Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (36): 5405-5411.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.36.013
Previous Articles Next Articles
Protective mechanism of cardiac stem cells against myocardial apoptosis
Gao Xue-dong1, Hu Ke2, Wei Hu3
- 1Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, 3Department of Geriatrics, Third People’s Hospital of Nanyang, Nanyang 473000, Henan Province, China; 2Department of Neurological Rehabilitation, Nanyang Central Hospital, Nanyang 473000, Henan Province, China
-
Revised:2016-08-01Online:2016-09-02Published:2016-09-02 -
Contact:Gao Xue-dong, Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Third People’s Hospital of Nanyang, Nanyang 473000, Henan Province, China -
About author:Gao Xue-dong, Attending physician, Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Third People’s Hospital of Nanyang, Nanyang 473000, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Gao Xue-dong, Hu Ke, Wei Hu. Protective mechanism of cardiac stem cells against myocardial apoptosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(36): 5405-5411.
share this article
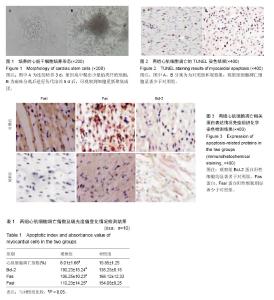
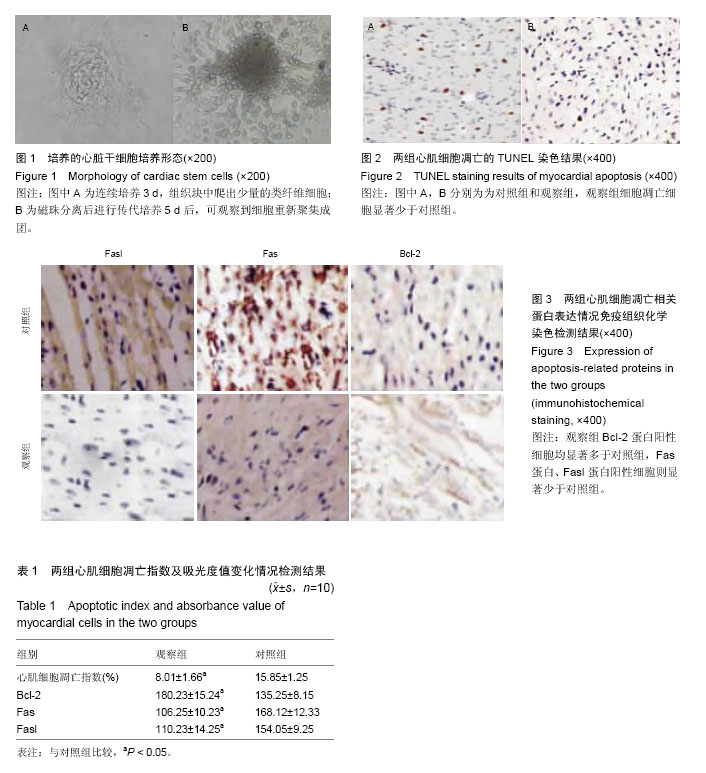
2.1 实验动物数量分析 纳入的20只Wistar大鼠均进入最终的结果分析,无脱落。 2.2 培养的心脏干细胞形态 连续培养3 d,组织块呈现出完全铺展生长状态,组织块中爬出少量的类纤维细胞(图1A)。磁珠分离后进行传代培养,5 d后,可以观察到细胞重新聚集成团(图1B)。 2.3 两组心肌细胞凋亡相关蛋白吸光度值变化 术后30 d,对两组的心肌细胞凋亡相关蛋白表达情况进行检测和比较,可得观察组的心肌细胞凋亡指数、Fas蛋白吸光度值和Fasl蛋白吸光度值均显著小于对照组(P < 0.05),Bcl-2蛋白吸光度值显著大于对照组(P < 0.05)。见表1。 2.4 两组心肌细胞凋亡情况 TUNEL细胞凋亡检测可以对正在凋亡的细胞予以特异准确地定位,TUNEL染色结果显示,凋亡阳性心肌细胞核呈棕褐色,正常心肌细胞核呈蓝色。对两组心肌细胞凋亡相关蛋白表达情况进行观察,观察组细胞凋亡细胞显著少于对照组,见图2。 经免疫组织化学染色检测,观察组Bcl-2蛋白阳性细胞均显著多于对照组,Fas蛋白、Fasl蛋白阳性细胞则显著少于对照组,见图3。"
| [1] 李树仁,齐晓勇.骨髓干细胞移植影响急性心肌梗死后心室重构的研究现状[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007,11(28):5574-5579. [2] 曾彬,林国生,张艳,等.血红素氧合酶-1修饰的骨髓间充质干细胞心肌移植对梗死后心肌细胞凋亡及左心室功能的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2009,25(9):1681-1685. [3] 黄景玲,杨水祥,陈一戎,等.人脐血间充质干细胞抗缺氧诱导心肌细胞凋亡的作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(32):5927-5930. [4] 姜帅,董士才,未东兴,等.骨髓基质干细胞缺血心肌内移植早期:可减少心肌细胞凋亡但未改善心功能[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(1):108-113. [5] 李树仁,齐晓勇,刘会良,等.经冠状动脉移植自体骨髓单个核细胞和间充质干细胞对急性心肌梗死模型心功能的改善[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(11):2081- 2086. [6] 杨水祥,黄景玲.脐血源性间充质干细胞与人心肌细胞共培养条件下对心肌细胞凋亡的抑制[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(27):4979-4983. [7] Iaflamme MA, Murry CE. Regenerating the heart. Nat Biotechnol. 2005;23:845456. [8] Hattori F. CD117, adult cardiac stem cell marker, is transiently expressed in methothelial epicardial cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010;49(5):711-712. [9] 方志成,王玮,王崇全,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植对心肌梗死后细胞凋亡的影响[J].中国临床康复,2006,10(33): 36-38. [10] Poynter JA, Herrmann JL, Manukyan MC, et al. Intracoronary mesenchymal stem cells promote postischemic myocardial functional recovery, decrease inflammation, and reduce apoptosis via a signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 mechanism. J Am Coll Surg. 2011;213(2):253-260. [11] Houtgraaf JH, DeJong R, Kazemi K, et al. Intracoronary infusion of allogeneic mesenchymal precursor cells directly after experimental acute myocardial infarction reduces infarct size, abrogates adverse remodeling, and improves cardiac function. Cir Res. 2013;113(2):153-166. [12] 李树仁,齐晓勇,张建清,等.不同种类自体骨髓干细胞移植对梗死心肌左室重构的效果比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(47):9371-9377. [13] 李树仁,齐晓勇,史力生,等.经冠脉移植骨髓单个核细胞和间充质干细胞治疗急性心肌梗死的对比实验研究[J].中国老年学杂志,2006,26(10):1299-1304. [14] D'Amario D, Cabral Da Silva MC, Zheng H, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor identifies a pool of human cardiac stem cells with superior therapeutic potential for myocardial regeneration. Cir Res. 2011; 108(12):1467-1481. [15] 谭兴琴,陈玉培,张文胜,等.乳化异氟醚对缺氧复氧乳鼠心肌细胞的保护作用及bcl-2、bar表达的影响[J].第三军医大学学报,2008,30(17):1611-1614. [16] 吴祖波,彭华,白燕,等.GYY4137通过Bcl-2/Bax/Cleaved caspase-3信号通路改善柯萨奇病毒B3引起的大鼠乳鼠心肌细胞凋亡[J].华中科技大学学报(医学版),2014,(4): 371-375. [17] 陈文华,孙畅,张颖,等.尼可地尔、谷氨酰胺、美托洛尔单独及合用对大鼠心肌缺血/再灌注损伤后心肌细胞抗凋亡和HSP70的影响[J].中国药理学通报,2014,30(9): 1242-1246. [18] Godier-Furnémont AFG, Tekabe Y, Kollaros M, et al. Noninvasive imaging of myocyte apoptosis following application of a stem cell-engineered delivery platform to acutely infarcted myocardium. J Nucl Med. 2013; 54(6):977-983. [19] Ferrari R, Ceconi C, Campo G, et al. Mechanisms of remodelling a question of life (stem cell production) and death (myocyte apoptosis). Cir J. 2009;73(11): 1973-1982. [20] 陈光辉,夏菁,刘宏斌,等.干细胞移植治疗在心血管疾病中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(11): 2190-2193. [21] 马东星,张永珍,谢道银,等.骨髓细胞移植对心肌梗死后大鼠心肌细胞凋亡及Bcl-2、Bax表达的调节[J].中国介入心脏病学杂志,2004,12(5):301-304. [22] Jin H, Sanberg PR, Henning RJ, et al. Human umbilical cord blood mononuclear cell-conditioned media inhibits hypoxic-induced apoptosis in human coronary artery endothelial cells and cardiac myocytes by activation of the survival protein Akt. Cell Transplantation. 2013;22(9):1637-1650. [23] Henning RJ, Dennis S, Sawmiller D, et al. Human umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells activate the survival protein Akt in cardiac myocytes and endothelial cells that limits apoptosis and necrosis during hypoxia. Transl Res. 2012;159(6):497-506. [24] Mirotsou M, Zhang ZY, Deb A, et al. Secreted frizzled related protein 2 (Sfrp2) is the key Akt-mesenchymal stem cell-released paracrine factor mediating myocardial survival and repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(5):1643-1648. [25] 孙勤暖,李冬梅,吴罡,等.甲状腺乳头状癌患者血清、癌组织中p53、Fas、TNF-α和Cyclin E的表达及临床意义[J].中国免疫学杂志,2014,31(10):1383-1387. [26] 杨水祥,黄景玲,朱希山,等.人脐血间充质干细胞抑制心肌细胞凋亡的作用与安全性[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志, 2010,12(9):829-832. [27] Kanashiro-Takeuchi RM, Tziomalos K, Takeuchi LM, et al. Cardioprotective effects of growth hormone- releasing hormone agonist after myocardial infarction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(6):2604-2609. [28] Hou M, Liu J, Liu F, et al. C1q tumor necrosis factor-related protein-3 protects mesenchymal stem cells against hypoxia- and serum deprivation-induced apoptosis through the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2014;33(1):97-104. [29] Glass C, Singla DK. MicroRNA-1 transfected embryonic stem cells enhance cardiac myocyte differentiation and inhibit apoptosis by modulating the PTEN/Akt pathway in the infarcted heart. Am J Physiol. 2011;301(5 Part 2):H2038-H2049. [30] 王志学,张晓侠,雷燕,等.Fas途径调控芬太尼与5-氟尿嘧啶联合诱导MCF-7乳腺癌细胞凋亡[J].中国老年学杂志, 2015,(4):1047-1048, 1049. [31] 黄黎月,庄国洪,丘劲华,等.DcR3重组蛋白对糖尿病大鼠心肌组织凋亡相关分子的表达及细胞凋亡的作用[J].中国免疫学杂志,2015,31(4):472-476. [32] 陈敬荣,郑尧杰,尤付玲,等.染料木素通过JNK调控Fas通路的抗Aβ诱导的PC12细胞凋亡机制研究[J].中国药理学通报,2015,(2):175-180. [33] 徐剑,王艳,姬怀雪,等.FoxO3a 激活 FasL 介导肾缺血再灌注中肾小管上皮细胞凋亡的作用及机制[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2014,30(10):929-931. [34] 高青,李树仁,荀丽颖,等.经 bcl-2基因修饰的骨髓间充质干细胞移植对缺血性心功能不全兔心功能及血管新生的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2015,32(4):640-646. [35] 高玉峰,王小杰,闫文翠,等.生黄合剂对缺血再灌注损伤大鼠心肌细胞凋亡相关基因Bax, Bcl-2和Caspase-3蛋白表达的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2012,18(13): 244-247. [36] 尹海燕,何志捷,王吉文,等.谷氨酰胺对脓毒症大鼠心肌细胞Bcl-2/Bax表达的影响[J].中华急诊医学杂志,2009, 18(10):1037-1042. [37] Tsubokawa T, Yagi K, Nakanishi C, et al. Impact of anti-apoptotic and anti-oxidative effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells with transient overexpression of heme oxygenase-1 on myocardial ischemia. Am J Physiol. 2010;298(5 Pt 2):H1320- H1329. [38] 柳向军,张令强,刘小林,等.细胞凋亡中的Bcl-2家族蛋白及其BH3结构域的功能研究[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2006,33(3):221-225. [39] 田黎明,谢红付,李吉,等.β联蛋白对过氧化氢诱导人皮肤成纤维细胞增殖活性及凋亡相关基因Bcl-2、Bax表达的影响[J].中华皮肤科杂志,2015,48(2):112-115. [40] 孙春玲,国晓瞳,赵园,等.黄芩苷对热应激条件下猪近端肾小管(LLC-PK1)细胞凋亡率及B细胞淋巴瘤-2基因(Bcl-2)和Bcl-2相关X蛋白基因(Bax)表达的影响[J].农业生物技术学报,2014,23(12):1553-1560. [41] Huang TF, Wu XH, Wang X, et al. Fas-FasL expression and myocardial cell apoptosis in patients with viral myocarditis. Genet Mol Res. 2016. [42] Zhang BY, Zhao Z, Jin Z. Expression of miR-98 in myocarditis and its influence on transcription of the FAS/FASL gene pair. Genet Mol Res. 2016. [43] Wu T, Chen J, Fan L, et al. Effects of Shenqi Fuzheng injection on Fas/FasL protein expression levels in the cardiomyocytes of a mouse model of viral myocarditis. Exp Ther Med. 2016;11(5):1839-1846. [44] Huby AC, Turdi S, James J, et al. FasL expression in cardiomyocytes activates the ERK1/2 pathway, leading to dilated cardiomyopathy and advanced heart failure. Clin Sci (Lond). 2016;130(4):289-299. [45] Zhang H, Wei T, Jiang X, et al. PEDF and 34-mer inhibit angiogenesis in the heart by inducing tip cells apoptosis via up-regulating PPAR-γ to increase surface FasL. Apoptosis. 2016;21(1):60-68. [46] Ham O, Lee SY, Song BW, et al. Modulation of Fas-Fas Ligand Interaction Rehabilitates Hypoxia-Induced Apoptosis of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Ischemic Myocardium Niche. Cell Transplant. 2015;24(7):1329-1341. [47] Nam SW, Liu H, Wong JZ, et al. Cardiomyocyte apoptosis contributes to pathogenesis of cirrhotic cardiomyopathy in bile duct-ligated mice. Clin Sci (Lond). 2014;127(8):519-526. [48] Su BC, Mo FE. CCN1 enables Fas ligand-induced apoptosis in cardiomyoblast H9c2 cells by disrupting caspase inhibitor XIAP. Cell Signal. 2014;26(6):1326- 1334. [49] Wu Z, He EY, Scott GI, et al.α,β-Unsaturated aldehyde pollutant acrolein suppresses cardiomyocyte contractile function: role of TRPV1 and oxidative stress. Environ Toxicol. 2015;30(6):638-647. [50] Lu C, Ren D, Wang X, et al. Toll-like receptor 3 plays a role in myocardial infarction and ischemia/reperfusion injury. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1842(1):22-31. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [5] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [6] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [7] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [8] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [9] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [10] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [11] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [12] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [13] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [14] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [15] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||