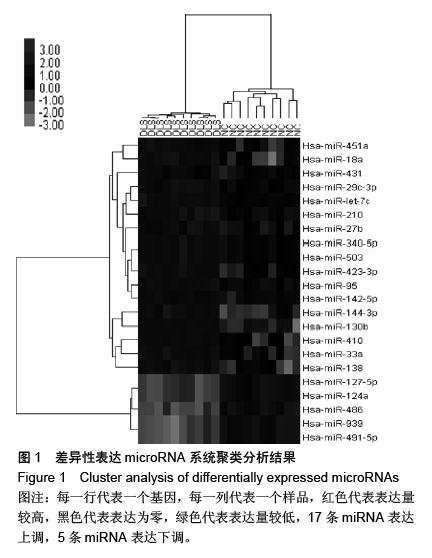
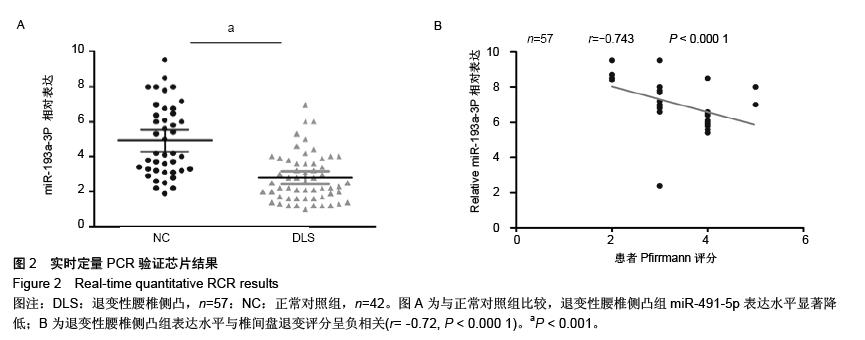
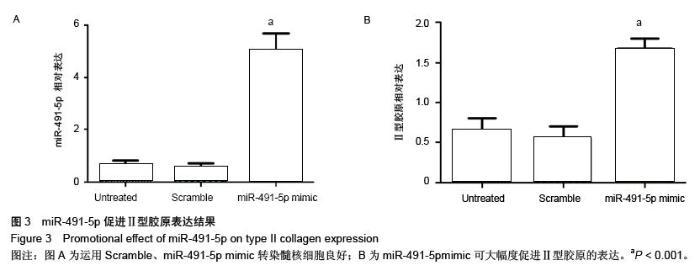
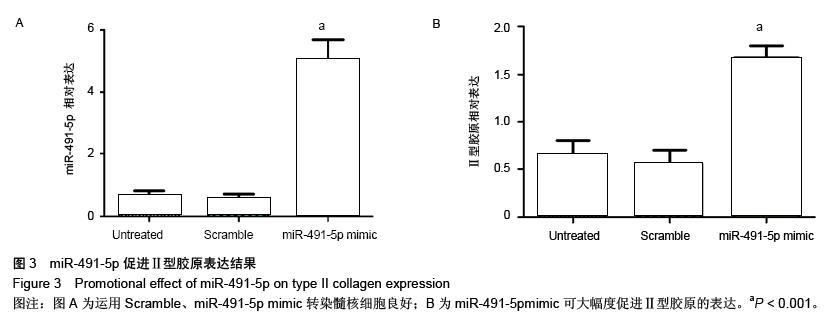
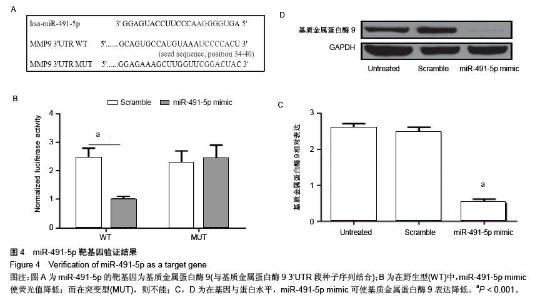
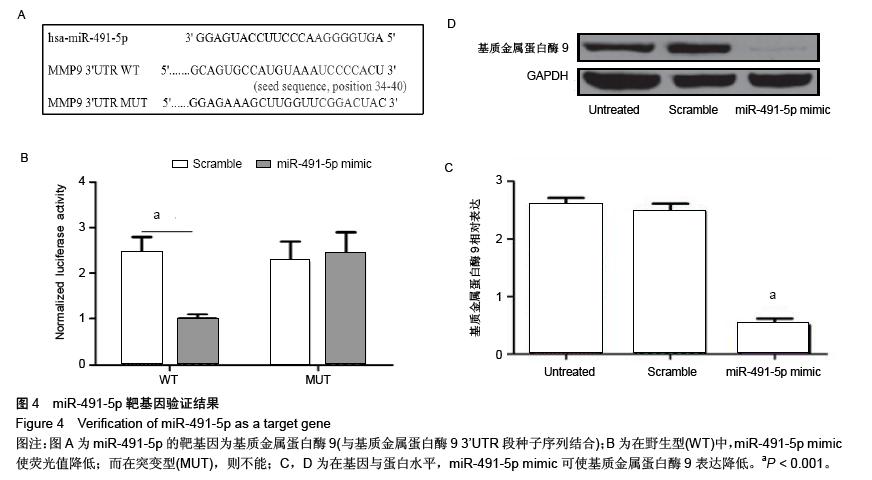
| [1] 郑杰,杨永宏,楼肃亮,等.退变性脊柱侧弯的生物力学有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(30):5490-5496.
[2] Schwab F, Dubey A, Gamez L, et al.Adult scoliosis: prevalence, SF-36, and nutritional parameters in an elderly volunteer population. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(9): 1082-1085.
[3] 喻林,石志才,白玉树,等.骨水泥加强长节段钉棒置入治疗伴骨质疏松症的退变性脊柱侧弯22例[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008, 12(35): 6963-6967.
[4] Schwab F, Patel A, Ungar B, et al. Adult spinal deformitypostoperative standing imbalance: how much can you tolerate? An overview of key parameters in assessing alignment and planning corrective surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2010;35(25):2224-2231.
[5] 孙郁雨,崔志明,保国锋,等. MAST QUADRANT 可扩张管下单侧椎弓根钉置入与椎体间融合治疗腰椎退变性疾病[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(39):7311-7314.
[6] Schwab FJ, Blondel B, Bess S, et al. Radiographical spinopelvic parameters and disability in the setting of adult spinal deformity. A prospective multicenter analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(13):E803-812.
[7] Richardson SM, Doyle P, Minogue BM,et al.Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinase-10, nerve growth factor and substance P in the painful degenerate intervertebral disc. Arthritis Res Ther.2009;11(4): R126
[8] Li Z, Yu X, Shen J, et al. MicroRNA in intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Prolif.2015;48(3):278-283.
[9] Wang HQ, Yu XD, Liu ZH, et al.Deregulated miR-155 promotes Fas-mediated apoptosis in human intervertebral disc degeneration by targeting FADD and caspase-3. J Pathol.2011;225(2):232-242.
[10] Gu SX, Li X, Hamilton JL,et al.MicroRNA-146a reduces IL-1 dependent inflammatory responses in the intervertebral disc. Gene.2015;555(2): 80-87.
[11] Yu X, Li Z, Shen J, et al.MicroRNA-10b promotes nucleus pulposus cell proliferation through RhoC-Akt pathway by targeting HOXD10 in intervetebral disc degeneration. PLoS One. 2013;8(12): e83080.
[12] Gandhi R, Healy B, Gholipour T, et al. Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers for disease staging in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol.2013;73(6):729-740.
[13] Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM,et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.2008;105(30):10513-10518.
[14] Santa-Maria I, Alaniz ME, Renwick N, et al. Dysregulation of microRNA-219 promotes neurodegeneration through post-transcriptional regulation of tau. J Clin Invest.2015; 125(2):681-686.
[15] Ng EK, Chong WW, Jin H, et al. Differential expression of microRNAs in plasma of patients with colorectal cancer: a potential marker for colorectal cancer screening. Gut.2009; 58(10):1375-1381.
[16] Carlsen AL, Schetter AJ, Nielsen CT, et al. Circulating microRNA expression profiles associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum.2013;65(5): 1324-1334.
[17] Xiao B, Wang Y, Li W, et al.Plasma microRNA signature as a noninvasive biomarker for acute graft-versus-host disease. Blood.2013;122(19): 3365-3375.
[18] Zhao Q, Zhai YX, Liu HQ, et al. MicroRNA-491-5p suppresses cervical cancer cell growth by targeting hTERT. Oncol Rep. 2015 May 28. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.4013. [Epub ahead of print]
[19] Denoyelle C, Lambert B, Meryet-Figuière M, et al.miR-491-5p-induced apoptosis in ovarian carcinoma depends on the direct inhibition of both BCL-XL and EGFR leading to BIM activation. Cell Death Dis. 2014;9(5):e1445.
[20] Huang WC, Chan SH, Jang TH, et al. miRNA-491-5p and GIT1 serve as modulators and biomarkers for oral squamous cell carcinoma invasion and metastasis. Cancer Res.2014; 74(3): 751-764.
[21] Yuan M, Zhan Q, Duan X, et al. A functional polymorphism at miR-491-5p binding site in the 3'-UTR of MMP-9 gene confers increased risk for atherosclerotic cerebral infarction in a Chinese population. Atherosclerosis.2013;226(2): 447-452. |