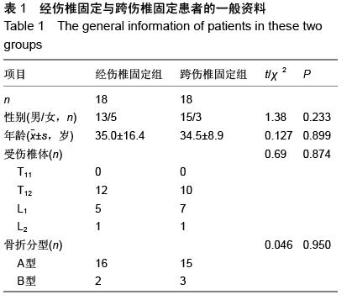
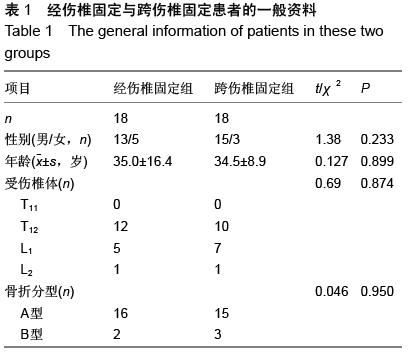
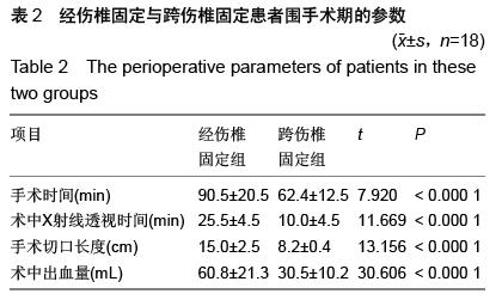
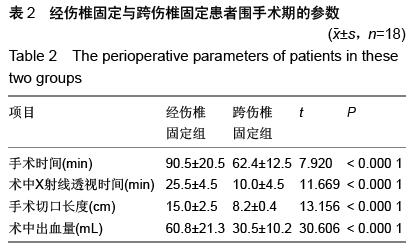
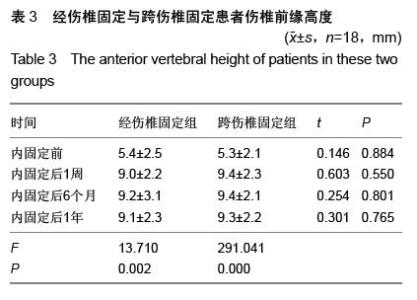
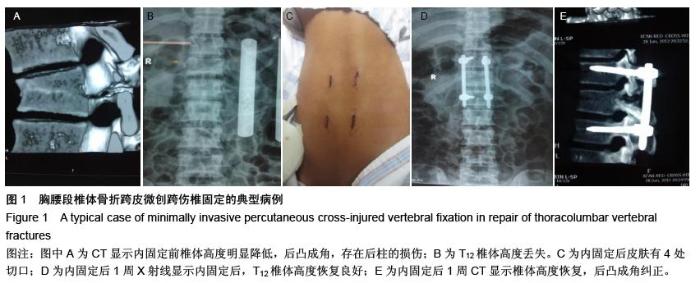
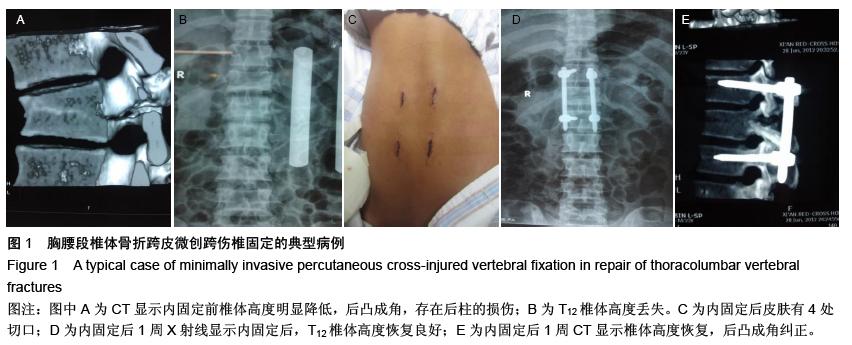
| [1] Kramer DL, Rodgers WB, Mansfield FL. Transpedicular instrumentation and short-segment fusion of thoracolumbar fractures: a prospective study using a single instrumentation system. J Orthop Trauma. 1995;9(6):499-506.[2] Antevil JL, Sise MJ, Sack DI, et al. Spiral computed tomography for the initial evaluation of spine trauma: A new standard of care? J Trauma. 2006;61(2): 382-387.[3] Palmisani M, Gasbarrini A, Brodano GB, et al. Minimally invasive percutaneous fixation in the treatment of thoracic and lumbar spine fractures. Eur Spine J. 2009;18 Suppl 1:71-74. [4] Ni WF, Huang YX, Chi YL, et al. Percutaneous pedicle screw fixation for neurologic intact thoracolumbar burst fractures. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2010;23(8):530-537. [5] Kim DY, Lee SH, Chung SK, et al. Comparison of multifidus muscle atrophy and trunk extension muscle strength: percutaneous versus open pedicle screw fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(1): 123-129.[6] 李长青,罗刚,周跃,等.微创三节段经皮椎弓根螺钉内固定选择性治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].第三军医大学学报,2009, 31(22):2284- 2287. [7] Mahar A, Kim C, Wedemeyer M, et al. Short-segment fixation of lumbar burst fractures using pedicle fixation at the level of the fracture. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(14):1503-1507.[8] 李晶,吕国华,王冰,等.胸腰椎骨折脱位伤椎固定的可行性研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2005,25(5):293-296.[9] 赵文明,柴俊,毛立彪,等.后路短节段钉棒系统结合经伤椎置钉固定治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折[J].临床骨科杂志, 2013,16(5): 487-489.[10] 谭家昌,徐鸿育,杨有猛,等.伤椎置钉与跨节段椎弓根螺钉内固定术治疗胸腰椎骨折的比较研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2009,17(14):1094-1096.[11] Alanay A, Acaroglu E, Yazici M, et al. Short-segment pedicle instrumentation of thoracolumbar burst fractures: does transpedicular intracorporeal grafting prevent early failure? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001; 26(2):213-217.[12] Leferink VJ, Zimmerman KW, Veldhuis EF, et al. Thoracolumbar spinal fractures: radiological results of transpedicular fixation combined with transpedicular cancellous bone graft and posterior fusion in 183 patients. Eur Spine J. 2001;10(6): 517-523.[13] Wang XY, Dai LY, Xu HZ, et al. Kyphosis recurrence after posterior short-segment fixation in thoracolumbar burst fractures. J Neurosurg Spine. 2008;8(3):246-254.[14] Bono CM, Lee CK. Critical analysis of trends in fusion for degenerative disc disease over the past 20 years: influence of technique on fusion rate and clinical outcome. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004; 29(4): 455-463; discussion Z5.[15] 汪学军,吴亚鹏,李开南,等.微创椎弓根钉内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折中期椎体运动节段高度维持的研究[J].四川医学,2010,31(1): 30-32. |