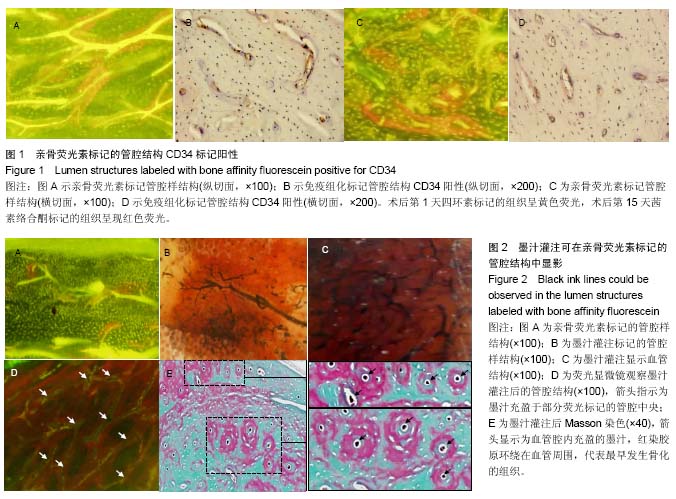
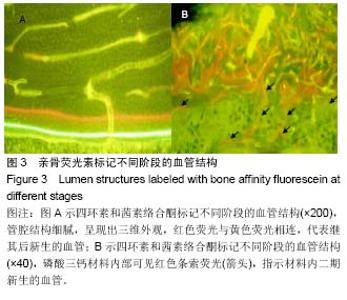
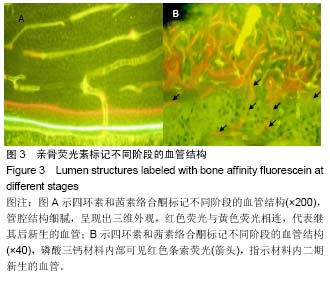
| [1] Wang L, Fan H, Zhang ZY, et al. Osteogenesis and angiogenesis of tissue-engineered bone constructed by prevascularized β-tricalcium phosphate scaffold and mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials. 2010;31(36):9452-9461. [2] 李文革, 郭永智, 王亚军,等. 骨折早期血管生成与骨形成的免疫组化及超微结构研究[J]. 吉林大学学报医学版, 1999, 25(3):251-252.[3] Khojasteh A, Fahimipour F, Eslaminejad MB, et al. Development of PLGA-coated β-TCP scaffolds containing VEGF for bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;69:780-788.[4] Bose S, Tarafder S. Calcium phosphate ceramic systems in growth factor and drug delivery for bone tissue engineering: A review. Acta Biomater. 2012;8(4):1401-1421.[5] Sukul M, Nguyen TB, Min YK, et al. Effect of Local Sustainable Release of BMP2-VEGF from Nano-Cellulose Loaded in Sponge Biphasic Calcium Phosphate on Bone Regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A. 2015;21(11-12):1822-1836. [6] Çak?r-Özkan N, E?ri S, Bekar E, et al. The Use of Sequential VEGF- and BMP2-Releasing Biodegradable Scaffolds in Rabbit Mandibular Defects. J Oral Maxillofacial Surg. 2017; 75(1) : 221. e1-221.e14.[7] 佟玮玮, 王健平, 赵千宁,等. 纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66盖髓对造牙本质细胞及微血管的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(16):2418-2424.[8] Ackermann M, Konerding MA. Vascular casting for the study of vascular morphogenesis. Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1214 (1214):49-66.[9] Wu T, Nan KH, Chen JD, et al. A new bone repair scaffold combined with chitosan/hydroxyapatite and sustained releasing icariin. Chin Sci Bull. 2009;54(17): 2953-2961.[10] Prisby RD. Bone marrow blood vessel ossification and “microvascular dead space” in rat and human long bone. Bone. 2014;64:195-203.[11] Fujita Y, Goto S, Ichikawa M, et al. Effect of dietary calcium deficiency and altered diet hardness on the jawbone growth: A micro-CT and bone histomorphometric study in rats. Arch Oral Biol. 2016;72:200.[12] Wang RK, An L. Doppler optical micro-angiography for volumetric imaging of vascular perfusion in vivo. Opt Express. 2009;17(11):8926-8940.[13] 简月奎, 吴雪晖, 田晓滨,等. 不同方法显像骨组织微血管的对比研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2008, 16(7):534-536.[14] 王亦璁.骨与关节损伤[M]. 3版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2001: 150.[15] 胥少汀,葛宝丰,徐印坎.实用骨科学[M]. 3版.北京:人民军医出版社,2005: 330-337.[16] Berendsen AD, Olsen BR. How Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-A (VEGF) Regulates Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 2014; 62(2):103.[17] Mark H, Penington A, Nannmark U, et al. Microvascular invasion during endochondral ossification in experimental fractures in rats. Bone. 2004; 35(2):535-542. [18] Sinder BP, Pettit AR, Mccauley LK. Macrophages: Their Emerging Roles in Bone. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(12): 2140-2149.[19] Raggatt LJ, Wullschleger ME, Alexander KA, et al. Fracture Healing via Periosteal Callus Formation Requires Macrophages for Both Initiation and Progression of Early Endochondral Ossification. Am J Pathol. 2014;184(12): 3192-3204.[20] 左艳萍, 苑迎娇, 刘昕,等.上颌矢状扩弓的四环素荧光积分光密度分析[J]. 河北医科大学学报, 2014, 35(1):84-86.[21] 吴拮, 吕荣, 孟国林,等. 钛合金、人工骨材料厚切片再研磨后显示新生骨-荧光双标法[J]. 临床与实验病理学杂志, 2014, 30(10): 1186-1187.[22] Bensimonbrito A, Cardeira J, Dionísio G, et al. Revisiting in vivo staining with alizarin red S--a valuable approach to analyse zebrafish skeletal mineralization during development and regeneration. BMC Dev Biol. 2016;16(1):1-10.[23] Wang H, Liu J, Tao S, et al. Tetracycline-grafted PLGA nanoparticles as bone-targeting drug delivery system. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015;10:5671-5685.[24] Buenzli PR, Pivonka P, Smith DW. Bone refilling in cortical basic multicellular units: insights into tetracycline double labelling from a computational model. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2014;13(1):185-203.[25] Roelofs AJ, Stewart CA, Sun S, et al. Influence of bone affinity on the skeletal distribution of fluorescently labeled bisphosphonates in vivo. J Bone Miner Res. 2012;27(4):835-847.[26] 苏畅, 梁林, 李楠,等. 骨靶向化合物研究进展[J]. 武警后勤学院学报医学版, 2007, 16(2):205-208.[27] 郭建刚,赵然,侯桂英,等.骨组织成分与Masson三色染色反应的关系分析[J].中医正骨,2001,13(11):5-6.[28] 谭丽思, 林晓萍, 刘尧,等. 组织工程化骨修复犬牙槽骨缺损的组织学观察[J]. 解剖科学进展, 2010, 16(6):492-495.[29] Jin SK, Lee JH, Hong JH, et al. Enhancement of osseointegration of artificial ligament by nano-hydroxyapatite and bone morphogenic protein-2 into the rabbit femur. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016;13(3):284-296.[30] Sellgren KL, Ma T. Effects of flow configuration on bone tissue engineering using human mesenchymal stem cells in 3D chitosan composite scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014; 103(8):2509-2520.[31] Hc KD, Jgc W, Phm S, et al. Bone inductive properties of rhBMP-2 loaded porous calcium phosphate cement implants in cranial defects in rabbits. Biomaterials. 2004;25(11):2123-2132.[32] Kroese-Deutman HC, Ruhé PQ, Spauwen PH, et al. Bone inductive properties of rhBMP-2 loaded porous calcium phosphate cement implants inserted at an ectopic site in rabbits. Biomaterials. 2005;26(10):1131-1138. |