Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (8): 1294-1300.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.08.025
Previous Articles Next Articles
Research progress of Hedgehog signaling pathway regulating RANKL expression in osteoblasts
Wu Xiu-tuan, Li Wen-liang, Xie Liu-rong, Liao Hong-bing
- Department of Prosthodontics, College of Stomatology Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2016-11-23Online:2017-03-18Published:2017-04-14 -
About author:Wu Xiu-tuan, Stdying for master’s degree, Department of Prosthodontics, College of Stomatology, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Regi n, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81260170
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Xiu-tuan, Li Wen-liang, Xie Liu-rong, Liao Hong-bing. Research progress of Hedgehog signaling pathway regulating RANKL expression in osteoblasts[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(8): 1294-1300.
share this article
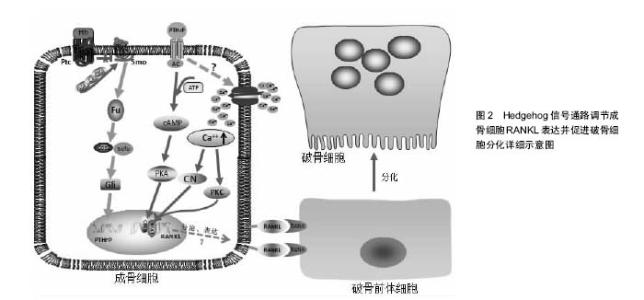
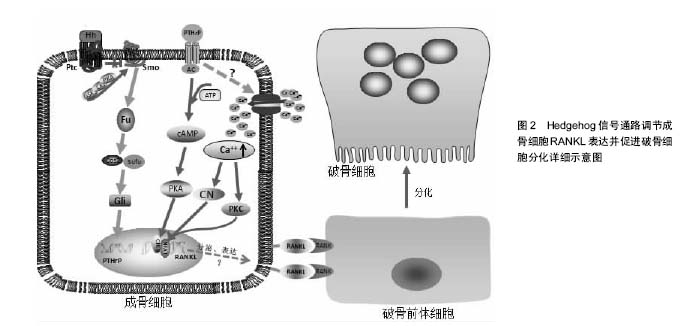
2.1 Hedgehog信号通路 在哺乳动物中,Hedgehog基因编码3种同源形式蛋白,即音速刺猬蛋白(Sonic hedgehog, SHedgehog)、印度刺猬蛋白(Indian hedgehog, IHedgehog)、沙漠刺猬蛋白(Desert hedgehog, DHedgehog) [3]。SHedgehog在神经系统、皮肤、消化道中广泛表达[4],IHedgehog主要在骨、软骨、消化道、胰腺中表达,DHedgehog主要在生殖器中表达,也在外周神经和胰腺中表达[5-6]。Hedgehog信号传递受靶细胞膜上2种受体Patched(Ptc)和Smoothened (Smo)的控制。Ptc由肿瘤抑制基因Patched编码,是12次跨膜蛋白,能与配体直接结合,对Hedgehog信号起负调控作用[7];Smo由原癌基因Smoothened编码,是7次跨膜蛋白,与G蛋白偶联受体同源,是Hedgehog信号传递所必须的受体[8]。在缺乏Hedgehog蛋白的情况下,Smo的活性被Ptc所抑制,而Hedgehog蛋白存在时,Hedgehog与 Ptc结合,解除Ptc对Smo的抑制作用,使得Smo被蛋白激酶A、CKI、GSK3磷酸化,同时Smo分子的C-末端发生构象改变,由闭合的无活性的状态转变为开放的有活性的状态,进而激活下游通路[9-11]。磷酸化的Smo通过与Cos2之间的动态相互作用将Cos2/Fu复合物招募到质膜上,从而诱导Fu二聚化。二聚化的Fu通过自我磷酸化激活,进而磷酸化其底物Cos2与Sufu,将Hedgehog信号传递至下游。这一过程将促使全长的转录因子Gli进入细胞核内启动目的基因的表达。Gli蛋白是分子量较大的多功能转录因子,定位于细胞核和细胞浆,将信号传递至核内。该蛋白家族成员只有在维持全长时才具有转录激活子的功能,启动下游靶基因的转录;当其羧基端被蛋白酶体水解后,就形成了转录抑制子,抑制下游靶基因的转录。 2.2 Hedgehog信号通路参与骨髓间充质干细胞成骨向分化的调节 既往研究中,Hedgehog信号通路在骨代谢中的作用最初主要表现为促进骨生成,对胚胎期骨骼发育至关重要,若胚胎发育阶段Hedgehog信号蛋白缺乏将导致次级骨化中心和生长板的缺失,从而导致各种骨骼相关性疾病的发生[12]。有研究发现,SHedgehog可通过上调核心结合因子2(Runt-related transcription factor 2,Runx2)、特异性转录因子表达而促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨细胞向分化,增加成骨细胞的形成,并阻断骨髓间充质干细胞的成脂向分化,其中,特异性转录因子是作为Runx2的下游靶物介导成骨细胞分化,而Tian等[13-14]研究发现,成骨细胞样细胞经SHedgehog处理后,特异性转录因子与Runx2基因表达均有提高,但特异性转录因子基因表达却早于Runx2,这表明特异性转录因子可能并不是单独由Runx2调控,或有可能作为SHedgehog促进成骨细胞分化的直接作用靶点。Shimoyama等[15]研究发现,IHedgehog可以通过激活下游转录因子Gli2而刺激骨髓间充质干细胞碱性磷酸酶与骨钙素表达以及钙化作用。Gli2缺失可以明显抑制IHedgehog对骨髓间充质干细胞成骨向分化的诱导作用,而且IHedgehog或Gli2过表达均可上调参与成骨分化的重要转录因子Runx2的表达,并激活Runx2的成骨功能。通过免疫共沉淀分析显示,Gli2和Runx2之间存在物理交互,骨髓间充质干细胞中Runx2缺乏时,即使IHedgehog或Gli2过表达也不能增强骨髓间充质干细胞中碱性磷酸酶活性。由此可知,Gli2在IHedgehog通过调节Runx2诱导骨髓间充质干细胞成骨向分化过程中具有重要作用,Runx2缺乏将抑制IHedgehog或Gli2过表达对骨髓间充质干细胞成骨向分化的促进作用。在Tu等[16]的实验中,Runx2过表达可以促使Runx2基因缺失胚胎发育过程中的正常骨形成,却不能促使IHedgehog基因缺失胚胎发育过程中的正常骨形成,说明IHedgehog诱导骨髓间充质干细胞成骨向分化除了Runx2外,很有可能还需要其他因子的参与。Hedgehog家族成员可在多种组织和细胞中上调骨形态发生蛋白的表达,也有可能是IHedgehog通过上调骨形态发生蛋白的表达而促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨向分化。总之,Hedgehog调节骨髓间充质干细胞成骨向分化的分子机制较复杂且尚未完全清楚,仍有待充分阐明。 2.3 Hedgehog信号通路参与成骨细胞RANKL表达的调节 而近几年的研究却发现,在已分化成熟的成骨细胞中Hedgehog信号活性增强却能间接导致破骨细胞增殖分化的活动明显增强。美国Ohba等[17]研究人员发现,小鼠出生后随着成骨细胞的不断分化成熟,Hedgehog信号通路的活性也随之逐渐下降。选择性上调Hedgehog信号通路的活性时,会引起骨形成的增加,但形成的骨质非常脆弱、疏松,同时也出现明显的骨吸收,最终导致突变老鼠产生严重的骨质缺乏。这说明,增强成骨细胞Hedgehog信号通路的活性,成骨改建活动与骨吸收活动均有所增强,但是骨吸收的速度要强于骨形成的速度。其中,骨形成可能是由于Hedgehog信号通路活性增强后,促进成骨细胞的增殖分化和减缓成骨细胞凋亡;而骨吸收则是成熟的成骨细胞中Hedgehog信号通路活性增强,进而促进与破骨细胞增殖分化密切相关的RANKL的表达而加快骨的吸收。 2.3.1 Hedgehog信号通路通过上调甲状旁腺激素相关蛋白调节RANKL的表达 有研究表明,Hedgehog信号通路对成骨细胞RANKL基因表达的调控,离不开甲状旁腺相关蛋白的介导作用[18]。甲状旁腺激素相关蛋白是一种旁分泌因子,由关节周围的骨细胞和软骨细胞分泌,而其受体主要由成骨细胞、前肥大软骨细胞、早期肥大软骨细胞以及一些骨髓细胞分泌。成骨细胞经过甲状旁腺激素相关蛋白处理培养后表现为RANKL的表达量增加,而骨保护素的表达量下降;然而用Hedgehog信号通路抑制剂环杷明处理后,其骨保护素基因表达未见明显改变,反而甲状旁腺激素相关蛋白和RANKL的表达量却明显减少[19],这说明Hedgehog信号通路在调节已分化成熟的成骨细胞RANKL表达时,需要有甲状旁腺激素相关蛋白的介导作用,通过激活其下游一连串的信号分子而促进RANKL的表达。增强SHedgehog信号活性能增加正常小鼠颅骨成骨细胞RANKL和甲状旁腺激素相关蛋白的表达,而甲状旁腺激素相关蛋白基因敲除小鼠成骨细胞的SHedgehog信号活性增强却不能增加RANKL的表达[19],也证实了甲状旁腺激素相关蛋白在Hedgehog信号通路调节成骨细胞RANKL表达中的关键作用。 RANKL和骨保护素主要由成骨细胞表达,是调节破骨细胞增殖分化的主要调节因子,两者的动态平衡调控着破骨细胞的增殖与分化,而且两者均受Hedgehog信号通路调节。在选择性上调小鼠成骨细胞Hedgehog信号通路活性的实验中,成骨细胞中RANKL和骨保护素的表达均有增加[20],但RANKL的表达更为明显,而且甲状旁腺激素相关蛋白的表达量也有所增加[9],这些相关因子的增加也早于成骨细胞标记物的出现,表明RANKL的分泌表达以及Hedgehog信号通路对甲状旁腺激素相关蛋白表达的调节作用并不依赖于成骨细胞分化的程度。总之,增强Hedgehog信号通路活性而导致的骨吸收主要是通过甲状旁腺激素相关蛋白提高了RANKL与骨保护素的比例[21],从而促进破骨细胞的增殖分化。 2.3.2 甲状旁腺激素相关蛋白调节RANKL表达的作用机制 Mak等[19]通过基因修饰敲除小鼠Hedgehog信号的膜结合性功能抑制性分子Ptch,建立成骨细胞Hedgehog信号增强的小鼠模型,结果发现,小鼠破骨细胞形成增多,骨量减少,出现骨质疏松症,而且该症状的出现与蛋白激酶A、环磷酸腺苷应答元件结合蛋白被激活密切相关。同时,Kim等[22-24]的研究也表明,甲状旁腺激素相关蛋白诱导成骨细胞RANKL表达过程中,cAMP/PKA/CREB信号调控轴是重要的轴路之一,其中环磷酸腺苷应答元件结合蛋白是该下游调节轴中的枢纽,而且蛋白激酶A被激活后也同时抑制了骨保护素的表达。环磷酸腺苷应答元件结合蛋白作为一种转录因子,经小鼠ORMDL3基因进一步研究,环磷酸腺苷应答元件结合蛋白信号分子的作用机制得以揭示,即环磷酸腺苷应答元件结合蛋白激活后将与目标基因启动子区域上的CRE位点或CRE半位点结合,促进基因的转录翻译[25]。蛋白激酶A在骨形成中扮演着重要角色,其位于细胞质基质中,是一种惰性酶,由2个调节亚基和2个酶催化亚基组成。甲状旁腺激素相关蛋白与成骨细胞膜上的受体结合后,通过激活细胞膜上的腺苷酸环化酶,使其分解ATP产生环磷酸腺苷,环磷酸腺苷水平提高后与蛋白激酶A上的调节亚基结合,将蛋白激酶A激活,紧接着蛋白激酶A上的酶催化亚基被释放,然后进入到细胞核,促使环磷酸腺苷应答元件结合蛋白磷酸化并与RANKL基因的远端增强子结合而发挥作用[26-27]。激活cAMP/PKA/CREB信号调控轴需要甲状旁腺激素相关蛋白作为引物启动,而甲状旁腺激素相关蛋白本身又受到Hedgehog信号的调控,因此,上述信号分子构成了一条串联信号轴,调控成骨细胞RANKL的表达。 近几年的实验研究中发现,在受甲状旁腺激素相关蛋白激活作用的成骨细胞中,环磷酸腺苷应答元件结合蛋白结合到RANKL基因增强子上的CRE结合位点,并激活其活性,该过程需要有活化T细胞核因子的协同参与,当活化T细胞核因子缺乏时,甲状旁腺激素相关蛋白对RANKL基因增强子活性的增强作用将受到抑制,而甲状旁腺激素相关蛋白诱导的环磷酸腺苷应答元件结合蛋白磷酸化水平却没有受到明显影响[28-29],说明活化T细胞核因子在甲状旁腺激素相关蛋白激活RANKL基因活化表达的作用中是不可或缺的。活化T细胞核因子是一种转录因子,其家族成员包括:活化T细胞核因子1(NFATc2)、活化T细胞核因子2(NFATc1)、活化T细胞核因子3(NFATc4)、活化T细胞核因子4(NFATc3)和活化T细胞核因子5。活化T细胞核因子发挥作用的过程可分为2个步骤: ①活化T细胞核因子的激活与核质穿梭;②DNA结合和反式激活。活化T细胞核因子的激活与核质穿梭主要是通过钙调磷酸酶与组成型激酶的动力学相互作用来调控。活化T细胞核因子在激活靶基因时常常与其他转录因子发生协同作用,在静息状态下,活化T细胞核因子处于一个高度磷酸化的状态位于胞浆内,当磷酸化的环磷酸腺苷应答元件结合蛋白与细胞核内的RANKL基因增强子结合时,活化T细胞核因子经过钙调磷酸酶去磷酸化后,由胞浆被转运至细胞核,与环磷酸腺苷应答元件结合蛋白共同调节RANKL基因的表达。 Takami等[30]经实验发现,激活成骨细胞膜上的Ca2+通道载体可同时增加RANKL和骨保护素的表达,但RANKL的表达水平是骨保护素的2倍,表明增加成骨细胞内Ca2+浓度可提高RANKL/OPG的比例,从而促进破骨细胞的增殖分化,其作用机制与促进活化T细胞核因子过表达密切相关。 甲状旁腺激素相关蛋白是参与形成高钙血症的一个重要因子,引起血中Ca2+浓度提高[31-33],而成骨细胞膜上存在Ca2+感受器,当细胞外Ca2+浓度提高时,可引起Ca2+向胞内转运,导致细胞内Ca2+水平升高[34]。成骨细胞中的Ca2+浓度升高达到阈值时,可激活CN/NFAT信号调控轴,增加活化T细胞核因子的表达水平和转录活性,促进活化T细胞核因子转运并聚集于细胞核内,"
| [1] Doerks T, Copley RR, Schultz J, et al. Systematic identification of novel protein domain families associated with nuclear functions. Genome Res. 2002;12(1):47-56.[2] Cannonier SA, Sterling JA. The Role of Hedgehog Signaling in Tumor Induced Bone Disease. Cancers (Basel). 2015;7(3): 1658-1683.[3] McMahon AP, Ingham PW, Tabin CJ, et al. Developmental roles and clinical significance of Hedgehog signaling. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2003;53:1-114.[4] Chiang C, Litingtung Y, Lee E, et al. Cyclopia and defective axial patterning in mice lacking Sonic hedgehog gene function. Nature. 1996;383(6599):407-413.[5] Bitgood MJ, Shen L, McMahon AP, et al. Sertoli cell signaling by Desert hedgehog regulates the male germline. Curr Biol. 1996;6(3):298-304.[6] Mirsky R, Parmantier E, McMahon AP, et al. Schwann Cell‐Derived Desert Hedgehog Signals Nerve Sheath Formation. Ann New York Acad Sci. 1999;883(1):196-202.[7] Marigo V, Davey RA, Zuo Y, et al. Biochemical evidence that patched is the Hedgehog receptor. Nature. 1996; 384(6605): 176-179.[8] Murone M, Rosenthal A, de Sauvage FJ, et al. Sonic hedgehog signaling by the patched–smoothened receptor complex. Curr Biol. 1999;9(2):76-84.[9] Jemtland R, Divieti P, Lee K, et al. Hedgehog promotes primary osteoblast differentiation and increases PTHrP mRNA expression and iPTHrP secretion. Bone. 2003; 32(6):611-620.[10] Zhang XM, Ramalho-Santos M, McMahon AP, et al. Smoothened mutants reveal redundant roles for Shh and Ihh signaling including regulation of L/R symmetry by the mouse node. Cell. 2001;106(2):781-792.[11] McMahon AP. More surprises in the Hedgehog signaling pathway. Cell. 2000;100(2):185-188.[12] Amano K, Densmore MJ, Lanske B, et al. Conditional Deletion of Indian Hedgehog in Limb Mesenchyme Results in Complete Loss of Growth Plate Formation but Allows Mature Osteoblast Differentiation. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(12): 2262-2272.[13] Tian Y, Xu Y, Fu Q, et al. Osterix is required for Sonic hedgehog-induced osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cell differentiation. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2012;64(3):169-176.[14] Nakamura T, Naruse M, Chiba Y, et al. Novel hedgehog agonists promote osteoblast differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Physiol. 2015. 230(4):922-929.[15] Shimoyama A, Wada M, Ikeda F, et al. Ihh/Gli2 signaling promotes osteoblast differentiation by regulating Runx2 expression and function. Mol Biol Cell. 2007;18(7): 2411-2418.[16] Tu X, Joeng KS, Long F, et al. Indian hedgehog requires additional effectors besides Runx2 to induce osteoblast differentiation. Dev Biol. 2012;362(1):76-82.[17] Ohba S, Kawaguchi H, Kugimiya F, et al. Patched1 haploinsufficiency increases adult bone mass and modulates Gli3 repressor activity. Dev Cell. 2008;14(5): 689-699.[18] Ben-awadh AN, Delgado-Calle J, Tu X, et al. Parathyroid hormone receptor signaling induces bone resorption in the adult skeleton by directly regulating the RANKL gene in osteocytes. Endocrinology. 2014;155(8):2797-2809.[19] Mak KK, Bi Y, Wan C, et al. Hedgehog signaling in mature osteoblasts regulates bone formation and resorption by controlling PTHrP and RANKL expression. Dev Cell. 2008; 14(5):674-688.[20] Huang JC, Sakata T, Pfleger LL, et al. PTH differentially regulates expression of RANKL and OPG. J Bone Miner Res. 2004;19(2):235-244.[21] Boabaid F, Berry JE, Koh AJ, et al. The role of parathyroid hormone-related protein in the regulation of osteoclastogenesis by cementoblasts. J Periodontol. 2004; 75(9):1247-1254.[22] Kim S, Yamazaki M, Shevde NK, et al. Transcriptional control of receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand by the protein kinase A activator forskolin and the transmembrane glycoprotein 130-activating cytokine, oncostatin M, is exerted through multiple distal enhancers. Mol Endocrinol. 2007; 21(1):197-214.[23] Fu Q, Manolagas SC, and O'Brien CA, et al. Parathyroid hormone controls receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand gene expression via a distant transcriptional enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26(17):6453-6468.[24] Fu Q, Jilka RL, Manolagas SC, et al. Parathyroid hormone stimulates receptor activator of NFkappa B ligand and inhibits osteoprotegerin expression via protein kinase A activation of cAMP-response element-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277(50):48868-48875.[25] Zhuang LL, Jin R, Zhu LH, et al. Promoter characterization and role of cAMP/PKA/CREB in the basal transcription of the mouse ORMDL3 gene. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e60630.[26] Sands WA, Palmer TM. Regulating gene transcription in response to cyclic AMP elevation. Cell Signal. 2008;20(3): 460-466.[27] Bidwell P, Joh K, Leaver HA, et al. Prostaglandin E2 activates cAMP response element-binding protein in glioma cells via a signaling pathway involving PKA-dependent inhibition of ERK. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2010;91(1-2):18-29.[28] Park HJ, Baek K, Baek JH, et al. The cooperation of CREB and NFAT is required for PTHrP-induced RANKL expression in mouse osteoblastic cells. J Cell Physiol. 2015;230(3): 667-679.[29] Lee HL, Bae OY, Baek KH, et al. High extracellular calcium-induced NFATc3 regulates the expression of receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand in osteoblasts. Bone. 2011;49(2): 242-249.[30] Takami M, Takahashi N, Udagawa N, et al. Intracellular calcium and protein kinase C mediate expression of receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand and osteoprotegerin in osteoblasts. Endocrinology. 2000;141(12):4711-4719.[31] Datta NS, Abou-Samra AB. PTH and PTHrP signaling in osteoblasts. Cell Signal. 2009;21(8):1245-1254.[32] Akhtari M, Mansuri J, Newman KA, et al. Biology of breast cancer bone metastasis. Cancer Biol Ther. 2008;7(1):3-9.[33] Hirai T, Kobayashi T, Nishimori S, et al. Bone Is a Major Target of PTH/PTHrP Receptor Signaling in Regulation of Fetal Blood Calcium Homeostasis. Endocrinology. 2015; 156(8):2774-2780.[34] Zayzafoon M. Calcium/calmodulin signaling controls osteoblast growth and differentiation. J Cell Biochem. 2006;97(1):56-70.[35] Shin J, Jang H, Lin J, et al. PKCbeta positively regulates RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by inactivating GSK-3beta. Mol Cells. 2014;37(10):747-752.[36] Yao J, Li J, Zhou L, et al. Protein kinase C inhibitor, GF109203X attenuates osteoclastogenesis, bone resorption and RANKL-induced NF-kappaB and NFAT activity. J Cell Physiol. 2015;230(6):1235-1242.[37] Malaval L, Prideaux M, Dallas SL, et al. Parathyroid Hormone Induces Bone Cell Motility and Loss of Mature Osteocyte Phenotype through L-Calcium Channel Dependent and Independent Mechanisms. Plos One. 2015;10(5):e0125731. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [3] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [4] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [5] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [6] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [7] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [8] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [9] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [10] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [11] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [12] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [13] | Huang Chuanjun, Zou Yu, Zhou Xiaoting, Zhu Yangqing, Qian Wei, Zhang Wei, Liu Xing. Transplantation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated in RADA16-BDNF hydrogel promotes neurological recovery in an intracerebral hemorrhage rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 510-515. |
| [14] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [15] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||