Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (22): 3279-3286.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.22.012
Previous Articles Next Articles
Foot drop after tibial lengthening osteotomy using Ilizarov and Orthofix external fixators
Yilihamujiang•Wusiman, Maimaitiming•Saiyiti, Abuduhaibier•Abula, Aihemaitijiang•Yusufu
- Department of Micro-Reconstructive Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Revised:2016-03-18Online:2016-05-27Published:2016-05-27 -
Contact:Aihemaitijiang?Yusufu, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Micro-Reconstructive Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Yilihamujiang?Wusiman, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Micro-Reconstructive Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yilihamujiang•Wusiman, Maimaitiming•Saiyiti, Abuduhaibier•Abula, Aihemaitijiang•Yusufu. Foot drop after tibial lengthening osteotomy using Ilizarov and Orthofix external fixators[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(22): 3279-3286.
share this article

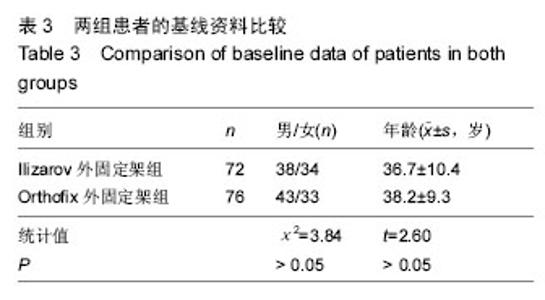
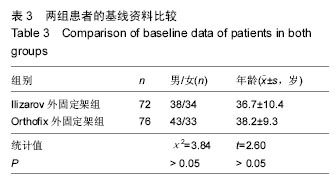
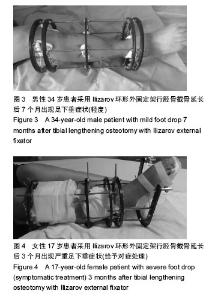
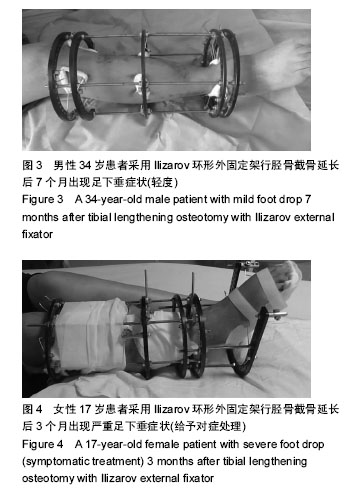
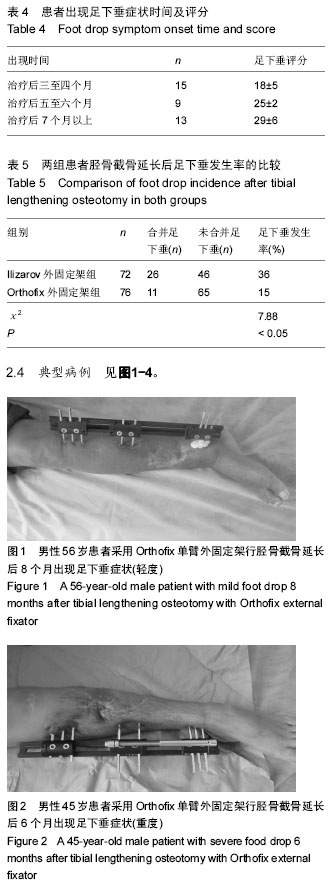
2.3 随访结果 148 例患者胫骨截骨延长长度4-7 cm,平均5.5 cm;带外固定架时间8-11个月,平均9.5个月。所有患者骨缺损均得到满意纠正。83例胫骨缺损伴有骨髓炎患者中65例患者的骨髓炎症状均一期纠正、其余经二至三次清创术后获得纠正。148例患者治疗前及治疗后2周内患者均未出现足下垂症状,踝关节功能评分> 36分(可排除术前及术中有腓总神经损伤可能性)。 治疗后每个月随访1次至拆除外固定架,随访时间 1-1.3年。148例患者中37例患者出现足下垂症状,出现时间及评分见表4。对术后出现足下垂的患者采取患者自我功能锻炼和踝关节关节松动术等相关处理后[9],有28例患者足下垂症状得以改善(评分> 36分);余9例患者因失去随访出现严重足下垂症状,患者自我功能锻炼和踝关节关节松动术等措施无法纠正患肢足下垂症状,此9例患者最终行跟腱延长术后患肢足下垂症状才得以改善。最终对两组患者行胫骨截骨延长后足下垂发生率的比较及分析见表5。"
| [1] Ilizarov GA. The tension-stress effect on the genesis and growth of tissues. Part IThe influence of stability of fixation and soft-tissue preservation. Clin Orthop.1989; 238:249-281. [2] Ilizarov GA.The tension-stress effect on the genesis and growth of tissues,Part II.The influence of the rate and frequency of distraction.Clin Orthop. 1989;239: 263-285. [3] 黄雷,赵刚,王慎东,等.短缩-延长肢体治疗胫骨骨缺损合并软组织缺损[J].中国骨科创伤杂志,2007,9(12): 1115-1119. [4] 沈型初,柳用墨,周江南.下肢延长术的实验和临床进展[J].中华骨科杂志,1989,9(8):438-440. [5] 汪土松,朱健儿,方弘伟,等. 降低胫骨延长术后跟腱延长手术率的探讨—附82例报告[J]. 中国康复,1991,6(4): 147-149. [6] 李长霜, 赵秀健. 47例短缩-延长肢体治疗胫骨骨缺损合并软组织缺损的术后护理[J].中华护理杂志, 2009, 44(3):226-227. [7] Phillips WA, Schwartz HS, Keller CS, et al. Prospective randomized study of the mangement of severe ankle fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985;67(1):67-78. [8] Fogel G. Delayed open reduction and fixtion of ankle fractures. Clin Orthop. 1987;215:187. [9] 陆廷仁.踝部扭伤的预后[J].国外医学:物理医学与康复学分册,1998,18(4):183-184. [10] 方玲,刘剑. 踝关节功能障碍的康复与评估[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2001,23(4):254-255. [11] 秦泗河,吴鸿飞.马蹄足畸形的分型和手术方案制定[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2000,7(4):317-319. [12] 张雪非,郭建中.胫骨上干骺端截骨延长术并发症及预防[J].中华骨科杂志,1990,10(6):420-422. [13] Saleh M, Rees A. Bifocal surgery for deformity and bone loss-bonetransport and compression distraction compared. J Bone Joint Surg(Br).1995;77:429-434. [14] 候忠亮,冯大雄.使用Ilizarov支架的并发症及克服方法[J].泸州医学院学报,1993,16(3):171-173. [15] Ilizarov GA. Transosseous osteosynthesis. Berlin, Heidelberg,London:Springer,1992. [16] De Bastiani G,Aldegheri R,Renzi Brivio L,et al.Limb lengthening by CallusDistraction (callostasis). J Paediatr Orthop. 1987;7:129-134. [17] 宋相建. Ilizarov外固定术并发症及处理[J].医药论坛杂志, 2006,27(16):59-61. [18] 宋相建,许志红.应用Ilizarov技术进行肢体延长[J].中国临床康复, 2003, 7(20): 2852-2853. [19] 王公长,高仲琰. 胫骨上端延长术几种并发症原因分析及预防[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2010,16(3):218-220. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||