Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (50): 7494-7499.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.50.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
Immune function regulation by bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in rats undergoing heart transplantation
Zhao Min, Li Xiu-fen
- School of Basic Medicine, Shuqing Medical College, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
-
Revised:2016-10-31Online:2016-12-02Published:2016-12-02 -
About author:Zhao Min, Master, Lecturer, School of Basic Medicine, Shuqing Medical College, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhao Min, Li Xiu-fen. Immune function regulation by bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in rats undergoing heart transplantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(50): 7494-7499.
share this article
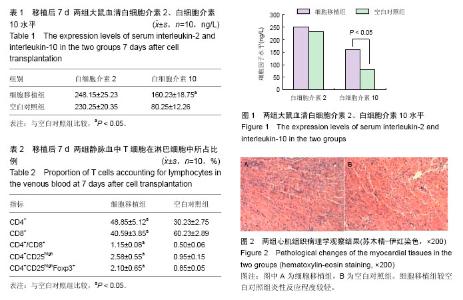
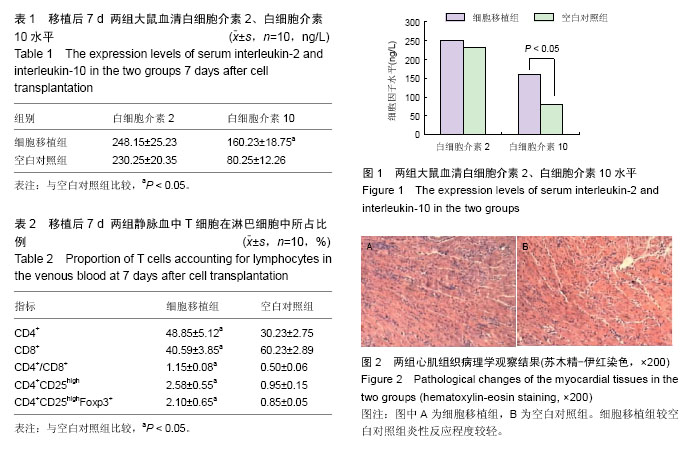
2.1 实验动物数量分析 20只Wistar大鼠进入最终的结果分析。 2.2 两组移植心脏的存活时间 细胞移植组心脏存活时间为(14.25±2.15) d,空白对照组心脏存活时间为(7.15±1.35) d,细胞移植组显著长于空白对照组(P < 0.05)。 2.3 两组大鼠血清白细胞介素2、白细胞介素10水平 两组血清白细胞介素2水平差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。细胞移植组血清白细胞介素10水平显著高于空白对照组(P < 0.05),见表1,图1。 2.4 两组静脉血中T细胞占总淋巴细胞的比例 移植后7 d,细胞移植组CD4+、CD4+/CD8+、CD4+ CD25high、CD4+CD25high Foxp3+ T细胞占总淋巴细胞的比例均显著高于空白对照组(P < 0.05),CD8+ T细胞占总淋巴细胞的比例显著低于空白对照组(P < 0.05),见表2。 2.5 两组心肌组织病理学观察结果 移植后7 d,空白对照组心肌组织有淋巴细胞以及单核细胞大量浸润现象,有末梢小血管内血栓形成这一超急性排斥反应的特征病变,存在明显的心肌间质水肿、出血,存在不同程度的心肌黏液性坏死和心肌细胞变性坏死;细胞移植组心肌组织中存在少量的淋巴细胞浸润,出现灶性心肌细胞损害,心肌间质可观察到轻微出血和水肿,较空白对照组炎性反应程度较轻(图2)。"
| [1] 沈兴,余更生,田杰,等.兔骨髓间充质干细胞心脏移植治疗扩张型心肌病的实验研究[J].第三军医大学学报,2008, 30(12):1159-1162.[2] 赵桂峰,范英昌,姜希娟,等.丹酚酸B对内皮祖细胞与骨髓间充质干细胞联合心脏移植后增殖状况的影响[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2012,32(5):671-675.[3] 刘德忠,刘奎利,金建刚,等.受者同系骨髓间充质干细胞对大鼠心脏移植急性排斥反应的影响[J].中华老年多器官疾病杂志,2011,10(6):536-540.[4] Barrett AJ, Savani BN. Stem cell transplantation with reduced-intensity conditioning regimens: a review of ten years experience with new transplant concepts and new therapeutic agents. Leukemia. 2006;20(10):1661-1672.[5] Rezvani K, Yong AS, Mielke S, et al. Lymphodepletion is permissive to the development of spontaneous T-cell responses to the self-antigen PR1 early after allogeneic stem cell transplantation and in patients with acute myeloid leukemia undergoing WT1 peptide vaccination following chemotherapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2012;61(7):1125-1136.[6] 章传凯.骨髓间充质干细胞联合IL-6单克隆抗体诱导心脏移植免疫耐受的研究[D].苏州:苏州大学,2012.[7] 刘德忠,刘奎利,金建刚,等.套管法建立同系与异系大鼠颈部心移植模型的比较[J].解剖学杂志,2010,33(1):107- 110.[8] 魏长江.骨髓间充质干细胞外周中枢联合预处理诱导异种心脏移植免疫耐受的研究[D].苏州:苏州大学,2009.[9] 刘奎利,刘德忠,金建刚,等.异体脐带间充质干细胞对大鼠心脏移植的免疫调节[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(6):1048-1052.[10] Loh Y, Oyama Y, Statkute L, et al. Autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with cardiac dysfunction: feasibility and reversibility of ventricular and valvular dysfunction with transplant-induced remission. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2007;40(1):47-53.[11] Nakane T, Nakamae H, Koh H, et al. Heart rate variability during and after peripheral blood stem cell leukapheresis in autologous transplant patients and allogeneic transplant donors. Int J Hematol. 2010;91(3): 478-484.[12] Yerebakan C, Kaminski A, Westphal B, et al. Impact of preoperative left ventricular function and time from infarction on the long-term benefits after intramyocardial CD133(+) bone marrow stem cell transplant. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011;142(6): 1530-1539.[13] 朱震,沈振亚,陈海军,等.MSCs修饰受体胸腺对异种心脏移植免疫排斥反应的作用研究[J].中国医药科学,2012, 2(21):35-38.[14] Ruf S, Behnke-Hall K, Gruhn B, et al. Comparison of six different specimen types for Epstein-Barr viral load quantification in peripheral blood of pediatric patients after heart transplantation or after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. J Clin Virol. 2012;53(3):186-194.[15] Nakane T, Nakamae H, Muro T, et al. Cardiac and autonomic nerve function after reduced-intensity stem cell transplantation for hematologic malignancy in patients with pre-transplant cardiac dysfunction. Ann Hematol. 2009;88(9):871-879.[16] 刘德忠,石炳毅,刘奎利,等.受者同系骨髓间充质干细胞对心脏移植大鼠的免疫调节作用[J].解放军医学杂志,2012, 37(3):185-189.[17] 刘俊东,唐滔,吴晓明,等.SHH转染骨髓间充质干细胞心肌移植后成活与分化[J].中国医师杂志,2014,16(2):203- 206,210.[18] Paul A, Chen G, Khan A, et al. Genipin-cross-linked microencapsulated human adipose stem cells augment transplant retention resulting in attenuation of chronically infarcted rat heart fibrosis and cardiac dysfunction. Cell Transplant. 2012;21(12):2735-2751.[19] Melenhorst JJ, Tian X, Xu D, et al. Cytopenia and leukocyte recovery shape cytokine fluctuations after myeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Haematologica. 2012;97(6):867-873.[20] Jimenez-Zepeda VH, Franke N, Reece DE, et al. Autologous stem cell transplant is an effective therapy for carefully selected patients with AL amyloidosis: experience of a single institution. Br J Haematol. 2014; 164(5):722-728.[21] 张长海.雷公藤甲素对HCN4基因修饰大鼠MSCs同种异体心脏移植后细胞存活影响的研究[D].重庆:第三军医大学,2013.[22] Majhail NS, Ness KK, Burns LJ, et al. Late effects in survivors of Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma treated with autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation: a report from the bone marrow transplant survivor study. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2007;13(10):1153-1159.[23] 余鹏程.供者骨髓间充质干细胞对大鼠肾移植慢性排斥的作用及其免疫调节机制的初步研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2011.[24] 徐长宪.鼠干细胞(胚胎、间充质)体外定向分化为心肌细胞及心脏移植的动物试验研究[D].济南:山东大学,2004.[25] Yanik GA, Horowitz MM, Weisdorf DJ, et al. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor: enbrel (etanercept) for the treatment of idiopathic pneumonia syndrome after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: blood and marrow transplant clinical trials network protocol. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014;20(6): 858-864.[26] 胡江文.TGF-β1基因转染联合BMC/MSCs诱导嵌合体在异种心脏移植免疫耐受中作用的实验研究[D]. 苏州:苏州大学,2006.[27] Brunvand MW, Bitter M. Amyloidosis relapsing after autologous stem cell transplantation treated with bortezomib: normalization of detectable serum-free light chains and reversal of tissue damage with improved suitability for transplant. Haematologica. 2010;95(3):519-521.[28] 杨超.骨髓间充质干细胞对心脏移植免疫调节作用的实验研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2008.[29] 翟光地.在异种心脏移植免疫耐受的诱导中MSCs修饰胸腺的可行性实验研究[D]. 苏州:苏州大学,2006.[30] 朱震,陈海军,沈振亚.MSCs修饰受体胸腺的异种心脏移植中Th2细胞的表达研究[J].中国医药科学,2012,2(20): 24-26,34.[31] 王海涛.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞诱导同种异体心脏移植免疫耐受[D].上海:复旦大学,2007.[32] 杨超,肖诗亮,刘成珪,等.间充质干细胞对大鼠心脏移植免疫的调节作用[J].临床心血管病杂志,2008,24(4): 307-310.[33] Martin-Rendon E, Sweeney D, Lu F, et al. 5-Azacytidine-treated human mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells derived from umbilical cord, cord blood and bone marrow do not generate cardiomyocytes in vitro at high frequencies.Vox Sang. 2008;95(2):137-148.[34] Mazo M, Gavira JJ, Abizanda G, et al. Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells exerts a greater long-term effect than bone marrow mononuclear cells in a chronic myocardial infarction model in rat. Cell Transplant. 2010;19(3):313-328.[35] 杨华.混合嵌合体在异种心脏移植产生免疫耐受作用中的实验研究[D]. 苏州:苏州大学,2006.[36] 汤天生.同基因骨髓间充质干细胞诱导大鼠心脏移植免疫耐受[D].福州:福建医科大学,2012.[37] Jui HY, Lin CH, Hsu WT, et al. Autologous mesenchymal stem cells prevent transplant arteriosclerosis by enhancing local expression of interleukin-10, interferon-γ, and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Cell Transplant. 2012;21(5):971-984.[38] McIver Z, Melenhorst JJ, Wu C, et al. Donor lymphocyte count and thymic activity predict lymphocyte recovery and outcomes after matched-sibling hematopoietic stem cell transplant. Haematologica. 2013;98(3):346-352.[39] 刘奎利.大鼠脐带来源间充质干细胞生物学特性及其对移植免疫耐受作用的研究[D].北京:军医进修学院, 2009.[40] 黄小进,王效民.骨髓间充质干细胞在移植免疫方面的研究进展[J].现代生物医学进展,2008,8(9):1771-1773. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [3] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [4] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [5] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [6] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [7] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [8] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [9] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [10] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [11] | Chen Junyi, Wang Ning, Peng Chengfei, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Bei Chaoyong. Decalcified bone matrix and lentivirus-mediated silencing of P75 neurotrophin receptor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| [12] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [13] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [14] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [15] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||