Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (51): 7731-7737.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.51.020
Previous Articles Next Articles
Dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine signaling pathways in the pathogenesis of spinal cord injury-induced osteoporosis: new theory and novel therapeutic strategies
Zhang Miao1, Zhang Xu-ran1, Li Rui2, Sun Yu3
- 1 Third Orthopaedics Ward, Fuxin Central Hospital, Fuxin 123000, Liaoning Province, China
2 Bethune Second Hospital, Changchun 130041, Jilin Province, China
3 Department of Orthopaedics (Joint Surgery and Sports Medicine), First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110001, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2016-10-29Online:2016-12-09Published:2016-12-09 -
Contact:Corresponding author: Sun Yu, Master, Lecturer, Attending physician, Department of Orthopaedics (Joint Surgery and Sports Medicine), First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110001, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Zhang Miao, Master, Associate chief physician, Third Orthopaedics Ward, Fuxin Central Hospital, Fuxin 123000, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the National Key Basic Research Development Program of China (973 Program), No. 2014LB542200
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Miao, Zhang Xu-ran, Li Rui, Sun Yu. Dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine signaling pathways in the pathogenesis of spinal cord injury-induced osteoporosis: new theory and novel therapeutic strategies[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(51): 7731-7737.
share this article
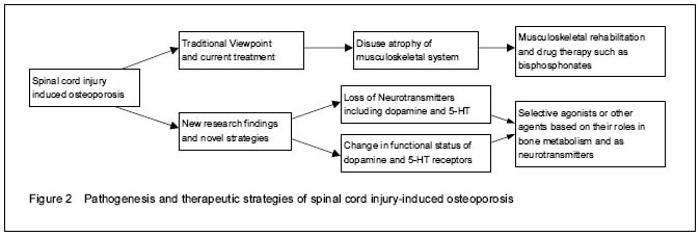
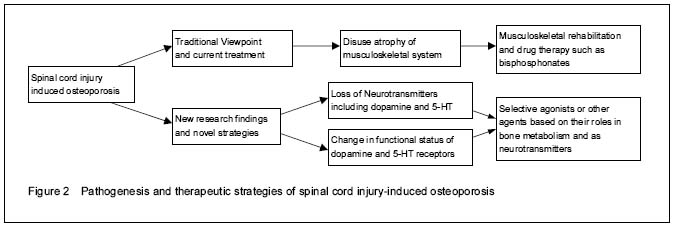
DA and 5-HT as neurotransmitters in spinal cord and their roles in modulating bone metabolism In SCI patients with lower limb paralysis, their upper extremities with biological loading conditions above spinal cord lesion level were found decrease in bone mineral content[14], which indicated that neurological and hormone disorders associated with SCI could be the underlying mechanism of osteoporosis, especially the changes in DA and 5-HT. This was also supported by the reduced anabolic functions of osteoblasts and magnified activity of osteoclasts showed by in vivo research of SCI[15]. 5-HT is a multifunctional molecule targeting on multiple tissues, converted from 5-hydroxy-L-tryptophan (5-HTP) in a reaction catalyzed by tryptophan hydroxylase (Tph)[16]. 5-HT is mostly gut-derived, produced by the enterochromaffin cells in duodenum, mediating peristalsis and cardiovascular functions[17]. While in the spinal neural networks, 5-HT is synthesized in brainstem as an important neurotransmitter regulating locomotion system[18]. 5-HT exerts biological effects via a large group of membrane"
| [1] Pelletier CA, Dumont FS, Leblond J, et al. Self-report of one-year fracture incidence and osteoporosis prevalence in a community cohort of canadians with spinal cord injury. Top Spinal Cord Inj Rehabil. 2014; 20(4):302-309. [2] Coupaud S, McLean AN, Purcell M, et al. Decreases in bone mineral density at cortical and trabecular sites in the tibia and femur during the first year of spinal cord injury. Bone. 2015;74:69-75. [3] Gifre L, Vidal J, Carrasco J, et al. Incidence of skeletal fractures after traumatic spinal cord injury: a 10-year follow-up study. Clin Rehabil. 2014;28(4):361-369. [4] Jiang SD, Jiang LS, Dai LY. Mechanisms of osteoporosis in spinal cord injury. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2006;65(5):555-565.[5] Galea MP. Spinal cord injury and physical activity: preservation of the body. Spinal Cord. 2012;50(5): 344-351.[6] Dolbow DR, Gorgey AS, Daniels JA, et al. The effects of spinal cord injury and exercise on bone mass: a literature review. NeuroRehabilitation. 2011;29(3): 261-269. [7] Chang KV, Hung CY, Chen WS, et al. Effectiveness of bisphosphonate analogues and functional electrical stimulation on attenuating post-injury osteoporosis in spinal cord injury patients- a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2013;8(11):e81124. [8] Nyandege AN, Slattum PW, Harpe SE. Risk of fracture and the concomitant use of bisphosphonates with osteoporosis-inducing medications. Ann Pharmacother. 2015;49(4):437-447.[9] McGreevy C, Williams D. Safety of drugs used in the treatment of osteoporosis. Ther Adv Drug Saf. 2011; 2(4):159-172. [10] Beggs LA, Ye F, Ghosh P, et al. Sclerostin inhibition prevents spinal cord injury-induced cancellous bone loss. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(4):681-689. [11] Maïmoun L, Couret I, Mariano-Goulart D, et al. Changes in osteoprotegerin/RANKL system, bone mineral density, and bone biochemicals markers in patients with recent spinal cord injury. Calcif Tissue Int. 2005;76(6):404-411.[12] Cummings SR, San Martin J, McClung MR, et al. Denosumab for prevention of fractures in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(8):756-765.[13] Morse LR, Sudhakar S, Danilack V, et al. Association between sclerostin and bone density in chronic spinal cord injury. J Bone Miner Res. 2012;27(2):352-359. [14] Garland DE, Stewart CA, Adkins RH, et al. Osteoporosis after spinal cord injury. J Orthop Res. 1992;10(3):371-378.[15] Jiang SD, Yang YH, Chen JW, et al. Isolated osteoblasts from spinal cord-injured rats respond less to mechanical loading as compared with those from hindlimb-immobilized rats. J Spinal Cord Med. 2013; 36(3):220-224. [16] Karsenty G, Yadav VK. Regulation of bone mass by serotonin: molecular biology and therapeutic implications. Annu Rev Med. 2011;62:323-331.[17] Amireault P, Sibon D, Côté F. Life without peripheral serotonin: insights from tryptophan hydroxylase 1 knockout mice reveal the existence of paracrine/autocrine serotonergic networks. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013;4(1):64-71. [18] Ghosh M, Pearse DD. The role of the serotonergic system in locomotor recovery after spinal cord injury. Front Neural Circuits. 2015;8:151. [19] Haney EM, Warden SJ. Skeletal effects of serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine) transporter inhibition: evidence from clinical studies. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2008;8(2):133-145.[20] Ducy P. 5-HT and bone biology. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2011;11(1):34-38. [21] Karsenty G, Gershon MD. The importance of the gastrointestinal tract in the control of bone mass accrual. Gastroenterology. 2011;141(2):439-442.[22] Westbroek I, van der Plas A, de Rooij KE, et al. Expression of serotonin receptors in bone. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(31):28961-28968.[23] Cosentino M, Marino F, Maestroni GJ. Sympathoadrenergic modulation of hematopoiesis: a review of available evidence and of therapeutic perspectives. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015;9:302.[24] Lambert AM, Bonkowsky JL, Masino MA. The conserved dopaminergic diencephalospinal tract mediates vertebrate locomotor development in zebrafish larvae. J Neurosci. 2012;32(39): 13488-13500.[25] Cobacho N, de la Calle JL, Paíno CL. Dopaminergic modulation of neuropathic pain: analgesia in rats by a D2-type receptor agonist. Brain Res Bull. 2014;106:62-71.[26] Ondo WG, He Y, Rajasekaran S, et al. Clinical correlates of 6-hydroxydopamine injections into A11 dopaminergic neurons in rats: a possible model for restless legs syndrome. Mov Disord. 2000;15(1): 154-158.[27] Miyake H, Nagashima K, Onigata K, et al. Allelic variations of the D2 dopamine receptor gene in children with idiopathic short stature. J Hum Genet. 1999;44(1): 26-29.[28] Yamada Y, Ando F, Niino N, et al. Association of a polymorphism of the dopamine receptor D4 gene with bone mineral density in Japanese men. J Hum Genet. 2003;48(12):629-633. [29] Hanami K, Nakano K, Saito K, et al. Dopamine D2-like receptor signaling suppresses human osteoclastogenesis. Bone. 2013;56(1):1-8. [30] Hanami K, Nakano K, Tanaka Y. Dopamine receptor signaling regulates human osteoclastogenesis. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2013;36(1):35-39.[31] Rizzoli R, Cooper C, Reginster JY, et al. Antidepressant medications and osteoporosis. Bone. 2012;51(3): 606-613. [32] Eom CS, Lee HK, Ye S, et al. Use of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and risk of fracture: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Bone Miner Res. 2012; 27(5): 1186-1195.[33] Tsapakis EM, Gamie Z, Tran GT, et al. The adverse skeletal effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Eur Psychiatry. 2012;27(3):156-169.[34] Meyer JM, Lehman D. Bone mineral density in male schizophrenia patients: a review. Ann Clin Psychiatry. 2006;18(1):43-48.[35] Wang M, Hou R, Jian J, et al. Effects of antipsychotics on bone mineral density and prolactin levels in patients with schizophrenia: a 12-month prospective study. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2014;29(2):183-189.[36] O'Keane V. Antipsychotic-induced hyperprolactinaemia, hypogonadism and osteoporosis in the treatment of schizophrenia. J Psychopharmacol. 2008;22(2 Suppl): 70-75.[37] Kunimatsu T, Kimura J, Funabashi H, et al. The antipsychotics haloperidol and chlorpromazine increase bone metabolism and induce osteopenia in female rats. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2010;58(3):360-368. [38] Lapointe NP, Guertin PA. Synergistic effects of D1/5 and 5-HT1A/7 receptor agonists on locomotor movement induction in complete spinal cord-transected mice. J Neurophysiol. 2008;100(1):160-168.[39] Lapointe NP, Rouleau P, Ung RV, et al. Specific role of dopamine D1 receptors in spinal network activation and rhythmic movement induction in vertebrates. J Physiol. 2009;587(Pt 7):1499-1511. [40] Jiang W, Huang Y, He F, et al. Dopamine D1 Receptor Agonist A-68930 Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation, Controls Inflammation, and Alleviates Histopathology in a Rat Model of Spinal Cord Injury. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41(6):E330-334.[41] Ganzer PD, Manohar A, Shumsky JS, et al. Therapy induces widespread reorganization of motor cortex after complete spinal transection that supports motor recovery. Exp Neurol. 2016;279:1-12. [42] Cornide-Petronio ME, Fernández-López B, Barreiro-Iglesias A, et al. Traumatic injury induces changes in the expression of the serotonin 1A receptor in the spinal cord of lampreys. Neuropharmacology. 2014;77:369-378.[43] Murray KC, Stephens MJ, Ballou EW, et al. Motoneuron excitability and muscle spasms are regulated by 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C receptor activity. J Neurophysiol. 2011;105(2):731-748. [44] S?awińska U, Miazga K, Jordan LM. 5-HT? and 5-HT? receptor agonists facilitate plantar stepping in chronic spinal rats through actions on different populations of spinal neurons. Front Neural Circuits. 2014;8:95. [45] Demirel G, Yilmaz H, Paker N, et al. Osteoporosis after spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 1998;36(12):822-825.[46] Ducy P, Karsenty G. The two faces of serotonin in bone biology. J Cell Biol. 2010;191(1):7-13. [47] Otake T, Ieshima H, Ishida H, et al. Bone atrophy in complex regional pain syndrome patients measured by microdensitometry. Can J Anaesth. 1998;45(9): 831-838. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Tang Hui, Yao Zhihao, Luo Daowen, Peng Shuanglin, Yang Shuanglin, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. High fat and high sugar diet combined with streptozotocin to establish a rat model of type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1207-1211. |
| [3] | Li Zhongfeng, Chen Minghai, Fan Yinuo, Wei Qiushi, He Wei, Chen Zhenqiu. Mechanism of Yougui Yin for steroid-induced femoral head necrosis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1256-1263. |
| [4] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [5] | Hou Guangyuan, Zhang Jixue, Zhang Zhijun, Meng Xianghui, Duan Wen, Gao Weilu. Bone cement pedicle screw fixation and fusion in the treatment of degenerative spinal disease with osteoporosis: one-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 878-883. |
| [6] | Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi, Liao Jianzhao, Zhang Xiaoyun, Zhang Xuan. Pathogenesis of hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head and the target effect of related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 935-941. |
| [7] | Xiao Fangjun, Chen Shudong, Luan Jiyao, Hou Yu, He Kun, Lin Dingkun. An insight into the mechanism of Salvia miltiorrhiza intervention on osteoporosis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 772-778. |
| [8] | Liu Bo, Chen Xianghe, Yang Kang, Yu Huilin, Lu Pengcheng. Mechanism of DNA methylation in exercise intervention for osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 791-797. |
| [9] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [10] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [11] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [12] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [13] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [14] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [15] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||