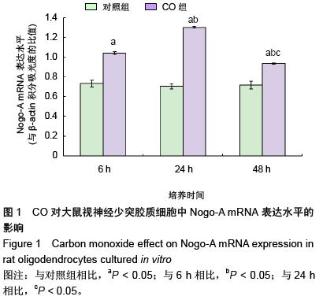
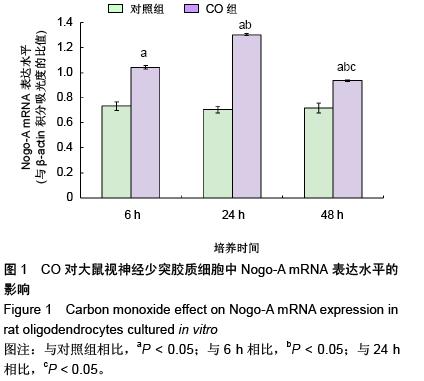
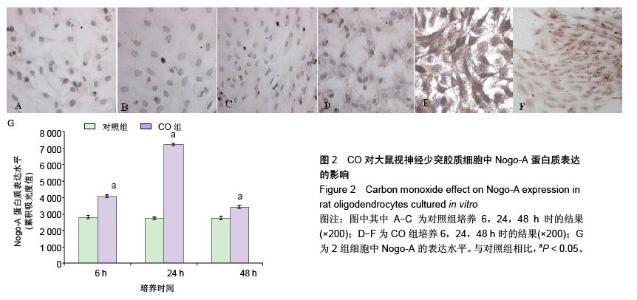
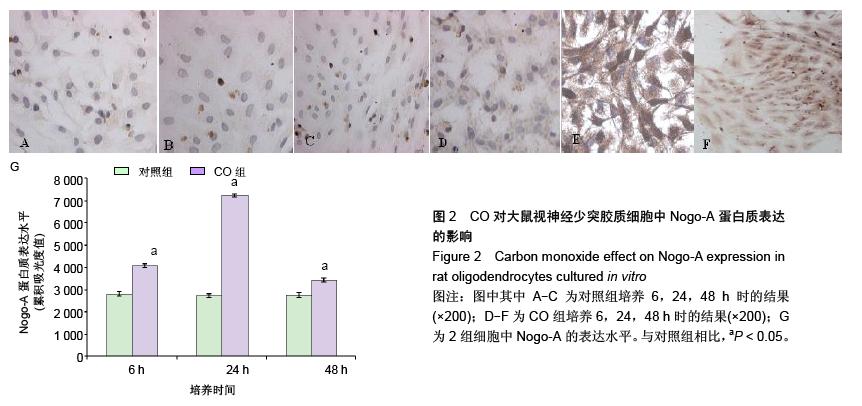
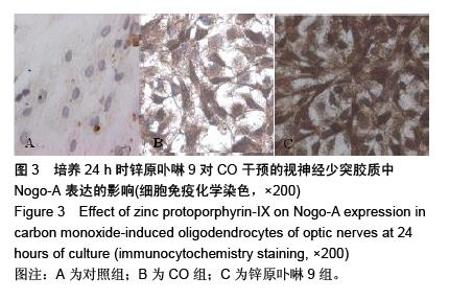
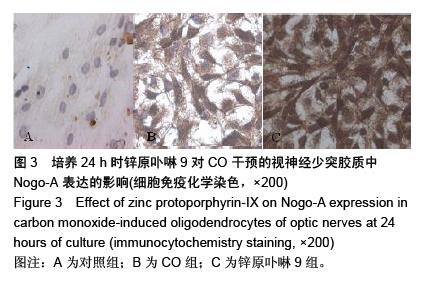
| [1] Sykes OT, Walker E. The neurotoxicology of carbon monoxide- Historical perspective and review. Cortex. 20155. in press.[2] Geraldo AF, Silva C, Neutel D, et al. Delayed leukoencephalopathy after acute carbon monoxide intoxication. J Radiol Case Rep. 2014;8(5):1-8. [3] Wu PE, Juurlink DN. Carbon monoxide poisoning. CMAJ. 2014;186(8):611. [4] Pernet V, Schwab ME. The role of Nogo-A in axonal plasticity, regrowth and repair. Cell Tissue Res. 2012;349(1):97-104. [5] Wang T, Xiong JQ, Ren XB, et al. The role of Nogo-A in neuroregeneration: a review. Brain Res Bull. 2012;87(6): 499-503. [6] Saha N, Kolev M, Nikolov DB. Structural features of the Nogo receptor signaling complexes at the neuron/myelin interface. Neurosci Res. 2014;87:1-7. [7] Leffler CW, Parfenova H, Jaggar JH. Carbon monoxide as an endogenous vascular modulator. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011;301(1):H1-H11. [8] 朱艳玲.外源性一氧化碳对体外培养星型胶质细胞血红素加氧酶系统的影响[D].大连:大连医科大学,2006.[9] 赵林岩,李芳,王苏平,等.一氧化碳中毒迟发性脑病小鼠脑HO-1表达变化及其与细胞凋亡的关系[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2014,32(6): 711-715.[10] Haines DD, Lekli I, Teissier P, et al. Role of haeme oxygenase-1 in resolution of oxidative stress-related pathologies: focus on cardiovascular, lung, neurological and kidney disorders. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2012;204(4): 487-501.[11] 王苏平,朱艳玲,王晓虹.血红素加氧酶系统与缺血性脑损伤[J].国际神经病学神经外科学杂志,2009,36(6):511-514.[12] Rochette L, Cottin Y, Zeller M, et al. Carbon monoxide: mechanisms of action and potential clinical implications. Pharmacol Ther. 2013;137(2):133-152.[13] 王晓虹,王苏平,车菊华,等.大鼠视神经少突胶质细胞培养方法的改良[J].转化医学杂志,2014,3(6):4.[14] Peng X, Liu S, Ye J, et al. Downregulation of Nogo-A expression of oligodendrocytes in vitro with antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Yan Ke Xue Bao. 2003;19(3): 195-200.[15] Baumann N, Pham-Dinh D. Biology of oligodendrocyte and myelin in the mammalian central nervous system. Physiol Rev. 2001;81(2):871-927.[16] Fumagalli M, Daniele S, Lecca D, et al. Phenotypic changes, signaling pathway, and functional correlates of GPR17- expressing neural precursor cells during oligodendrocyte differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(12): 10593-10604.[17] 胡建国,陆佩华,徐晓明.少突胶质细胞生物学功能与相关疾病研究进展[J].生理科学进展,2004,35(1):39-41.[18] Chen ZJ, Ughrin Y, Levine JM. Inhibition of axon growth by oligodendrocyte precursor cells. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2002; 20(1):125-139.[19] Son YJ.Synapsing with NG2 cells (polydendrocytes), unappreciated barrier to axon regeneration? Neural Regen Res. 2015; 10 (3): 346-348.[20] Kempf A, Schwab ME. Nogo-A represses anatomical and synaptic plasticity in the central nervous system. Physiology (Bethesda). 2013;28(3):151-163.[21] Schwab ME, Strittmatter SM. Nogo limits neural plasticity and recovery from injury. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2014;27:53-60.[22] Peng X, Zhou Z, Hu J, et al. Soluble Nogo receptor down-regulates expression of neuronal Nogo-A to enhance axonal regeneration. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(4):2783-2795.[23] Wang JW, Yang JF, Ma Y, et al.Nogo-A expression dynamically varies after spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2015; 10(2): 225-229.[24] Fournier AE, Gould GC, Liu BP, et al. Truncated soluble Nogo receptor binds Nogo-66 and blocks inhibition of axon growth by myelin. J Neurosci. 2002;22(20):8876-8883.[25] Liu BP, Fournier A, GrandPré T, et al. Myelin-associated glycoprotein as a functional ligand for the Nogo-66 receptor. Science. 2002;297(5584):1190-1193.[26] Zagrebelsky M, Korte M. Maintaining stable memory engrams: new roles for Nogo-A in the CNS. Neuroscience. 2014;283: 17-25.[27] Hayakawa N, Kato H, Araki T. Age-related changes of astorocytes, oligodendrocytes and microglia in the mouse hippocampal CA1 sector. Mech Ageing Dev. 2007;128(4): 311-316.[28] 刘苹,彭锡嘉,叶剑,等.新生大鼠视神经少突胶质细胞原代培养及鉴定[J].重庆医学,2003,32(3):330-331.[29] Thom SR, Bhopale VM, Fisher D, et al. Delayed neuropathology after carbon monoxide poisoning is immune-mediated. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101(37): 13660-13665.[30] 项文平,张帆,薛慧,等.大鼠急性一氧化碳中毒迟发性脑病的发病机制及鼠神经生长因子早期干预防治作用的研究[J].中国药学杂志,2013,(24):2123-2127.[31] 孙瑞佼,郭大志,李航,等.急性一氧化碳中毒对大鼠少突胶质前体细胞的影响[J].中国康复,2015(1):10-13.[32] 王晓虹,王虹,车菊华,等.神经节苷脂对体外培养一氧化碳损伤少突胶质细胞Nogo-A的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(6): 945-949.[33] Aztatzi-Santillán E, Nares-López FE, Márquez-Valadez B, et al. The protective role of heme oxygenase-1 in cerebral ischemia. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2010;10(4): 310-316.[34] 曹立平,张治中,白文,等.血红素加氧酶1基因多态性与老年缺血性卒中预后的关系[J].中国脑血管病杂志,2013,10(11):566-570.[35] Panahian N, Yoshiura M, Maines MD. Overexpression of heme oxygenase-1 is neuroprotective in a model of permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in transgenic mice. J Neurochem. 1999;72(3):1187-1203.[36] Bidmon HJ, Emde B, Oermann E, et al. Heme oxygenase-1 (HSP-32) and heme oxygenase-2 induction in neurons and glial cells of cerebral regions and its relation to iron accumulation after focal cortical photothrombosis. Exp Neurol. 2001;168(1):1-22.[37] Dulak J, Józkowicz A. Carbon monoxide -- a "new" gaseous modulator of gene expression. Acta Biochim Pol. 2003; 50(1): 31-47.[38] 汪涛,王苏平,王晓虹,等.内源性一氧化碳致PC12细胞凋亡的实验研究[J].中风与神经疾病杂志,2008,25(3):359-360.[39] Morita T, Kourembanas S. Endothelial cell expression of vasoconstrictors and growth factors is regulated by smooth muscle cell-derived carbon monoxide. J Clin Invest. 1995; 96(6):2676-2682. |