Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (45): 6726-6732.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.45.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of CM-Dil labeling on biological characteristics of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Zhang Ya-ni1, Yu Mei-juan2, Feng Shan-wei2, Wang Shu-hui2, Li Mei-shan2, Xiong Fu2, Zhang Cheng2
- 1Department of Pediatric Neurology, Guangzhou Women and Children’s Medical Center, Guangzhou 510623, Guangdong Province, China
2Department of Neurology, First Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China
-
Revised:2016-08-26Online:2016-11-04Published:2016-11-04 -
Contact:Zhang Cheng, Professor, Department of Neurology, First Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Zhang Ya-ni, M.D., Attending physician, Department of Pediatric Neurology, Guangzhou Women and Children’s Medical Center, Guangzhou 510623, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 30370510; the Scientific Research Plan of Guangdong Province, No. 2011A030400006
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Ya-ni, Yu Mei-juan, Feng Shan-wei, Wang Shu-hui, Li Mei-shan, Xiong Fu, Zhang Cheng. Effect of CM-Dil labeling on biological characteristics of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(45): 6726-6732.
share this article
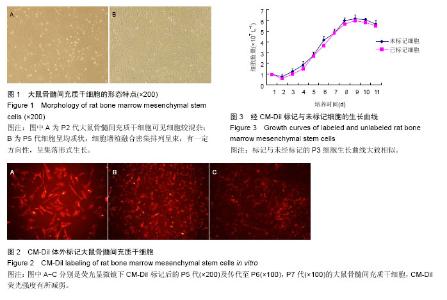
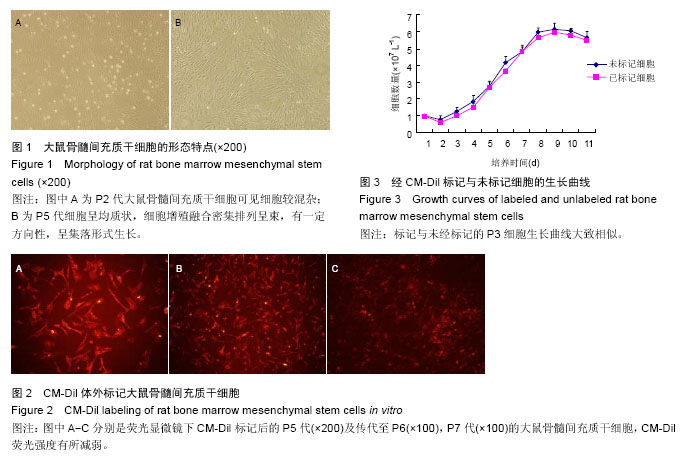
2.1 大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的形态与生长特点 以差速贴壁法原代培养的大鼠骨髓细胞,在刚分离接种时镜下可见大量密集悬浮细胞,接种后三四小时,细胞开始少量贴壁,在瓶底散在分布;8-12 h细胞约60%贴壁;24 h后约80%细胞贴壁,多呈扁平形、梭形或多角形,其中有大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞也有杂质细胞,悬浮细胞多呈圆形,大部分为造血干细胞和血细胞,生存寿命较短,两三次换液后可基本清除。3 d后细胞增殖明显,形态趋于纺锤状,5-7 d可见细胞集落,10-14 d细胞融合,多数呈均一典型的“纺锤状”成纤维样细胞形态;细胞间排列呈“旋涡状”、“辐射状”或“栅栏状”。刚传代的细胞呈圆形,6-8 h内又可贴壁、伸展重新成为梭形细胞;24 h后开始增殖,细胞集落增多;7-10 d后可传代,每传一代细胞数量可增加约2.5倍。P3代以上的大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞趋于纯化,细胞呈均质状,细胞增殖融合密集排列呈束,有一定方向性,呈集落形式生长。一般应用P5代作后续实验(图1)。 2.2 大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞表面标记物的检测结果 流式细胞检测显示,体外培养传代贴壁生长的P5代大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞均一性好,纯度达95%以上。大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞表面CD11b和CD45检测阴性,而CD29和CD44表达阳性。 2.3 CM-Dil标记大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞后的形态观察及荧光强度追踪 在相差显微镜下观察5 μmol/L浓度标记P5代细胞后其形态与未标记细胞相比未见明显差异。荧光显微镜下以绿色荧光激发标记细胞后,可见胞浆均匀发出强烈的红色荧光,细胞核无荧光发出,经流式细胞仪检测标记率>98%。体外传代至P6,P7代仍可检测到红色荧光,但随着体外传代荧光强度出现一定程度减弱(图2)。 2.4 标记后大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的细胞生长曲线 经CM-Dil标记与未经标记的P3代细胞生长曲线大致相似,在培养1 d时细胞量稍有减少,为细胞适应期,3 d后细胞数迅速增长,至第8天进入平台期,细胞增殖减慢(图3)。 2.5 体外Transwell细胞迁移能力 CM-Dil标记后的P5代大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞[(407±20)个/视野]向mdx鼠腓肠肌匀浆液的迁移能力与未标记细胞[(417±27)个/视野]相比差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),标记细胞向mdx鼠腓肠肌匀浆液的迁移能力[(407±20)个/视野]显著高于其向空白液迁移能力[(378±16)个/视野,P < 0.01]。"
| [1] Askari N, Yaghoobi MM, Shamsara M, et al. human dental pulp stem cells differentiate into oligodendrocyte progenitors using the expression of olig2 transcription factor. Cells Tissues Organs. 2014;200(2):93-103. [2] Ji AT, Chang YC, Fu YJ, et al. Niche-dependent regulations of metabolic balance in high-fat diet-induced diabetic mice by mesenchymal stromal cells. Diabetes. 2015;64(3):926-936. [3] Shang YC, Wang SH, Xiong F, et al. Wnt3a signaling promotes proliferation, myogenic differentiation, and migration of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2007;28(11):1761-1774. [4] Liu X, Wang X, Li A, et al. Effect of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in rats with Tourette syndrome. Exp Ther Med. 2016;11(4):1211-1216. [5] Li M, Zhang YX, Zhang Z, et al. Endomicroscopy Will Track Injected Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Rat Colitis Models. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2015;21(9):2068-2077. [6] Hendijani F, Javanmard SH, Sadeghi-aliabadi H. Human Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cell secretome display antiproliferative effect on leukemia cell line and produce additive cytotoxic effect in combination with doxorubicin. Tissue Cell. 2015;47(3):229-234. [7] Lin CS, Xin ZC, Dai J, et al. Commonly used mesenchymal stem cell markers and tracking labels: limitations and challenges. Histol Histopathol. 2013; 28(9):1109-1116. [8] Huntsman HD, Zachwieja N, Zou K, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells contribute to vascular growth in skeletal muscle in response to eccentric exercise. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013;304(1): H72-H81. [9] Price MJ, Chou CC, Frantzen M, et al. Intravenous mesenchymal stem cell therapy early after reperfused acute myocardial infarction improves left ventricular function and alters electrophysiologic properties. Int J Cardiol. 2001;11(2):231-239. [10] Dai W, Hale SL, Martin BJ, et al. Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in postinfarcted rat myocardium: short- and long-term effects. Circulation. 2005;112(2):214-223. [11] Feng SW, Chen F, Cao J, et al. Restoration of muscle fibers and satellite cells after isogenic MSC transplantation with microdystrophin gene delivery. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;419(1):1-6. [12] Spitzer N, Sammons GS, Price EM,et al. Autofluorescent cells in rat brain can be convincing impostors in green fluorescent reporter studies. J Neurosci Methods. 2011;197(1):48-55. [13] Coyne TM, Marcus AJ, Woodbury D, et al. Marrow stromal cells transplanted to the adult brain are rejected by an inflammatory response and transfer donor labels to host neurons and glia. Stem Cells. 2006;24(11):2483-2492. [14] Lin CS, Xin ZC, Dai J, et al. Commonly used mesenchymal stem cell markers and tracking labels: Limitations and challenges. Histol Histopathol. 2013; 28(9):1109-1116. [15] Li N, Yang H, Lu L, et al. Comparison of the labeling efficiency of BrdU, DiI and FISH labeling techniques in bone marrow stromal cells. Brain Res. 2008;1215: 11-19. [16] Chen B, Bo CJ, Jia RP, et al. The renoprotective effect of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cell transplantation on acute ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Transplant Proc. 2013;45(5):2034-2039. [17] Gong J, Meng HB, Hua J, et al. The SDF-1/CXCR4 axis regulates migration of transplanted bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells towards the pancreas in rats with acute pancreatitis. Mol Med Rep. 2014;9(5): 1575-1582. [18] Qiao PF, Yao L, Zhang XC, et al. Heat shock pretreatment improves stem cell repair following ischemia-reperfusion injury via autophagy. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(45):12822-12834. [19] Omidi A, Kashani IR, Akbari M, et al. Homing of allogeneic nestin-positive hair follicle-associated pluripotent stem cells after maternal transplantation in experimental model of cortical dysplasia. Biochem Cell Biol. 2015;93(6):619-625. [20] Cai J, Yu X, Zhang B, et al. Atorvastatin improves survival of implanted stem cells in a rat model of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Nephrol. 2014;39(6): 466-475. [21] Edalatmanesh MA, Bahrami AR, Hosseini E, et al. Neuroprotective effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in animal model of cerebellar degeneration. Neurol Res. 2011;33(9):913-920. [22] Sun S, Chen G, Xu M, et al. Differentiation and migration of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transplanted through the spleen in rats with portal hypertension. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e83523. [23] Schormann W, Hammersen FJ, Brulport M, et al. Tracking of human cells in mice. Histochem Cell Biol. 2008;130(2):329-338. [24] 陈朝,黎奔,郭建文,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的分离培养及CM-Dil标记的脑内示踪[J].解放军医学杂志,2010, 35(8):946-953. [25] 李朝中,肖践明,陈丽星,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞体外分离培养与CM-DiI荧光标记[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(1):39-44. [26] 陈丽,吴本清,程涵蓉,等.CM-Dil体外标记人脐带间充质干细胞传代示踪的可行性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(40):7435-7438. [27] Ji F, Duan HG, Zheng CQ, et al. Comparison of chloromethyl-dialkylcarbocyanine and green fluorescent protein for labeling human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells. Biotechnol Lett. 2015;37(2): 437-447. [28] Naaldijk Y, Johnson AA, Ishak S, et al. Migrational changes of mesenchymal stem cells in response to cytokines, growth factors, hypoxia, and aging. Exp Cell Res. 2015;338(1):97-104. [29] Zhou SB, Wang J, Chiang CA, et al. Mechanical stretch upregulates SDF-1α in skin tissue and induces migration of circulating bone marrow-derived stem cells into the expanded skin. Stem Cells. 2013;31(12): 2703-2713. [30] Consentius C, Akyüz L, Schmidt-Lucke JA, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells prevent allostimulation in vivo and control checkpoints of Th1 priming: migration of human dc to lymph nodes and nk cell activation. Stem Cells. 2015;33(10):3087-3099. [31] Lee SH, Jin KS, Bang OY, et al. Differential migration of mesenchymal stem cells to ischemic regions after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. PLoS One. 2015;10(8):e0134920. [32] Motaln H, Turnsek TL. Cytokines play a key role in communication between mesenchymal stem cells and brain cancer cells. Protein Pept Lett. 2015;22(4): 322-331. [33] Hengartner NE, Fiedler J, Schrezenmeier H, et al. Crucial role of IL1beta and C3a in the in vitro-response of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells to inflammatory mediators of polytrauma. PLoS One. 2015;10(1):e0116772. [34] Marquez-Curtis LA, Janowska-Wieczorek A. Enhancing the migration ability of mesenchymal stromal cells by targeting the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:561098. [35] Joos H, Wildner A, Hogrefe C, et al. Interleukin-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibit migration activity of chondrogenic progenitor cells from non-fibrillated osteoarthritic cartilage. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(5):R119. [36] Slørdahl TS, Denayer T, Moen SH, et al. Anti-c-MET Nanobody - a new potential drug in multiple myeloma treatment. Eur J Haematol. 2013;91(5):399-410. [37] Hengartner NE, Fiedler J, Ignatius A, et al. IL-1β inhibits human osteoblast migration. Mol Med. 2013;19: 36-42. [38] Zou C, Luo Q, Qin J, et al. Osteopontin promotes mesenchymal stem cell migration and lessens cell stiffness via integrin β1, FAK, and ERK pathways. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2013;65(3):455-462. [39] Dittmar T, Entschladen F. Migratory properties of mesenchymal stem cells. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2013;129:117-136. [40] Wobus M, Benath G, Ferrer RA, et al. Impact of lenalidomide on the functional properties of human mesenchymal stromal cells. Exp Hematol. 2012;40(10): 867-876. [41] Hurst NJ Jr, Najy AJ, Ustach CV, Movilla L, Kim HR, et al. Platelet-derived growth factor-C (PDGF-C) activation by serine proteases: implications for breast cancer progression. Biochem J. 2012;441(3):909-918. [42] Hu J, Qin K, Zhang Y, et al. Downregulation of transcription factor Oct4 induces an epithelial-to- mesenchymal transition via enhancement of Ca2+ influx in breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;411(4):786-791. [43] Zou C, Song G, Luo Q, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells require integrin β1 for directed migration induced by osteopontin in vitro. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2011; 47(3):241-250. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [5] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [6] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [7] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [8] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [9] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [10] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [11] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [12] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [13] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [14] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| [15] | Li Cai, Zhao Ting, Tan Ge, Zheng Yulin, Zhang Ruonan, Wu Yan, Tang Junming. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB promotes proliferation, differentiation and migration of skeletal muscle myoblast [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1050-1055. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||