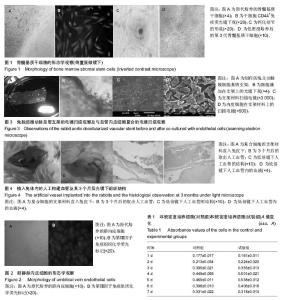
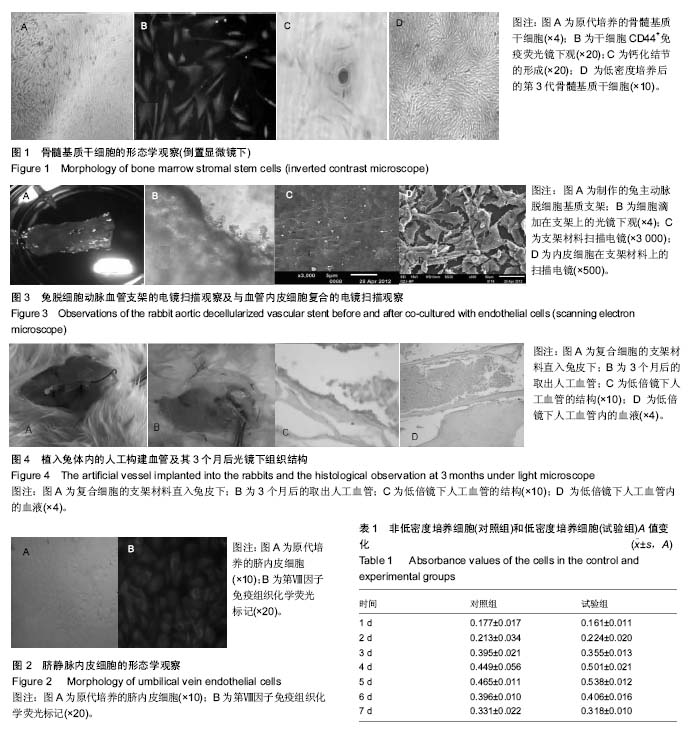
| [1] 杨兴华,彭琳,杨旭峰,等.低密度培养兔骨髓基质干细胞的生物学特性[J].山东医药,2012,52(41):8-11.[2] Prockop DJ, Sekiya I, Colter DC.isolation and characterization of rapidkly self-renewing stem cells from cultures of humen marrow stomal cells.cytotherapy.2001;3(5):396-396.[3] 穆亚妹,杜冠华.血管内皮细胞体外培养方法的研究进展[J].国外医学药学分册,2004, 31(6):361-365.[4] 黄华梅,谢德明,罗洁芳.应用脱细胞血管基质构建组织工程血管的初步研究[J].中国病理生理杂志,2008,24 (4 ):792-796.[5] 史雨林,刘彦普,张海霞.组织工程骨血管化的研究进展[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志,2011,38(2):242-245.[6] Kanczler JM, Ginty PJ, White L, et al. The effect of the delivery of vascular endothelial growth factor and bone morphogenic protein-2 to osteoprogenitor cell populations on bone formation.Biomaterias.2010;31(6):1242-1250.[7] 赵亮,李敏.间充质干细胞与组织工程血管[J].中国生物医学工程学报, 2013, 32(2):220-225.[8] 李琪佳,郭静,甘洪全,等.成骨细胞及血管内皮细胞复合同种异体颗粒骨治疗大鼠股骨头坏死[J].第三军医大学学报,2011,33(6): 591-595.[9] 李富航,靳宇飞,毕龙,等.P物质对骨髓基质干细胞来源的成骨细胞与内皮细胞体外联合培养体系的影响[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2014;16(5):427-432.[10] 汪川,李京倬,辛毅,等.人脱细胞脐动脉支架与兔骨髓内皮祖细胞构建组织工程血管的实验研究[J].心肺血管病杂志,2014, 33(4): 586-591.[11] Zhang HW, Chen XL, Lin ZY,et al.Fibronectin chorused cohesion between endothelial progenitor cells and mesenchymal stem cells of mouse bone marrow. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand).2015;61(2):26-32.[12] 肖友华,陈杨,焦海峰,等.组织工程血管支架制备工艺的研究进展[J].高分子通报,2012,10:21-25. [13] 赵亮,徐艳丽,何孟,等.骨髓间充质干细胞复合蛛丝蛋白血管支架构建小直径组织工程血管的研究[J].中国生物医学工程学报, 2015,34(1):70-76.[14] 刘宾,张蔓菁,夏炜,等.冻干法保存脱细胞组织工程血管支架的实验研究[J].中国美容医学,2010,19(2):218-221. [15] Hodonsky C, Mundada L, Wang S, et al. Effects of scaffold material used in cardiovascular surgery on mesenchymal stem cells and cardiac progenitorcells. Ann Thorac Surg. 2015;99(2):605-11.[16] 王德元,白峰,高文魁,等.复合血管内皮细胞的不同孔径磷酸钙陶瓷体内血管化的比较研究[J]. 现代生物医学进展,2014, 14(20): 3815-3901 |