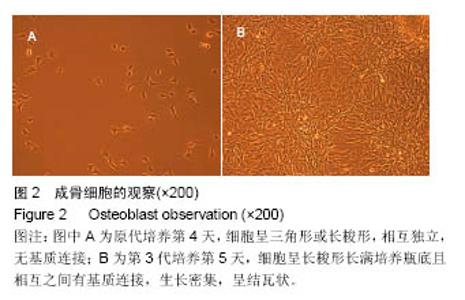
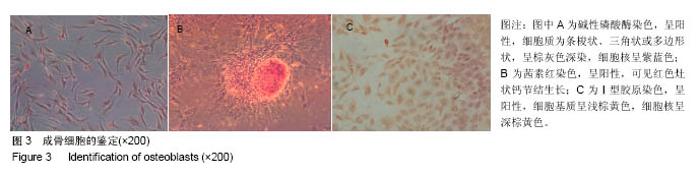
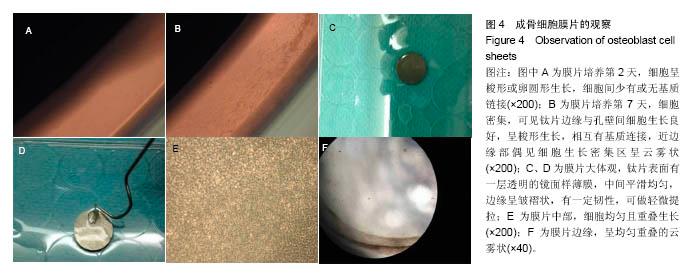
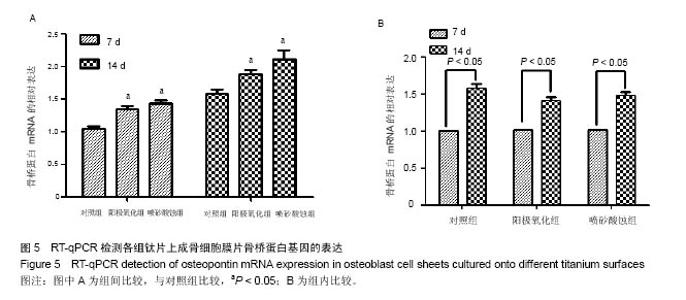
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (10): 1501-1507.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.10.005
Previous Articles Next Articles
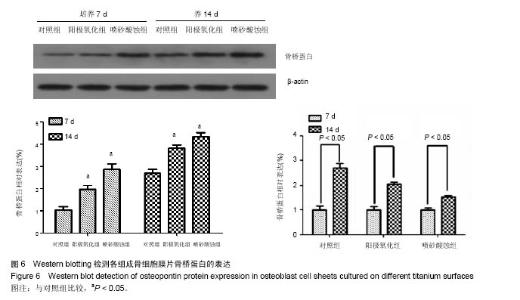
Expression of osteopontin mRNA and protein in osteoblast cell sheets cultured on different titanium surfaces
Wu Lei1, Xia Qian2, Mao Jiu-feng3, Guo Yi1, Zeng Xiao4, Li Zhi1, Wang Bi-chao5, Dong Qiang4
- 1 Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 2 Department of Oral Medicine, 4 Department of Prosthodontics, 5 Department of Orthodontics, the Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 3 Department of Prosthodontics, Guizhou Provincial Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2017-02-14Online:2017-04-08Published:2017-05-08 -
Contact:Dong Qiang, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Prosthodontics, the Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Wu Lei, Studying for master’s degree, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:the Guizhou Province & University Cooperation Projects of the Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Department, No. [2014]7115; Guiyang Municipal Science and Technology Project, No. [20141001]39
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Lei, Xia Qian, Mao Jiu-feng, Guo Yi, Zeng Xiao, Li Zhi, Wang Bi-chao, Dong Qiang. Expression of osteopontin mRNA and protein in osteoblast cell sheets cultured on different titanium surfaces[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(10): 1501-1507.
share this article
| [1]Gilmore J,Ballenger J,Burg K.Bone tissue engineering.Sci Scope.2016;9(39):26-34.[2]Ohashi K,Okano T.Functional tissue engineering of the liver and islets.Anat Rec(Hoboken).2014;297(1):73-82. [3]Shimizu T,Sekine H,Yang J,et al.Polysurgery of cell sheet grafts overcomes diffusion limits to produce thick , vascularized myocardial tissues.FASEB J.2006; 20(6): 708-710. [4]Sakaguchi K,Shimizu T,Okano T.Construction of three-dimensional vascularized cardiac tissue with cell sheet engineering.J Control Release. 2015;205:83-88. [5]Amagai Y,Karasawa K,Kyungsook J,et al.Development of a novel carrier optimized for cell sheet transplantation. Biomatter. 2015;5(1):1027-1036.[6]唐霞,王少安.种植体的表面改性与促进成骨[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2008,35(S1):225-228.[7]Reichert JC,Wullschleger ME,Cipitria A,et al.Custom-made composite scaffolds for segmental defect repair in long bones.Int Orthop.2011;35(8):1229-1236.[8]den Boer FC,Wippermann BW,Blokhuis TJ,et al.Healing of segmental bone defects with granular porous hydroxyapatite augmented with recombinant human osteogenic protein-1 or autologous bone marrow.J Orthop Res.2003;21(3):521-528.[9]Lundgren S,Sjöström M,Nyström E,et al.Strategies in reconstruction of the atrophic maxilla with autogenous bone grafts and endosseous implants.Periodontol 2000.2008; 47: 143-161.[10]Liu Y,Wu G,de Groot K.Biomimetic coatings for bone tissue engineering of critical-sized defects.J R Soc Interface. 2010; 7(5):S631-S647.[11]文艺,杨鸿旭,刘倩,等.骨髓间充质干细胞联合血管内皮祖细胞修复骨质疏松性牙槽骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(19): 2748-2755.[12]肖琦科,魏玉珊,赵轶男,等.多孔磷酸钙骨水泥与转染骨形态发生蛋白2基因的骨髓间充质干细胞复合修复股骨髁骨缺损[J],中国组织工程研究,2016,20(43):6403-6408.[13]Karagianni M,Brinkmann l,Kinzebach S,et al.A comparative analysis of the adipogenic potential in human mesenchymal stromal cells from cord blood and other sources.Cytotherapy. 2013;15(1):76-88.[14]Zhang W,Li Z,Huang Q,et al.Effects of a hybrid micro/ nanorod topography -modified titanium implant on adhesion and osteogenic diferentiation in rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.Int J Nanomedicine.2013;8:257-265.[15]Mohammadi Z,Afshari JT,Keramati MR,et al.Differentiation of adipocytes and osteocytes from human adipose and placental mesenchymal stem cells.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015;18(3):259-266.[16]Du M,Liang H,Mou C,et al.Regulation of human mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into chondrocytes in extracellular matrix-based hydrogel scaffolds.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2014;114:316-323. [17]Nakamura A,Akahane M,Shigematsu H,et al.Cell sheet transplantation of cultured mesenchymal stem cells enhances bone formation in a rat nonunion model.Bone.2010,46(2): 418-424. [18]董海,周之德,戴力扬,等.骨髓间充质干细胞成骨定向分化的研究进展[J].创伤外科杂志,2003,5(5):394-397.[19]Choi BH,Cheong H,Ahn JS,et al.Engineered mussel bioglue as a functional osteoinductive binder for grafting of bone substitute particles to accelerate in vivo bone regeneration.J Mater Chem B.2015;3(4):546-555.[20]雷鸣,高丽娜.细胞膜片技术在牙周、牙髓牙本质再生中的应用研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2014,30(5):705-708.[21]周成菊,周建奖,杨红,等.抗坏血酸对大鼠成骨细胞膜片BMP-2 mRNA表达的影响[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2015,31(3):305-308.[22]Shiba Y.New strategy for the treatment of myocarditis by cell-sheet technology. Circ J.2015;79(1):51-52.[23]Ohki T,Yamato M,Ota M,et al.Application of regenerative medical technology using tissue-engineered cell sheets for endoscopic submucosal dissection of esophageal neoplasms. Dig Endosc.2015;27(2):182-188.[24]Yang J, Yamato M,Shimizu T,et al.Reconstruction of functional tissues with cell sheet engineering. Biomaterials. 2007;28(34):5033-5043.[25]Uchihara Y,Akahane M,Shimizu T,et al.Osteogenic Matrix Cell Sheets Facilitate Osteogenesis in Irradiated Rat Bone. Biomed Res Int.2015;2015:629168. [26]王增田,王心,杨静,等.骨桥蛋白影响破骨细胞、成骨细胞参与骨重塑过程的研究进展[J]. 武警后勤学院学报(医学版), 2014, 23(12):1062-1065.[27]Chen HT,Tsou HK,Chang CH,et al.Hepatocyte Growth Factor Increases Osteopontin Expression in Human Osteoblasts through P13K Akt,c-Src,and AP-1 Signaling Pathway.PLoS One.2012;7(6):38378-38389.[28]符策广,刘洁,夏海斌.骨桥蛋白的生物学特性及在骨改建中的作用[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2012,28(8):506-507.[29]曲露露,李美华,罗云纲.纯钛种植体表面处理技术促进骨整合研究进展[J].中国老年学杂志,2015,35(12):3474-3476.[30]闵阳,李宝娥,李莺,等.阳极氧化法改变钛表面的生物活性和生物相容性[J].河北工业大学学报,2015,44(6):63-67.[31]雷欣,李世铁,钟凡,等.流体剪切力和表面处理对钛表面成骨细胞增殖的影响[J].广东牙病防治,2015,23(6):285-288.[32]王亚敏.不同粗化喷砂-酸蚀纯钛表面的性能研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2011.[33]闵曦,夏荣,孙磊,等.紫外光照射纳米钛表面生物抗老化的体外研究[J].安徽医科大学学报,2015,50(1):37-40.[34]Minagar S,Wang J,Berndt CC,etal.Cell response of anodized nanotubes on titanium and titanium alloys.J Biomed Mater Res A.2013;101(9):2726-2739. [35]Pirraco RP,Iwata T,Yoshida T,et al.Endothelial cells enhance the in vivo bone-forming ability of osteogenic cell sheets.Lab Invest.2014;94(6):663-673.[36]Haraguchi Y,Shimizu T,Sasagawa T,et al.Fabrication of functional three dimensional tissues by stacking cell sheets in vitro.Nat Protoc.2012;7(5):850-858.[37]Flores MG,Hasegawa M,Yamato M,et al.Cementum- periodontal ligament complex regeneration using the cell sheets in a canine model.Biomaterials.2009;30(14): 2716-2723.[38]Chen FM,Sun HH,Lu H,et al.Stem cell-delivery therapeutics for periodontal tissue regeneration.Biomaterials. 2012;33(27): 6320-6344.[39]于卫强,徐玲,张富强.钛表面TiO2纳米管仿生修饰对成骨细胞骨功能基因表达的影响[J].口腔医学研究,2015,31(4):320-323.[40]牛宇霆,伍妍,叶展怡,等.阳极氧化促进钛表面生物矿化的研究[J].口腔医学研究,2009,25(3):282-284.[41]韩雪,宋九余,华泽权,等.阳极氧化处理后的新型钛合金体外诱导实验及对成骨细胞早期附着的影响[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2007, 23(6):781-784.[42]Wang Y,Wen C,Hodgson P,et al.Biocompatibility of TiO2 nanotubes with different topographies.J Biomed Mater Res A.2014;102(3):743-751.[43]Gu YX,Du J,Si MS,et al.The roles of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in regulating MC3T3-E1 preosteoblast proliferation and differentiation on SLA and SLActive titanium surfaces.J Biomed Mater Res A.2013;101(3):748-754. [44]Marletta G,Ciapetti G,Satriano C,et al.The effect of irradiation modification and RGD sequence adsorption on the response of human osteoblasts to polycaprolactone. Biomaterials. 2005;23(26):4793-4804.[45]Cirano FR,Togashi AY,Marques MM,et al.Role of rhBMP-2 and rhBMP-7 in the Metabolism and Differentiation of Osteoblast-Like Cells Cultured on Chemically Modified Titanium Surfaces.J Oral Implantology.2014;40(6):655-659.[46]Thurgood LA,Cook AF,Sørensen ES,et al.Face-specific incorporation of osteopontin into urinary and inorganic calcium oxalate monohydrate and dihydrate crystals.Urol Res. 2010;38(5):357-376.[47]Lai M,Hermann CD,Cheng A,et al.Role of α2β1 integrins in mediating cell shape on microtetured titanium surfaces.J Biomed Mater Res A.2015;103(2):564-573.[48]Keselowsky BG,Wang L,Schwarta Z,et al.Integrin α5 controls osteoblastic proliferation and differentiation responses to titanium substrates presenting different roughness characteristics in a roughness independent manner.J Bomed Mater Res A,2007,80(3):700-710.[49]付晓龙,李莺,李宝娥.纯钛表面阳极氧化增强成骨细胞生物活性及护骨素基因的表达,[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,39(18): 6240-6245.[50]Huang CF,Chiang HJ,Lin HJ,et al.Comparison of Cell Response and Surface Characteristics on Titanium Implant with SLA and SLAffinity Functionalization.JES. 2014;3(161): G15-G20. [51]尹星,谢利,徐鸿,等.钛植入体表面多级孔结构的构建及体外生物学评价[J].稀有金属材料与工程,2014,43(S1):310-313. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Xue Yadong, Zhou Xinshe, Pei Lijia, Meng Fanyu, Li Jian, Wang Jinzi . Reconstruction of Paprosky III type acetabular defect by autogenous iliac bone block combined with titanium plate: providing a strong initial fixation for the prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1424-1428. |
| [3] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [4] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [5] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [6] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [7] | Hu Weifan, Zheng Li, Li Dadi, Sun Yang, Zhao Fengchao. Overexpression of miR-25 downregulates titanium particle-induced osteoclast differentiation through the NFATc1 signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 682-687. |
| [8] | Qiu Peng, Fu Qilin, Liu Min, Lan Yuyan, Wang Pin. Comparison of oral micro-adhesion on polyetheretherketone, zirconium dioxide, and pure titanium abutment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 540-545. |
| [9] | Chen Shuo, Xiao Dongqin, Li Xingping, Ran Bin, Shi Feng, Zhang Chengdong, Deng Li, Huang Nanxiang, Liu Kang, Feng Gang, Duan Ke. Preparation and characterization of tantalum functional coating on titanium implant [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 546-552. |
| [10] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [11] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [12] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [13] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [14] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [15] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||