
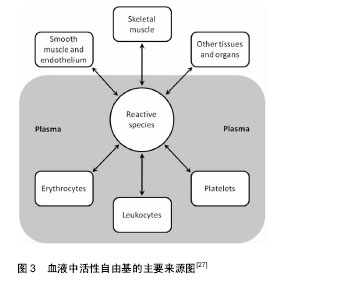
近期研究证实运动诱发产生的活性氧可能通过激活丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(p38MAPK)及蛋白激酶B(Akt/PKB)在内的氧化还原敏感性信号通路及下游的转录因子(如Nrf2、核因子kB等)[9],调节抗氧化酶基因等氧化还原敏感型靶基因的表达,诱导具有保护作用的蛋白质(如热休克蛋白)产生,使骨骼肌细胞产生运动预适应性变化,以抵抗更严重的氧化应激,进而清除应激原、保护组织细胞。 研究表明体内活性氧产生的引发因素主要包括:人内线粒体呼吸链氧化磷酸化过程中ComplexⅠ (NADH-辅酶Q还原酶)和ComplexⅢ (泛醌细胞色素C还原酶)的电子泄漏与氧结合生成超氧阴离子(活性氧主要形式)及单线态氧等,此外,包括铁离子(Ⅲ价)等金属离子的催化作用,以及病原体或者外源性药物的侵入都可以使得体内活性氧迅速产生。越来越多的研究表明哺乳动物线粒体中大多数O2•-是由ComplexⅠ生成的, O2•-最初发生在线粒体内膜(IMM)[10]的基质面。同时ComplexⅠ产生 O2•-能被Complex Ⅱ的底物琥珀酸所激发[11]。除ComplexⅠ之外,Complex Ⅲ也是生成O2•-的主要位置[12-13],特别当线粒体呼吸作用被抗霉素antimycin (complex Ⅲ的抑制剂)所抑制时,O2•-在complex Ⅲ产生于线粒体内膜(IMM)的内外两面[14]。泛醌(辅酶Q10)作为线粒体呼吸链中连接complex Ⅲ和ComplexⅠ,complex Ⅲ和complex Ⅱ的的脂溶性电子载体被认为是化物complex Ⅲ合成O2•-的主要调节者[15],而不稳定的泛半醌则与氧结合导致产生O2•- [16]。除线粒体外,内质网、过氧化物酶体(peroxisome)等体系也能产生部分活性氧。在正常生理情况下人体摄入的氧气有1%-2%在线粒体呼吸过程中转化为高反应活性的超氧游离基,参与活性氧的产生[17]。一个电子还原的氧分子生成了一个相对稳定的过度态中间体超氧负离子(O2•-),超氧负离子(O2•-)在超氧化物歧化酶(M-SOD) 的作用下进而被氧化为H2O2。H2O2和O2•- 在Haber-Weiss反应中相互作用,或者通过金属离子Fe2+ (或者Cu2+)催化的芬顿反应裂解生成羟自由基•OH[18],而研究表明尽管•OH的半衰期(约为10-9 s)极短,但由于是生物体内氧化性最活泼的自由基,对核酸、蛋白和脂类均可造成氧化损 伤[19]。Cadenas等[20]通过研究发现线粒体基质中O2•-稳定态浓度是细胞浆或细胞核的5-10倍。因此,线粒体可能是活性氧损伤的最早的靶点,而活性氧可损坏线粒体内大分子结构和细胞器功能,影响细胞活力甚至触发细胞凋亡。 Alessio等[21]比较了力竭性有氧运动(AE)及力竭性等长收缩运动后氧化应激反应,对12名受试者受试前后血液中硫代巴比妥酸活性物质、羰基(蛋白质氧化)、脂质过氧化物及氧自由基吸收能力的变化进行分析,结果表明两种力竭性运动方式之后,受试者血液中羰基(蛋白质氧化)、脂质过氧化物(LH)均有显著变化,但无氧等长收缩运动更容易引发脂质过氧化反应(P < 0.01),而力竭性有氧收缩运动(AE)更容易使蛋白质氧化为羰基氧化物(P < 0.01),氧自由基吸收能力则分别增加了25%和9%,表明无氧力竭性运动虽然整体氧耗(VO2)没有明显增加,但同样可以引发明显的氧化应激损伤。 Shi等[22]对分别进行中高强度有氧运动及等同运动负载的无氧运动的两组受试者运动后即刻和运动后3,9和24 h的血液和尿液样本采集,并对尿液中F2-异前列腺素、血清4-羟基壬烯醛、血清蛋白羰基化合物及8-羟基脱氧鸟苷(分别作为脂质、蛋白质和DNA氧化损伤标记物)和血清尿素及肌酸激酶进行测定,结果发现相对于无氧运动组,有氧运动组运动后即刻血清尿酸显著升高(P < 0.01),而在运动后3 h恢复至运动前水平;无氧运动组在运动后即刻及运动后3 h血清尿酸均升高(P < 0.05),并持续至运动后24 h;有氧运动及无氧运动组尿液中的DNA氧化损伤标记物8-羟基-2'-脱氧鸟苷水平在运动后均显著升高(P < 0.05),并分别在24 h和3 h时血液浓度达到峰值;两运动组血液中4-羟基壬烯醛和F2-异前列腺素分别在运动后3 h和6 h显著升高(P < 0.01),并在运动后24 h恢复至运动前水平;血清蛋白羰基化合物在运动前后均无显著变化,各氧化应激特异性标记物指标在两运动组间均无明显差异。Cardoso等[23]研究对比了间歇性有氧运动及抗阻运动对于中年女性的红细胞计数及氧化应激指标的影响,发现抗阻练习运动组(75%-80% 最大力量练习60 min)及有氧运动组(室内团体自行车训练60 min)运动后1 h相比运动后即刻淋巴细胞和单核细胞均显著减少(P < 0.05),而在运动后即刻两组血清中和蛋白质羰基及 硫代巴比妥酸反应物质均明显升高(P < 0.05),抗氧化活性物质(非蛋白巯基,超氧化物歧化酶,过氧化氢酶)的下降水平也与氧化应激损伤标志物呈负相关(P < 0.05),进而提示了间歇性有氧运动及抗阻运动均可以诱导体内免疫抑制和氧化应激损伤升高。Bailey等[24]通过基于氧依赖延迟原卟啉IX荧光淬火技术(PpIX)对微血管和线粒体氧分压氧进行监测,发现细胞浆氧分压在不同运动强度下维持稳定,而线粒体氧分压则有所下降,均提示了运动所引起的线粒体内氧分压的变化而非运动中氧气通量及耗氧量的升高是运动引起活性氧增加的主要因素,同时证实了急性运动及力竭性运动都可以导致内源性氧自由基生成增多而导致运动性疲劳及损伤;而过量的活性氧还会导致呼吸链功能进一步下降、肌纤维中肌球蛋白和线粒体酶的氧化损伤以及干扰骨骼肌运动的动作电位使运动能力下降。 2.2 机体的氧化-抗氧化平衡与抗氧化剂补充 机体抗氧化防御系统有两类:酶促系统和非酶促系统[25]。体内主要的酶类抗氧化剂包括细胞组织内的超氧化物歧化酶、过氧化氢酶、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶、铜、锌-歧化酶(Cu、Zn-SOD)、醛酮还原酶(AR)等。非酶类抗氧化剂主要包括:维生素E、类胡萝卜素、黄酮类化合物、硫醇类等脂溶性物质;维生素C和谷胱甘肽等水溶性物质,主要通过猝灭自由基、防止脂质、核酸及蛋白质过氧化、稳定细胞功能而发挥作用[26]。另外,微量元素(锌、镁、硒等)对于超氧化物歧化酶、过氧化氢酶、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶等抗氧化酶也为必需成分,各种氧化剂在组织细胞中协同消除多余自由基以维持细胞稳定的内环境。 在正常生理条件下,体内氧化和抗氧化系统保持动态平衡,研究证实运动过程中骨骼肌及血细胞产生的活性自由基(尤其是在组织液中具有相对较长半衰期的•NO、H2O2和HOCl)可以渗透过细胞质膜扩散入血液中,因而血浆等体液中的抗氧化物的活性/浓度及氧化应激标记物可以有效反映组织肌肉及血细胞中的氧化应激状态[27](见图3)。强度适中的运动有利于清除体内活性氧,降低机体氧化应激水平,而运动产生的自由基在骨骼肌的运动适应性收缩功能改善,以及促进骨骼肌基因表达完整性相关的细胞通路激活中起着重要作用[28]。但运动强度过大时,体内生成大量活性氧,导致抗氧化酶表达不足、氧化和抗氧化平衡失调,就需要对机体合理补充抗氧化剂以预防活性氧在体内大量积蓄而引发细胞和组织的损伤[28](见图4)。"

Bryer和Goldfarb[29]对受试者在大强度离心运动开始前两周及运动结束后4 d内补充维生素C(3 g/d),发现补充维生素C对运动后肌肉力量的下降无明显干预作用,但可以显著降低运动后24 h内的肌肉酸痛感(MS)和血液中谷胱甘肽氧化型与还原型(GSH/GSSG)比值及运动后48 h内血液中肌酸激酶水平。Slattery等[30]通过随机双盲安慰剂对照的交叉设计研究了短期口服N-乙酰半胱氨酸对高强度运动后体内氧化还原平衡和炎症反应的影响,实验选取了10名训练良好的运动员作为受试者进行SRM功率自行车模拟比赛(105 min的力竭运动),连续9 d每天进行口服给药N-乙酰半胱氨酸1 200 mg及高强度运动,所有受试者每次均被要求进行最大能力冲刺,并由SRM记录平均功率输出以及心率变化。采集受试者第1天运动前及第9天运动前、运动后即刻和运动后1,24 h的血液和尿液,对血浆中总抗氧化能力、三价铁还原能力(FRAP)、氧化型谷胱甘肽、还原型谷胱甘肽、硫代巴比妥酸反应物质、白细胞介素6、黄嘌呤氧化酶、次黄嘌呤、单核细胞趋化蛋白1、核因子κB及尿液中异构前列腺素浓度进行了评估,实验结果表明口服N-乙酰半胱氨酸可以显著改善自行车模拟比赛中受试者运动成绩(P=0.001);此外补充N-乙酰半胱氨酸组运动后血浆总抗氧化能力(P=0.005),运动诱导的氧化损伤及炎症反应降低(P=0.002),运动后核因子κB活性增加;证明了口服N-乙酰半胱氨酸补充剂能够有效改善优秀运动员力竭性运动中的氧化—抗氧化平衡以及机体对高强度运动的生理适应性,同时也有利于运动成绩的提高。 Casuso等[31]对Wistar大鼠进行持续6周的跑台运动,实验期间隔天通过灌胃给予榭皮素,实验结束后对大鼠股四头肌中的对运动诱导骨骼肌的适应机制中起重要调节作用的氧化物酶体运动性过氧化物酶体增殖物受体γ共激活因子1α的mRNA、线粒体DNA(mtDNA)的含量及肌肉组织中柠檬酸合酶活性、超氧化歧化酶、过氧化氢酶和蛋白质羰基含量(PCC,蛋白质氧化损伤标记物)进行测定,结果发现静止组与运动组相比,补充榭皮素增加了静止组大鼠肌肉组织中的蛋白质氧化损伤标记物PCC含量(P < 0.001),同时提高了静止组大鼠肌肉中过氧化氢酶(P < 0.001)和超氧化歧化酶超氧化歧化酶( P< 0.05)的活性,并增加了过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ共激活因子1α的mRNA表达水平(P < 0.001);另外,补充榭皮素还使得运动组大鼠肌肉中线粒体DNA的含量及柠檬酸合酶活性相比未补充榭皮素的运动组大鼠明显降低(P < 0.05),提示在运动中过度补充榭皮素可能会导致骨骼肌运动适应性的明显下降[32]。 Tong等[33]选取普通成年人和优秀长跑运动员及自行车运动员进行专业耐力运动训练,并对训练后血液中硫代巴比妥酸反应物,黄嘌呤氧化酶,过氧化物酶,还原型谷胱甘肽含量,总抗氧化能力(T-AOC)进行了分析,结果自行车运动员血浆中黄嘌呤氧化酶、还原型谷胱甘肽和过氧化氢酶的含量明显高于普通成年人及长跑运动员(P < 0.05);长跑运动员血浆中过氧化氢酶的含量明显高于普通成年人(P < 0.05);研究还对从运动受试前1周开始的膳食营养摄入与血清氧化还原状态之间进行了相关性分析,结果发现血浆中还原型谷胱甘肽含量与碳水化合物、蛋白质、脂类、总摄入热量、硒、锌、铁和镁摄入量显著相关(P < 0.05);过氧化氢酶含量与碳水化合物、蛋白质摄入量、总摄入热量、硒和摄入量显著相关(P < 0.05),血清中黄嘌呤氧化酶含量则与膳食摄入的胆固醇量显著相关(r=0.57);同时受试者血液中过氧化氢酶含量与还原型谷胱甘肽含量呈现显著相关(r=0.70,n=36,P < 0.05),表明了优秀运动员体内长期训练对抗氧化系统产生的运动适应性提高,内源性抗氧化酶活力提高,并且膳食营养摄入情况可能会直接影响到机体抗氧化系统。而Fischer等[34]对经常锻炼的男性给予连续4周的维生素C(500 mg/d)及天然维生素E(RRR-α-生育酚,400 IU/d),发现在进行双侧膝关节50%最大力量训练后血浆中白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1、白细胞介素1受体拮抗剂(IL-1ra)、C-反应蛋白及皮质醇含量均显著低于无补充组;Zhang等[35]采用联合维生素C(600 mg/d)、维生素E(500 mg/d)及硒元素(200 μg/d)对运动员进行2周抗氧化剂补充,结果表明补充组在大强度离心运动后48 h内血液中超氧化物歧化酶活性、GSH-Px活性均显著高于对照组,而丙二醛升高的水平则显著低于对照组;都表明联合使用抗氧化剂可以有效提高机体抗氧化能力,减轻免疫系统氧化应激损伤。上述研究提示多种抗氧化剂结合补充比单一氧化剂有更好的抗氧化效果,抗氧化剂之间具有协同作用[22],同时也都表明在运动训练过程中需要对运动员进行针对个体化的、更加科学合理的抗氧化剂补充。运动持续时间、强度、运动类型及受试者的抗氧化能力状况都会对抗氧化剂补充效果产生影响。 2.3 线粒体DNA的运动氧化损伤及评定方法 线粒体呼吸链是运动性内源活性氧产生的主要部位,而由于线粒体DNA(mtDNA)的结构功能特征,特别容易受到运动中产生的活性氧氧化损伤,表现见表1。"

| [1] Niess AM, Simon P.Response and adaptation of skeletal muscle to exercise—the role of reactive oxygen species.Front Biosci.2007;1(12):4826-4838.[2] Kramer HF, Goodyear LJ.Exercise, MAPK, and NF-kappaB signaling in skeletal muscle.J Appl Physiol. 2007;103(1): 388-395. [3] Malcolm J.Jackson, Anne McArdle. Age-related changes in skeletal muscle reactive oxygen species generation and adaptive responses to reactive oxygen species.J Physiol. 2011;589(9):2139-2145. [4] Filaire E,Toumi H.Reactive oxygen species and exercise on bone metabolism: friend or enemy? .Joint Bone Spine.2012; 79(4):341-346.[5] Lokanatha V,Subramanyam D,Rajendra W.Role of free radicals and antioxidants in gynecological cancers: current status and future prospects. Oxidants & Antioxidants in Medical Science.2014;3(1):15-26.[6] Zsolt R, Hae YC, Erika K, et al.Exercise, oxidative stress and hormesis.Ageing Research Reviews.2008;7(1):34-42.[7] Duan Y, Gross RA, Sheu SS.Ca2+-dependent generation of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species serves as a signal for poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 activation during glutamate excitotoxicity.J Physiol. 2007;585(3): 741-758. [8] Mari-C,Gomez-C,Elena D,et al.Moderate exercise is an antioxidant: Upregulation of antioxidant genes by training.Free Radical Biology and Medicine.2008; 44(2): 126-131.[9] Ji LL.Modulation of skeletal muscle antioxidant defense by exercise: Role of redox signaling.Free Radic Biol Med.2008; 44(2):142-152. [10] Slattery K,Bentley D,Coutts AJ.The role of oxidative, inflammatory and neuroendocrinological systems during exercise stress in athletes: implications of antioxidant supplementation on physiological adaptation during intensified physical training.Sports Medicine.2015; 45(4): 453-471.[11] Liu Y,Fiskum G,Schubert D.Generation of reactive oxygen species by the mitochondrial electron transport chain. J Neurochem.2002;80:780-787.[12] Waypa GB,Guzy R,Mungai PT,et al.Increases in mitochondrial reactive oxygen species trigger hypoxia-induced calcium responses in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells.Circ Res. 2006;9(9): 970-978. [13] Yeong-RC, Chwen-LC, Liwen Z,et al. Superoxide Generation from Mitochondrial NADH Dehydrogenase Induces Self-inactivation with Specific Protein Radical Formation. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(45):37339-37348.[14] Muller FL,Liu Y,Van Remmen H.Complex Ⅲ releases superoxide to both sides of the inner mitochondrial membrane. J Biol Chem.2004;279: 49064-49073.[15] William MN. Detection of superoxide anion and hydrogen peroxide production by cellular NADPH oxidases. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA).2014; 1840(2): 757-767.[16] Burhans WC,Heintz NH.The Cell Cycle is a Redox Cycle: Linking phase-specific targets to cell fate. Free Radical Biology and Medicine.2009;47:1282-1293. [17] Balaban R,Nemoto S,Finkel T.Mitochondria, oxidants, and aging.Cell.2005;120(4):483-495.[18] St-Pierre J, Buckingham JA, Roebuck SJ, et al. Topology of superoxide production from different sites in the mitochondrial electron transport chain.J Biol Chem. 2002;277(47): 44784-44790.[19] Andreyev AY, Kushnareva YE, Starkov AA. Mitochondrial metabolism of reactive oxygen species.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2005;70:200-214.[20] [Cadenas E, Davies KJ. Mitochondrial free radical generation, oxidative stress, and aging. Free RadicBiolMed. 2000;29(3-4): 222-230.[21] Alessio HM,Hagerman AE,Fulkerson BK,et al.Generation of reactive oxygen species after exhaustive aerobic and isometric exercise.Med Sci Sports Exerc.2000; 32(9): 1576-1581.[22] Shi M, Wang X, Yamanaka T, et al.Effects of anaerobic exercise and aerobic exercise on biomarkers of oxidative stress. Environ Health Prev Med. 2007;12(5): 202-208.[23] Cardoso AM, Bagatini MD, Roth MA, et al.Acute effects of resistance exercise and intermittent intense aerobic exercise on blood cell count and oxidative stress in trained middle-aged women. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2012 ;45(12):1172-1182.[24] Bailey DM, Davies B, Young IS. Intermittent hypoxic training: Implications for lipid peroxidation induced by acute normoxic exercise in active men.Clin Sci (Lond). 2001;101(5): 465-475.[25] Moukette BM, Pieme CA, Njimou JR, et al.In vitro antioxidant properties, free radicals scavenging activities of extracts and polyphenol composition of a non-timber forest product used as spice: Monodora myristica.Biol Res.2015;48:15-17.[26] Dong J.S, Kim S, Kim J, et al.Role of l-carnitine in sports performance: Focus on ergogenic aid and antioxidant.Science & Sports.2016;4:177-188.[27] Michalis GN,Athanasios ZJ.Blood as a reactive species generator and redox status regulator during exercise. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2009;490(2):77-84.[28] Alessandro P,Giuseppina P,Francesca M,et al.Exercise and oxidative stress: Potential effects of antioxidant dietary strategies in sports.Nutrition.2015;31(7-8):916-922.[29] Bryer SC, Goldfarb AH. Effect of high dose vitamin C supplementation on muscle soreness, damage, function and oxidative stress to eccentric exercise.Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab.2006;16(3):270-280.[30] Slattery KM, Dascombe B, Wallace LK,et al. Effect of N-acetylcysteine on cycling performance after intensified training.Med Sci Sports Exerc.2014;46(6):1114-1123.[31] Casuso RA,Martínez-López EJ,Nordsborg NB,et al.Oral quercetin supplementation hampers skeletal muscle adaptations in response to exercise training.Scand J Med Sci Sports.2014;24: 920-927.[32] Djordjevic DZ,Cubrilo DG,Barudzic NS,et al.Comparison of blood pro/antioxidant levels before and after acute exercise in athletes and non-athletes.Gen Physiol Biophys. 2012;31(2): 211-219.[33] Tong TK,Lin H,Lippi G,et al.Serum oxidant and antioxidant status in adolescents undergoing professional endurance sports training.Oxid Med Cell Longev.2012;1155(10): 1-7.[34] Fischer C, Hiscock N, Penkowa M, et al.Vitamin C and E supplementation inhibits the release of interleukin-6 from contracting human skeletal muscle.J Physiol.2004; 558: 633-645.[35] Zhang H,Su QS. Effects of combined antioxidants on T-AOC, SOD, GSH-Px and MDA of athletes after a high intensity exercise.Journal of Beijing Sport University. 2008;31(4): 483-487. [36] Afshar J, MA H, Massoud H, et al. Effect of aerobic exercise training on mtDNA deletion in soleus muscle of trained and untrained Wistar rats.Br J Sports Med. 2005;39:517-520. [37] Lee S, Kim M, Lim W, et al.Strenuous exercise induces mitochondrial damage in skeletal muscle of old mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;461(2):354-360.[38] Dizdaroglu M, Jaruga P, Birincioglu M, et al. Free radical-induced damage to DNA:mechanisms and measurement.Free Radic Biol Med.2002;32(11):1102-1115.[39] Olive PL,Banáth JP.The comet assay: a method to measure DNA damage in individual cells.Nat Protoc.2006;1(1):23-29.[40] Wu LL, Chiou CC, Chang PY, et al. Urinary 8-OHdG: a marker of oxidative stress to DNA and a risk factor for cancer, atherosclerosis and diabetics. Clin Chim Acta. 2004;339(1-2):1-9.[41] Dong QY,Cui Y,Chen L,et al.Urinary 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine levels in diabetic retinopathy patients. Eur J Ophthalmol.2008;18(1):94-98.[42] Ock CY, Kim EH, Choi DJ, et al.8-Hydroxydeoxyguanosine: not mere biomarker for oxidative stress, but remedy for oxidative stress-implicated gastrointestinal diseases. World J Gastroenterol.2012;18(4):302-308.[43] Laura S, Anna B, Marco T.A method for routine quantitation of urinary8-hydroxy-2’-deoxy-guanosine based on solid-phase extraction and micro-high-performance liquid chromatography/ electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom.2005;19: 147-152.[44] Xu B, Kang L, Zhang G, et al.The changes of 8-OHdG, hOGG1, APE1 and Pol β in lenses of patients with age-related cataract. Curr Eye Res.2015;40(4):378-385.[45] Valavanidis A,Vlachogianni T,Fiotakis C.8-hydroxy- 2'-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG): A critical biomarker of oxidative stress and carcinogenesis.J Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev.2009;27(2):120-139.[46] Barcia JM, Flores-Bellver M, Muriach M,et al. Matching Diabetes and Alcoholism: Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Neurogenesis Are Commonly Involved.Mediators Inflamm. 2015;6: 242-287. [47] Radák Z, Pucsuk J, Boros S.Changes in urine 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine levels of super-marathon runners during a four-day race period. Life Sci.2000; 66(18):1763-1767.[48] Almar M, Villa JG, Cuevas MJ,et al.Urinary levels of 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine as a marker of oxidative damage in road cycling.Free Radic Res.2002;36(3):247-253.[49] Tanimura Y, Shimizu K, Tanabe K, et al. Effects of three consecutive days exercise on lymphocyte DNA damage in young men.Eur J Appl Physiol.2010;110(2):307-314. [50] Tsai K, Hsu TG, Hsu KM,et al.Oxidative DNA damage in human peripheral leukocytes induced by massive aerobic exercise.Free Radic Biol Med.2001;31(11):1465-1472.[51] Neubauer O, Reichhold S, Nics L, et al. Antioxidant responses to an acute -ultra-endurance exercise: impact on DNA stability and indications for an increased need for nutritive antioxidants in the early recovery phase. Br J Nutr.2010; 104(8): 1129-1138.[52] Reichhold S,Neubauer O, Hoelzl C, et al. DNA damage in response to an Ironman triathlon.Free Radic Res.2009;43(8): 753-760. [53] Powers SK, Jackson MJ.Exercise-induced oxidative stress:cellular mechanisms and impact on muscle force production.Physiol Rev.2008;88 (4):1243-1276. |
| [1] | Cui Wei, Cui Di, Ouyang Ting, Li Xiang, Wei Huiting, Xue Weiyue, Zhou Gang, Qiu Ye. Inhibiting NOX alleviates alcoholic liver damage and lipid metabolism disorder [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-8. |
| [2] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [3] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [4] | Wang Shuo, Liu Wenying, Lü Chaofan, Li Jiacong, Geng Yi, Zhao Yungang. Cardioprotective effect of 3-nitro-N-methyl salicylamide on the isolated rat heart under cold ischemia preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1194-1201. |
| [5] | Yang Shenglin, Pu Xingwei, Luo Chunshan, Yang Jianwen. Neuroprotective effects of tetrandrine preconditioning in rabbits with spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1223-1227. |
| [6] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [7] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [8] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [9] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [10] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [11] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [12] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [13] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [14] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [15] | Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi. Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||