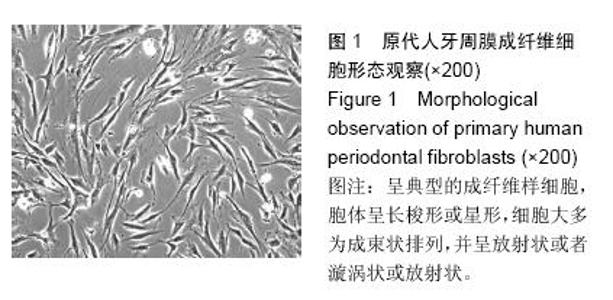
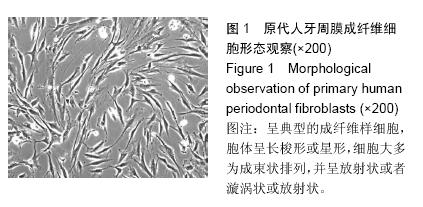
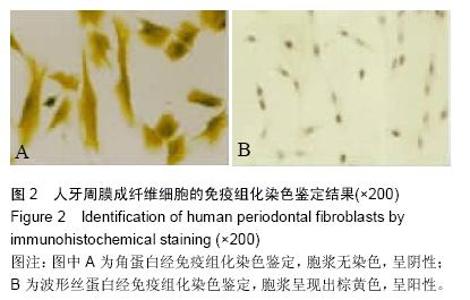
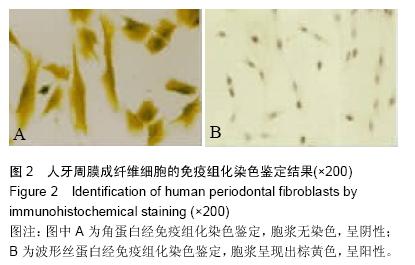
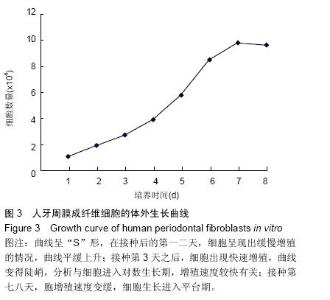
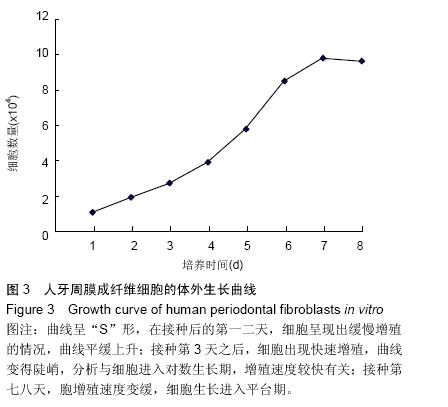
| [1] 雷丽珊.Filtek<'TM>Z350纳米复合树脂生物相容性的实验研究[D].福建医科大学,2010.
[2] 梁景章,汤应联,潘文仪,等.不同口腔修复材料生物相容性及3种材料充填恒磨牙邻面龋的临床验证[J].医药前沿, 2013, 35 (17): 191-192.
[3] 刘峰,吴军正.细胞培养在牙科材料生物相溶性试验中的运用[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,1999,9(2):177-179.
[4] 石瑾.纳米蒙脱土/聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯义齿基托复合材料生物安全性的临床前评价[D].天津医科大学,2008.
[5] 黄丽娟,俞立英,王丽珍,等.不同粘结剂对纵折牙根粘结后再植的疗效观察[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2009,25(5):302-304.
[6] 黄丽娟.Beagle犬实验性牙根纵折粘结再植术的组织学研究和预后多因素回归分析[D].复旦大学,2005.
[7] 邹颖.4种粘结材料生物学及力学性能评价[D].南京大学,2009.
[8] 盛乾斌,俞立英.后牙纵折粘结再植术中离体时间与术后愈合方式的关系[J].生物医学工程学进展,2012,33(3):156-159.
[9] 王利力.超级粘结剂在脱位牙再植术中的应用[C].//第八届全国创伤学术会议论文集,2011:1404-1404.
[10] 杜姗姗,周娟,解龙川,等.N-乙酰半胱氨酸对牙本质粘结剂生物相容性的影响[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2011,27(6):328-330.
[11] 张明.自酸蚀粘结系统与牙髓组织生物相容性的实验研究[D].福建医科大学,2007.
[12] 刘燕舞,刘月华,张敬,等.新型光固化正畸釉质粘结剂的生物相容性研究[J].口腔正畸学,2006,13(1):14-17.
[13] 姜红.Super-Bond 在纵折磨牙保存修复中的应用[J].医学理论与实践,2008,21(12):1436-1437.
[14] 徐燕,路晶晶,程楠,等.超级粘结剂固定牙周病松动牙1年的临床疗效观察[J].安徽医科大学学报,2013,48(8):970-972.
[15] 姜锦,张晖.超级粘结剂的性质及其应用[J].宁夏医科大学学报, 2011,33(7):698-700.
[16] 孟小睿,王晶.Super Bond C&B应用于后牙金属烤瓷修复体大面积崩瓷的临床疗效研究[J].中国医疗前沿,2011,6(23):51,94.
[17] 顾茜平.隐裂牙完全纵折Super-Bond粘结后银合金冠修复[J].泰州职业技术学院学报,2014,14(4):75-76.
[18] 刘文胜,龙路平,马运柱,等.催化脱脂型粘结剂组分的相容性[J].中国有色金属学报,2012,22(7):2097-2102.
[19] 钟宏,李海普,祝爱兰,等.水溶性MIM粘结剂组分相容性的预测方法[J].粉末冶金工业,2007,17(5):14-18.
[20] 贾翠,谢志鹏,刘伟,等.陶瓷注射成型中水萃取脱脂粘结剂体系的相容性研究[J].陶瓷学报,2011,32(2):145-149.
[21] 易长海,余训民,许家瑞,等.水悬浮法制备玻璃纤维/聚氯乙烯树脂复合材料-悬浮液高分子粘结剂与基体相容性研究[J].江汉石油学院学报,2002,24(2):113-115.
[22] 张卫群,朱智敏.全瓷修复的粘结剂及粘结技术[J].国外医学:口腔医学分册,2004,31(4):314-316.
[23] Xi-xun Y,Fei L,Yuan-ting X,et al.In vitro study in the endothelial cell compatibility and endothelialization of genipin-crosslinked biological tissues for tissue-engineered vascular scaffolds.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010; 21(2): 777-785.
[24] Ode PJ,Crompton DS.Compatibility of aphid resistance in soybean and biological control by the parasitoid Aphidius colemani (Hymenoptera: Braconidae).Biol Control. 2013; 64(3):255-262.
[25] Cheuk KKL,Li BS,Lam JWY,et al.Synthesis, chain helicity, assembling structure, and biological compatibility of poly(phenylacetylene)s containing L-alanine moieties. Macromolecules.2008;41(16):5997-6005.
[26] 姜涛.口腔用湿性粘结剂(UB-1)的研制及粘结性能检测[D].吉林大学,2004.
[27] 黄哲玮,薛淼.口腔材料的生物相容性(Ⅱ)[J].口腔材料器械杂志, 2009,18(4):210-220.
[28] Gioka C,Bourauel C,Hiskia A,et al.Light-cured or chemically cured orthodontic adhesive resins? A selection based on the degree of cure, monomer leaching, and cytotoxicity.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop.2005;127(4):413-419.
[29] Kaga M,Noda M,Ferracane JL, et al.The in vitro cytotoxicity of eluates from dentin bonding resins and their effect on tyrosine phosphorylation of L929 cells. Dent Mater. 2001; 17 (4): 333-339.
[30] 石平.口腔材料细胞毒性评价方法的研究进展[J].中国美容医学, 2014,23(14):1222-1224.
[31] 赵云刚,高翔.口腔科材料引起变态反应3例分析[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2010,19(24):3080-3081.
[32] Danti S,Ciofani G,Moscato S,et al.Boron nitride nanotubes and primary human osteoblasts: In vitro compatibility and biological interactions under low frequency ultrasound stimulation.Nanotechnology.2013;24(46):465102.
[33] Franz A,Koenig F,Lucas T,et al.Cytotoxic Effects Of Dental Bonding Substances As A Function Of Degree Of Conversion. Dent Mater.2009;25(2):232-239.
[34] 黄哲玮,薛淼.口腔材料的生物相容性[J].口腔材料器械杂志, 2009,18(3):156-161.
[35] Denisova LA,Maev RG,Leontjeu VK,et al.A study of the adhesion between dental cement and dentin using a nondestructive acoustic microscopy approach.Dent Mater. 2009;25(5):557-565.
[36] 廖伟,周年苟,扈祚文,等.不同口腔修复材料生物相容性及3种材料充填恒磨牙邻面龋的临床验证[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(8):1467-1470.
[37] Ertl K,Graf A,Watts D,et al.Stickiness of dental resin composite materials to steel, dentin and bonded dentin.Dent Mater.2010;26(1):59.
[38] Aboushelib MN,Mirmohamadi H,Matinlinna JP,et al. Innovations in bonding to zirconia-based materials. Part II: Focusing on chemical interactions.Dent Mater. 2009; 25(8): 947-951.
[39] Robert L.Erickson.The role of etching in bonding to enamel: A comparison of self-etching and etch-and-rinse adhesive systems. Dent Mater.2009;25(11):1459.
[40] 李伟,周京琳.代谢组学用于生材材料分子相容性评价的可能性[C].//第七次全国口腔材料学术交流会论文集,2011:17-18. |