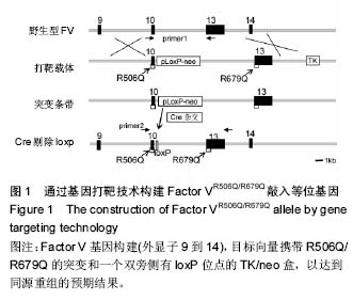
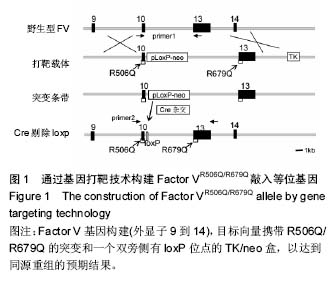
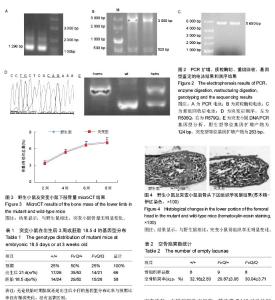
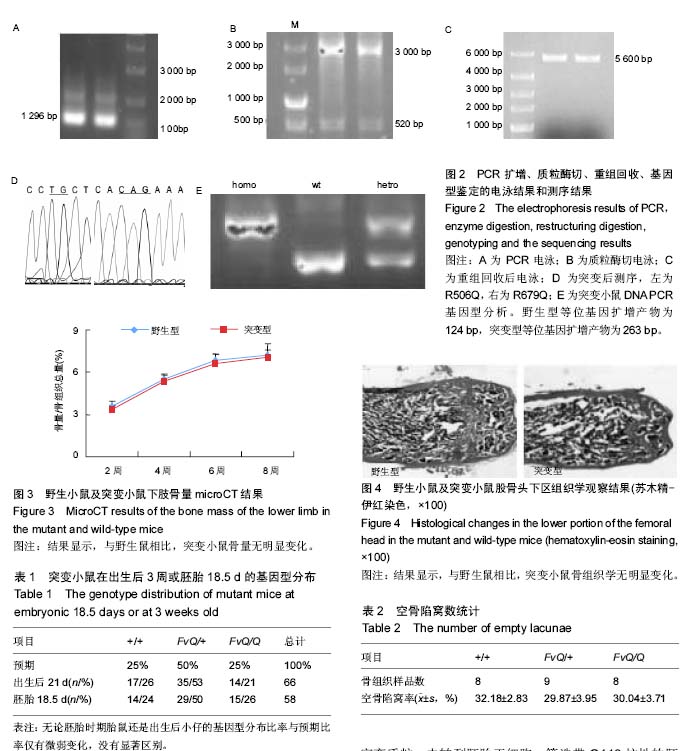
| [1] Arlet J. Nontraumatic avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Past, Present, and Future. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992;277:12-21.
[2] Mont MA, Hungerford DS. Current concepts review. Non-traumatic avascular necrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995;77:459-474.
[3] Fisher DE. The role of fat embolism in the etiology of corticosteroid-induced avascular necrosis: clinical and experimental results. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1978;130: 68-80.
[4] Wang Y, Li Y, Mao K, et al. Alcohol-induced adipogenesis in bone and marrow: a possible mechanism for osteonecrosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;410:213-224.
[5] Abu-Shakra M, Buskila D, Shoenfeld Y. Osteonecrosis in patients with SLE. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2003; 25:13-24.
[6] Wang TY, Avlonitis EG, Relkin R. Systemic necrotizing vasculitis causing bone necrosis. Am J Med. 1988;84: 1085-1086.
[7] Massin P, Duparc J. Total hip replacement in irradiated hips: a retrospective study of 71 cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995;77:847-852.
[8] Milner PF, Kraus AP, Sebes JI, et al. Sickle cell disease as a cause of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. N Engl J Med. 1991;325:1476-1481.
[9] Lehner CE, Wilson MA, Dueland RT, et al. Sheep model of dysbaric osteonecrosis in divers and cais-son workers. In: Urbaniak JR, Jones JP Jr, eds. Osteonecrosis - Etiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Rosemont, IL: American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 1997:145-152.
[10] Yang L, Boyd K, Kaste SC, et al. A mouse model for glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis: effect of a steroid holiday. J Orthop Res.2009;27(2):169-175.
[11] Takaoka K, Yoshioka T, Hosoya T, et al. The repair process inexperimentally inducedavascular necrosis of the femoral head in dogs. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg, 1981;99(2): 109-115.
[12] Li Y, Han R, Geng C, et al. A new osteonecrosis animal model of the femoral head induced by microwave heating and repaired with tissue engineered bone. Int Orthop. 2009;33(2):573-580.
[13] Chang G. Non-traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head - from clinical to bench. Med J. 2010;33(4): 351-360.
[14] Jones JP Jr. Risk factors potentially activating intravascu-lar coagulation and causing nontraumatic osteonecrosis. In: Urbaniak JR, Jones JP Jr, eds. Osteonecrosis: Etiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Rosemont, IL: American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 1997:89-97.
[15] Glueck CJ, Freiberg RA, Wang P. Detecting thrombophilia, hypo-fibrinolysis, and reduced nitric oxide production in osteonecrosis. Semin Artrhoplasty. 2007;18:184-191.
[16] Vosmaer A, Pereira RR, Koenderman JS, et al. Coagulation abnormalities in Legg-Calve-Perthes disease. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(1):121-128.
[17] Glueck CJ, McMahon RE, Bouquot JE, et al. Heterozygosity for the Leiden mutation of the factor V gene, a common pathoetiology for osteonecrosis of the jaw, with thrombophilia augmented by exogenous estrogens. J Lab Clin Med. 1997;130(5): 540-543.
[18] Björkman A, Svensson PJ, Hillarp A, et al. Factor V leiden and prothrombin gene mutation: risk factors for osteonecrosis of the femoral head in adults. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(425):168-172.
[19] Glueck CJ, Freiberg RA, Boriel G, et al. The Role of the Factor V Leiden Mutation in Osteonecrosis of the Hip. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2013;19(5):499-503.
[20] Esmon CT. Role of coagulation inhibitors in inflammation. Thromb Haemost.2001;86: 51-56.
[21] Kalafatis M, Rand MD, Mann KG. The mechanism of inactivation of human factor V and human factor Va by activated protein C. J Biol Chem. 1994;269(50): 31869-31880.
[22] Gale AJ, Yegneswaran S, Xu X, et al.Characterization of a factor Xa binding site on factor Va near the Arg-506 activated protein Ccleavage site. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(30):21848-21855.
[23] van der Neut Kolfschoten M, Dirven RJ, Vos HL, et al. Factor Va is inactivated by activated protein C in the absence of cleavage sites at Arg-306, Arg-506, and Arg-679. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(8):6567-6575.
[24] Reitsma PH, van de Stolpe A. From gene to disease; risk factors for venous thrombosis: factor V Leiden and prothrombin 20210A. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2001; 145(38):1843-1845.
[25] Glueck CJ, Glueck HI, Greenfield D, et al. Protein C and S deficiency, thrombophilia, and hypofibrinolysis: pathophysiologic causes of Legg-Perthes disease. Pediatr Res. 1994;35(4 Pt 1):383-388.
[26] Glueck CJ, Brandt G, Gruppo R,et al. Resistance to activated protein C and Legg-Perthes disease. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997;(338):139-152.
[27] Bertina RM, Koeleman BP, Koster T, et al. Mutation in blood coagulation factor V associated with resistance to activated protein C. Nature. 1994;369:64-67.
[28] Greengard JS, Sun X, Xu X,et al. Activated protein C resistance caused by Arg506Gln mutation in factor Va. Lancet. 1994;343(8909):1361-1362.
[29] Rosendaal FR, Koster T, Vandenbroucke JP, et al. High risk of thrombosis in patients homozygous for factor V Leiden (activated protein C resistance). Blood. 1995;85(6):1504-1508.
[30] Voorberg J, Roelse J, Koopman R, et al. Association of idiopathic venous thromboembolism with single point-mutation at Arg506 of factor V. Lancet. 1994;343 (8912):1535-1536.
[31] Ridker PM, Hennekens CH, Lindpaintner K,et al. Mutation in the gene coding for coagulation factor V and the risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, and venous thrombosis in apparently healthy men. N Engl J Med. 1995;332(14):912-917.
[32] Rees DC, Cox M, Clegg JB. World distribution of factor V Leiden. Lancet. 1995;346(8983):1133-1134.
[33] Williamson D, Brown K, Luddington R, et al. Factor V Cambridge: a new mutation (Arg306-->Thr) associated with resistance to activated protein C. Blood. 1998; 91(4): 1140-1144.
[34] Chan WP, Lee CK, Kwong YL, et al. A novel mutation of Arg306 of factor V gene in Hong Kong Chinese. Blood. 1998;91(4):1135-1139.
[35] Franco RF, Maffei FH, Lourenço D, et al. Factor V Arg306-->Thr (factor V Cambridge) and factor V Arg306-->Gly mutations in venous thrombotic disease. Br J Haematol. 1998;103(3):888-890.
[36] Barhoover MA, Kalafatis M. Cleavage atboth Arg306 and Arg506 is required and sufficient for timely and efficient inactivation of factor Va by activated protein C. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2011;22(4):317-324.
[37] Norstrøm E, Thorelli E, Dahlbäck B. Functional characterization of recombinant FV Hong Kong and FV Cambridge. Blood. 2002;100(2):524-530.
[38] Kita T, Banno F, Yanamoto H, et al. Large infarct and high mortality by cerebral ischemia in mice carrying the factor V Leiden mutation. J Thromb Haemost. 2012; 10(7):1453-1455.
[39] Shanmugam VK, McNish S, Duncan J, et al. Late failure of a split-thickness skin graft in the setting of homozygous factor V Leiden mutation: a case report and correlative animal model from the Wound Etiology and Healing (WE-HEAL) study. Int Wound J. 2015; 12(5):537-544.
[40] Kerschen E, Hernandez I, Zogg M, et al. Survival advantage of heterozygous factor V Leiden carriers in murine sepsis. J Thromb Haemost. 2015;13(6): 1073-1080.
[41] Liang HP, Kerschen EJ, Basu S, et al. Coagulation factor V mediates inhibition of tissue factor signaling by activated protein C in mice. Blood. 2015;126(21):2415- 2423. |