Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (32): 4778-4784.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.32.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of lovastatin on proliferation and apoptosis of glioma stem cells
Wen Gong-ling, Wen Chang-ming, Wang Yan-ping, Kang Mei-juan, Zhou Jing, Zhang Bao-chao
- Department of Neurology, Nanyang Central Hospital, Nanyang 473009, Henan Province, China
-
Revised:2016-07-19Online:2016-08-05Published:2016-08-05 -
About author:Wen Gong-ling, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Neurology, Nanyang Central Hospital, Nanyang 473009, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wen Gong-ling, Wen Chang-ming, Wang Yan-ping, Kang Mei-juan, Zhou Jing, Zhang Bao-chao. Effect of lovastatin on proliferation and apoptosis of glioma stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(32): 4778-4784.
share this article
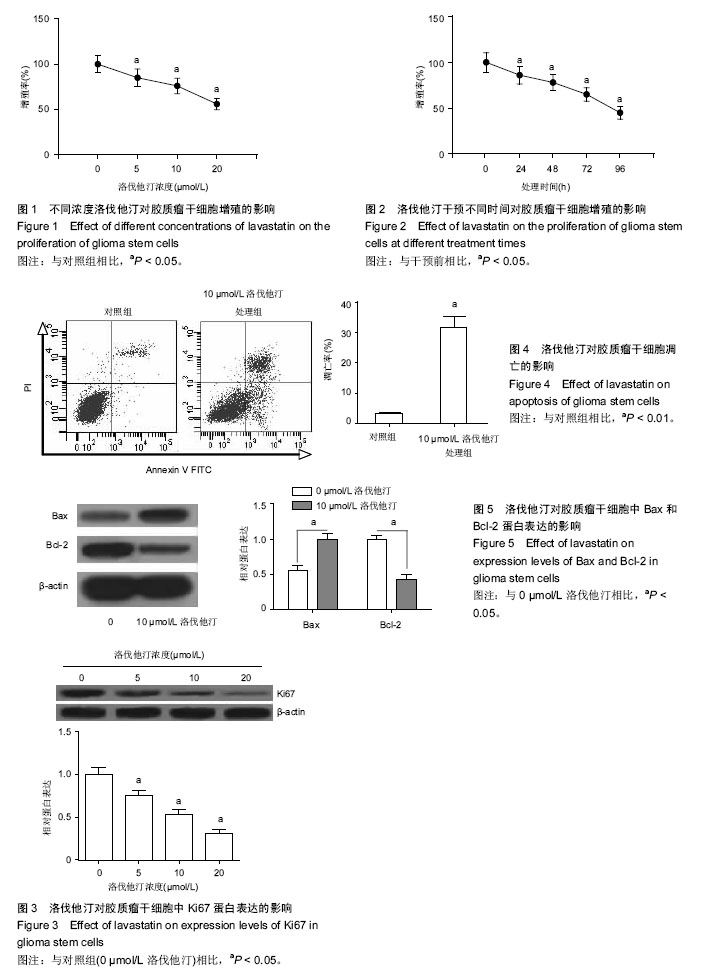
2.1 U87胶质瘤干细胞分选结果 流式细胞仪分选之前,人类恶性胶质母细胞瘤细胞系U87中CD133阳性细胞比率为0.5%,分选后CD133阳性细胞比率为85%,分选前后差异有非常显著性意义,胶质瘤干细胞纯度较高,可以进行后续实验。 2.2 洛伐他汀对胶质瘤干细胞增殖的影响 图1结果显示,不同浓度洛伐他汀(5,10,20 μmol/L)处理胶质瘤干细胞48 h后,各组细胞的增殖率分别为对照组的85%(P < 0.05)、76%(P < 0.05)及56%(P < 0.05),说明5-20 μmol/L洛伐他汀均能显著抑制胶质瘤干细胞的增殖,且药物浓度越高,细胞的增殖率越低。图2结果显示,10 μmol/L洛伐他汀处理胶质瘤干细胞24,48,72,96 h后细胞的增殖率分别为86%(P < 0.05)、78%(P < 0.05)、65%(P < 0.05)及45%(P < 0.05),说明随着时间的延长洛伐他汀对胶质瘤干细胞的抑制性越强,细胞的增殖率越低。 实验又进一步使用Western blot检测不同浓度洛伐他汀(5,10,20 μmol/L)处理胶质瘤干细胞48 h后Ki67的表达情况,由图3结果可知,随着药物浓度的升高,Ki67的表达量逐渐降低,处理组的蛋白相对表达量分别为对照组的76%(P < 0.05)、53%(P < 0.05)及31%(P < 0.05),说明5-10 μmol/L洛伐他汀能够剂量依赖性抑制胶质瘤细胞中Ki67的表达。Ki67是细胞增殖的标记性蛋白,Ki67蛋白表达水平的降低,意味着细胞增殖速度的降低,洛伐他汀能够抑制Ki67的表达,进一步验证了其能够抑制胶质瘤干细胞的增殖[20-21]。 2.3 洛伐他汀对胶质瘤干细胞凋亡的影响 图4结果显示,对照组即未使用洛伐他汀处理的细胞凋亡率为3.36%,10 μmol/L洛伐他汀处理48 h后,细胞凋亡率为31.62%,与对照组相比差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01)。 实验进一步检测10 μmol/L洛伐他汀处理胶质瘤干细胞48 h后细胞中凋亡相关蛋白Bax及Bcl-2的表达情况,图5结果显示,10 μmol/L洛伐他汀能够提高Bax的表达(P < 0.05),同时降低Bcl-2的表达(P < 0.05)。在细胞凋亡过程中,Bax属于促凋亡蛋白,Bcl-2属于抗凋亡蛋白,Bax的增加及Bcl-2的减少说明洛伐他汀促进了胶质瘤干细胞的凋亡,进一步验证了流式细胞仪的检测结果,即洛伐他汀能够诱导胶质瘤干细胞的凋亡[22-25]。"
| [1] Chen J, McKay RM, Parada LF. Malignant glioma: lessons from genomics, mouse models, and stem cells. Cell. 2012;149(1):36-47. [2] Marumoto T, Saya H. Molecular biology of glioma. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;746:2-11. [3] De Witt Hamer PC, Robles SG, Zwinderman AH, et al. Impact of intraoperative stimulation brain mapping on glioma surgery outcome: a meta-analysis.J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(20):2559-2565. [4] 杨学军.恶性胶质瘤生物治疗的现状及前景[J].中华神经外科疾病研究杂志, 2013, 12(4): 289-292. [5] Kasiske BL, Velosa JA, Halstenson CE, et al. The effects of lovastatin in hyperlipidemic patients with the nephrotic syndrome. Am J Kidney Dis. 1990;15(1): 8-15. [6] Gupta EK, Ito MK. Lovastatin and extended-release niacin combination product: the first drug combination for the management of hyperlipidemia. Heart Dis. 2002; 4(2):124-137. [7] 国风,岑建农,陈子兴,等. 胆固醇合成抑制剂洛伐他汀对 NB4 细胞体外作用的研究[J]. 中华血液学杂志, 2001, 22(11): 584-588. [8] Rao S, Porter DC, Chen X, et al. Lovastatin-mediated G1 arrest is through inhibition of the proteasome, independent of hydroxymethyl glutaryl-CoA reductase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96(14):7797-7802. [9] Dimitroulakos J, Thai S, Wasfy GH, et al. Lovastatin induces a pronounced differentiation response in acute myeloid leukemias.Leuk Lymphoma. 2000;40(1-2): 167-178. [10] Xia Z, Tan MM, Wong WW, et al. Blocking protein geranylgeranylation is essential for lovastatin-induced apoptosis of human acute myeloid leukemia cells. Leukemia. 2001;15(9):1398-1407. [11] Yu J, Man J, Jocelyn S, et al. Semaphorin 3C mediates glioma stem cell tumorigenicity and radioresistance. Cancer Research. 2015; 75(23 Supplement): A45. [12] Gao X, McDonald JT, Hlatky L, et al. Acute and fractionated irradiation differentially modulate glioma stem cell division kinetics. Cancer Res. 2013;73(5): 1481-1490. [13] Park SY, Piao Y, Tiao N,et al. TGF beta regulates tumor resistance to antiangiogenic therapy through POSTN in glioma stem cell models.Cancer Res. 2015; 75(15 Supplement):1385. [14] Ignatova TN, Kukekov VG, Laywell ED, et al. Human cortical glial tumors contain neural stem-like cells expressing astroglial and neuronal markers in vitro. Glia. 2002;39(3):193-206. [15] Yamada R, Nakano I. Glioma stem cells: their role in chemoresistance. World Neurosurg. 2012;77(2): 237-240. [16] Zhao Y, Huang Q, Zhang T, et al. Ultrastructural studies of glioma stem cells/progenitor cells. Ultrastruct Pathol. 2008;32(6):241-245. [17] Brescia P, Ortensi B, Fornasari L, et al. CD133 is essential for glioblastoma stem cell maintenance. Stem Cells. 2013;31(5):857-869. [18] 王淑为,张剑宁,郭欣茹,等. 25 例恶性胶质瘤中肿瘤干细胞的分离与检测[J].中华神经外科疾病研究杂志, 2013, 12(4): 314-317. [19] 张明菲,陆伟跃. 脑胶质瘤干细胞及干预策略研究进展[J].世界临床药物, 2015, 36(3): 204-209. [20] Kramer E, Herman O, Frand J, et al. Ki67 as a biologic marker of basal cell carcinoma: a retrospective study. Isr Med Assoc J. 2014;16(4):229-232. [21] Polley MY, Leung SC, McShane LM, et al. An international Ki67 reproducibility study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013;105(24):1897-1906. [22] Follis AV, Llambi F, Merritt P,et al.Pin1-Induced Proline Isomerization in Cytosolic p53 Mediates BAX Activation and Apoptosis.Mol Cell. 2015;59(4): 677-684. [23] Colin J, Garibal J, Clavier A, et al. Screening of suppressors of bax-induced cell death identifies glycerophosphate oxidase-1 as a mediator of debcl-induced apoptosis in Drosophila. Genes Cancer. 2015;6(5-6):241-253. [24] Czabotar PE, Lessene G, Strasser A, et al. Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family: implications for physiology and therapy.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014; 15(1):49-63. [25] Volkmann N, Marassi FM, Newmeyer DD, et al.The rheostat in the membrane: BCL-2 family proteins and apoptosis.Cell Death Differ. 2014;21(2):206-215. [26] Wei Y, Jiang Y, Zou F, et al. Activation of PI3K/Akt pathway by CD133-p85 interaction promotes tumorigenic capacity of glioma stem cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(17):6829-6834. [27] Holmberg Olausson K, Maire CL, Haidar S, et al. Prominin-1 (CD133) defines both stem and non-stem cell populations in CNS development and gliomas. PLoS One. 2014;9(9):e106694. [28] Chau MJ, McCrary MR, Mukherjee S, et al. Microenvironmental influences on glioma stem cell migration. Cancer Research. 2015; 75(15 Supplement): 5217. [29] Fessler E, Borovski T, Medema JP. Endothelial cells induce cancer stem cell features in differentiated glioblastoma cells via bFGF. Mol Cancer. 2015;14:157. [30] Venere M, Hamerlik P, Wu Q,et al.Therapeutic targeting of constitutive PARP activation compromises stem cell phenotype and survival of glioblastoma- initiating cells. Cell Death Differ. 2014;21(2):258-269. [31] Lehnus KS, Donovan LK, Huang X, et al. CD133 glycosylation is enhanced by hypoxia in cultured glioma stem cells.Int J Oncol. 2013;42(3):1011-1017. [32] Bostad M, Berg K, Høgset A, et al. Photochemical internalization (PCI) of immunotoxins targeting CD133 is specific and highly potent at femtomolar levels in cells with cancer stem cell properties. J Control Release. 2013;168(3):317-326. [33] Jin X, Jin X, Jung JE, et al. Cell surface Nestin is a biomarker for glioma stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;433(4):496-501. [34] 周永,糜漫天,朱俊东,等.洛伐他汀对MCF-7细胞增殖分化功能及间隙连接细胞通讯的影响[J].癌症, 2003, 22(3): 257-261. [35] Marcelli M, Cunningham GR, Haidacher SJ, et al. Caspase-7 is activated during lovastatin-induced apoptosis of the prostate cancer cell line LNCaP. Cancer Res. 1998;58(1):76-83. [36] Agarwal B, Bhendwal S, Halmos B, et al. Lovastatin augments apoptosis induced by chemotherapeutic agents in colon cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 1999; 5(8):2223-2229. [37] 刘磊,龚彪,别里克,等.洛伐他汀联合KRN633对胆管癌细胞株QBC939生物学行为的影响[J].胃肠病学和肝病学杂志, 2012, 20(11): 1054-1059. [38] 刘明,刘熙鹏,丁奇,等.瑞舒伐他汀对人胶质瘤 U251 细胞增殖和凋亡的影响[J]. 现代药物与临床, 2016, 31(4): 415-418. [39] Guessous F, Zhang Y, Kofman A, et al. microRNA-34a is tumor suppressive in brain tumors and glioma stem cells. Cell Cycle. 2010;9(6):1031-1036. [40] Lomonaco SL, Finniss S, Xiang C, et al. The induction of autophagy by gamma-radiation contributes to the radioresistance of glioma stem cells.Int J Cancer. 2009; 125(3):717-722. [41] Wang J, Wakeman TP, Lathia JD, et al. Notch promotes radioresistance of glioma stem cells. Stem Cells. 2010;28(1):17-28. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [3] | Liu Cong, Liu Su. Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
| [4] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [5] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [6] | Li Cai, Zhao Ting, Tan Ge, Zheng Yulin, Zhang Ruonan, Wu Yan, Tang Junming. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB promotes proliferation, differentiation and migration of skeletal muscle myoblast [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1050-1055. |
| [7] | Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi, Liao Jianzhao, Zhang Xiaoyun, Zhang Xuan. Pathogenesis of hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head and the target effect of related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 935-941. |
| [8] | Ma Zetao, Zeng Hui, Wang Deli, Weng Jian, Feng Song. MicroRNA-138-5p regulates chondrocyte proliferation and autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 674-678. |
| [9] | Xu Yinqin, Shi Hongmei, Wang Guangyi. Effects of Tongbi prescription hot compress combined with acupuncture on mRNA expressions of apoptosis-related genes,Caspase-3 and Bcl-2, in degenerative intervertebral discs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 713-718. |
| [10] | Zhang Wenwen, Jin Songfeng, Zhao Guoliang, Gong Lihong. Mechanism by which Wenban Decoction reduces homocysteine-induced apoptosis of myocardial microvascular endothelial cells in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 723-728. |
| [11] | Liu Qing, Wan Bijiang. Effect of acupotomy therapy on the expression of Bcl-2/Bax in synovial tissue of collagen-induced arthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 729-734. |
| [12] | Xie Chongxin, Zhang Lei. Comparison of knee degeneration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with or without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 735-740. |
| [13] | Nie Huijuan, Huang Zhichun. The role of Hedgehog signaling pathway in transforming growth factor beta1-induced myofibroblast transdifferentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 754-760. |
| [14] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [15] | Wang Yujiao, Liu Dan, Sun Song, Sun Yong. Biphasic calcium phosphate loaded with advanced platelet rich fibrin can promote the activity of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 504-509. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||