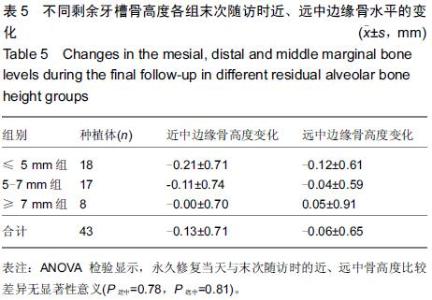
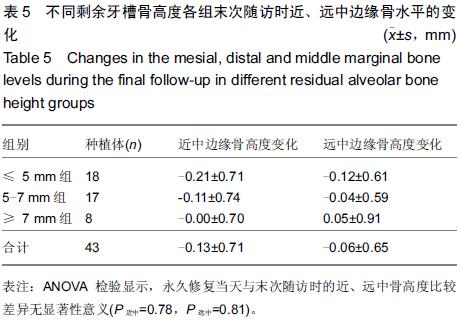
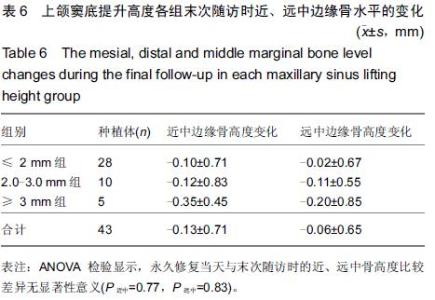
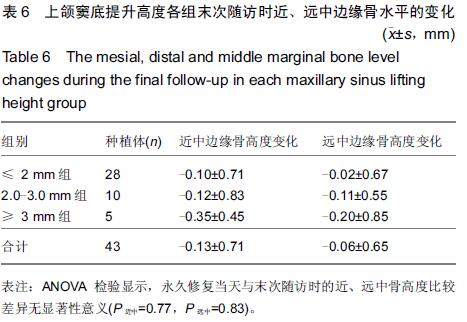
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (47): 7575-7582.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.47.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application of concentrated growth factor in maxillary sinus lift: variation in peri-implant bone levels
Huang Na, Wu Feng, Li Ping, Liu Zi-ping, Lin Ju, Tang You-chao, Wang Yuan-qin
- Huizhou Stomatological Hospital, School of Medicine, Jinan University, Huizhou 516000, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2015-08-31Online:2015-11-19Published:2015-11-19 -
Contact:Wang Yuan-qin, Chief physician, Huizhou Stomatological Hospital, School of Medicine, Jinan University, Huizhou 516000, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Huang Na, Master, Attending physician, Huizhou Stomatological Hospital, School of Medicine, Jinan University, Huizhou 516000, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Plan Project of Huizhou City in 2014, No. 2014Y112
Cite this article
Huang Na, Wu Feng, Li Ping, Liu Zi-ping, Lin Ju, Tang You-chao, Wang Yuan-qin. Application of concentrated growth factor in maxillary sinus lift: variation in peri-implant bone levels[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(47): 7575-7582.
share this article
| [1] Dohan Ehrenfest DM,Rasmusson L,Albrektsson T. Classification of platelet concentrates: From pure platelet-rich plasma (p-prp) to leucocyte-and platelet-rich fibrin (l-prf). Trends Biotechnol.2009;27(3):158-167. [2] Cochran DL,Buser D,Ten Bruggenkate CM,et al.The use of reduced healing times on iti® implants with a sandblasted and acid-etched (sla) surface. Clin Oral Implants Res.2002;13(2): 144-153.
[3] Lindh C,Petersson A,Rohlin M.Assessment of the trabecular pattern before endosseous implant treatment: Diagnostic outcome of periapical radiography in the mandible. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod.1996;82(3):335-343.
[4] Summers RB.The osteotome technique: Part 3--less invasive methods of elevating the sinus floor. Compendium. 1994; 15(6):698, 700.
[5] Nedir R,Bischof M,Vazquez L,et al.Osteotome sinus floor elevation without grafting material: A 1‐year prospective pilot study with iti implants.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006; 17(6): 679-686.
[6] Rosen PS,Summers R,Mellado JR,et al.The bone-added osteotome sinus floor elevation technique : Multicenter retrospective report of consecutively treated patients. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.1999;14(6):853-858.
[7] 符志锋,郭庆平,繆颖.上颌窦内外提升不植骨替代材料同期种植牙:随访周围骨量及稳定性的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2015, 19(3): 394-398.
[8] Palma VC,Magro-Filho O,de Oliveria JA,et al.Bone reformation and implant integration following maxillary sinus membrane elevation: An experimental study in primates.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res.2006;8(1):11-24.
[9] Lundgren S,Anderson S,Gualini F,et al.Bone reformation with sinus membrane elevation: A new surgical technique for maxillary sinus floor augmentation.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res.2004;6(3):165-173.
[10] Hatano N, Sennerby L, Lundgren S. Maxillary sinus augmentation using sinus membrane elevation and peripheral venous blood for implant‐supported rehabilitation of the atrophic posterior maxilla: Case series.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res.2007;9(3): 150-155.
[11] Sohn DS,Kim WS,An KM,et al.Comparative histomorphometric analysis of maxillary sinus augmentation with and without bone grafting in rabbit.Implant Dent.2010;19(3): 259-270.
[12] Esposito M,Grusovin MG,Rees J,et al.Effectiveness of sinus lift procedures for dental implant rehabilitation: A cochrane systematic.Eur J Oral Implantol.2010; 3(1): 7-26.
[13] Si MS,Mo JJ,Zhuang LF,et al.Osteotome sinus floor elevation with and without grafting: An animal study in labrador dogs.Clin Oral Implants Res.2013;26(2):197-203.
[14] Rodella LF,Favero G,Boninsegna R,et al.Growth factors, cd34 positive cells, and fibrin network analysis in concentrated growth factors fraction. Microsc Res Tech.2011; 74(8):772-777.
[15] 柳宏志,邹高峰,王天祥,等.浓缩生长因子促进犬软组织损伤修复的实验研究[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2013,23(1):28-31.
[16] Dohan DM.Platelet-rich fibrin (prf): A second-generation platelet concentrate. Part i: Technological concepts and evolution.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006;101(3):e37-44.
[17] Choukroun J,Diss A,Simonpieri A,et al.Platelet-rich fibrin (prf): A second-generation platelet concentrate. Part iv: Clinical effects on tissue healing. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod.2006;101(3):e56-e60.
[18] Kim TH,Kim SH,Sándor GK,et al.Comparison of platelet-rich plasma (prp), platelet-rich fibrin (prf), and concentrated growth factor (cgf) in rabbit-skull defect healing.Arch Oral Biol.2014;59(5):550-558.
[19] Choukroun J. Platelet-rich fibrin (prf): A second-generation platelet concentrate. Part v: Histologic evaluations of prf effects on bone allograft maturation in sinus lift.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod.2006;101(3):299-303.
[20] Sohn DS.Bone regeneration in the maxillary sinus using an autologous fibrin-rich block with concentrated growth factors alone.Implant Dent.2011;20(5):389-395.
[21] Kim JM.Minimally invasive sinus augmentation using ultrasonic piezoelectric vibration and hydraulic pressure: A multicenter retrospective study. Implant Dent. 2012; 21(6):536-542.
[22] Tan WC,Lang NP,Zwahlen M,et al.A systematic review of the success of sinus floor elevation and survival of implants inserted in combination with sinus floor elevation. Part ii: Transalveolar technique.J Clin Periodontol.2008;35(8 Suppl):241-254.
[23] Reiser GM,Rabinovitz Z,Bruno J,et al.Evaluation of maxillary sinus membrane response following elevation with the crestal osteotome technique in human cadavers. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2001;16(6):833-840.
[24] Nkenke E,Schlegel A,Schultze-Mosgau S,et al.The endoscopically controlled osteotome sinus floor elevation: A preliminary prospective study.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2001; 17(4):557-566.
[25] Nkenke E,Schlegel A,Schultze-Mosgau S,et al.The endoscopically controlled osteotome sinus floor elevation: A preliminary prospective study.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2002;17(4):557-566.
[26] Doud Galli SK,Lebowitz RA,Giacchi RJ,et al.Chronic sinusitis complicating sinus lift surgery.Am J Rhinol.2001;15(3):181-186.
[27] Cavicchia F,Bravi F,Petrelli G.Localized augmentation of the maxillary sinus floor through a coronal approach for the placement of implants.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2001;21(5): 475-485.
[28] Abrahamsson I,Berglundh T.Tissue characteristics at microthreaded implants: An experimental study in dogs.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res.2006;8(3):107-113.
[29] Diss A,Dohan DM,Mouhyi J,et al.Osteotome sinus floor elevation using choukroun's platelet-rich fibrin as grafting material: A 1-year prospective pilot study with microthreaded implants.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008; 105(5):572–579.
[30] Toffler M.Osteotome-mediated sinus floor elevation using only platelet-rich fibrin: An early report on 110 patients.Implant Dent.2010;19(5):447-456.
[31] Kanayama T,Sigetomi T,Sato H,et al.Crestal approach sinus floor elevation in atrophic posterior maxilla using only platelet rich fibrin as grafting material: A computed tomography evaluation of 2 cases. J Oral MaxillofacSurgery Med Pathol.2013.
[32] Choukroun J.Platelet-rich fibrin (prf): A second-generation platelet concentrate. Part iv: Clinical effects on tissue healing. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod.2006; 101(3):e56-e60.
[33] Sohn DS,Heo JU,Kwak DH,et al.Bone regeneration in the maxillary sinus using an autologous fibrin-rich block with concentrated growth factors alone.Implant Dent.2011;20(5):389-395.
[34] Tajima N.Evaluation of sinus floor augmentation with simultaneous implant placement using platelet-rich fibrin as sole grafting material.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2013; 28(1):77-83.
[35] Simonpieri A,Choukroun J,Del CM,et al.Simultaneous sinus-lift and implantation using microthreaded implants and leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin as sole grafting material: A six-year experience.Implant Dent.2011;20(1):2-12.
[36] Toffler M.Osteotome-mediated sinus floor elevation: A clinical report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2004;19(2):266-273. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [12] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [13] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [14] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| [15] | Bi Qingwei, Liu Chengpu, Li Yan, Zhao Wenwen, Han Mei. Structure analysis of platelet-rich fibrin derived from two centrifugation procedures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3534-3539. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||