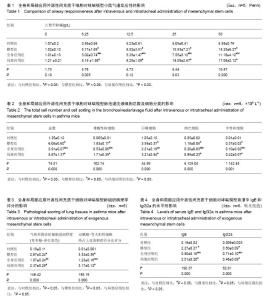
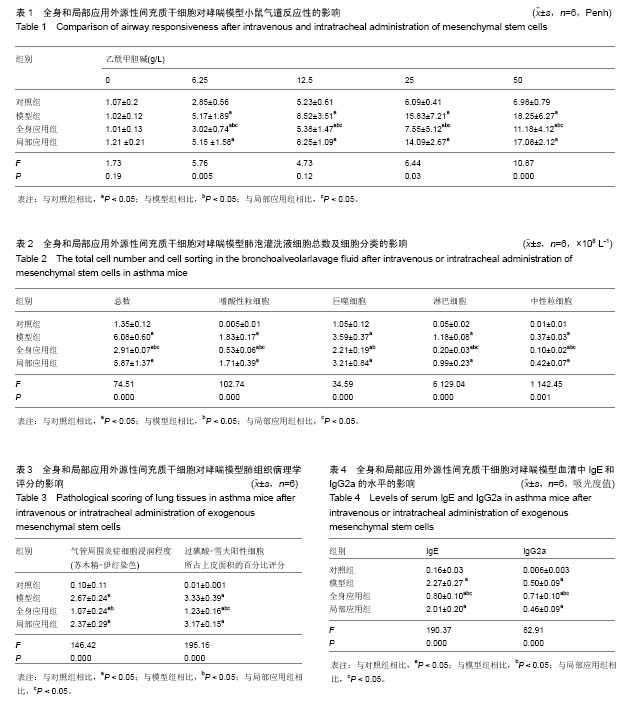
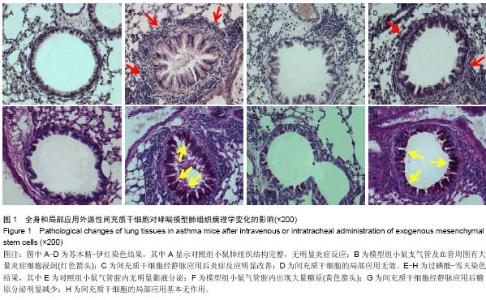
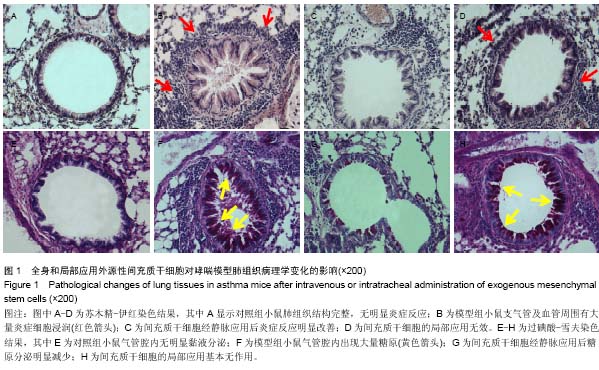
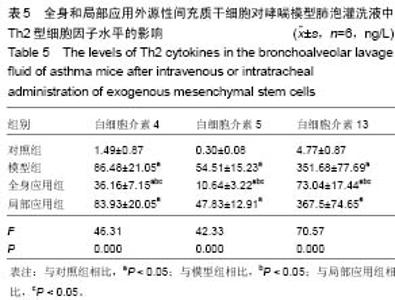
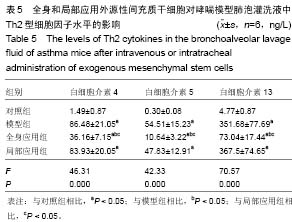
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (28): 4478-4484.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.28.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Intravenous versus intratracheal administration of mesenchymal stem cells in a mouse model of asthma
Yao Yin1, 2, Guo Jie-bo1, Deng Xue-quan1, 2, Sun Yue-qi1, 2, Fu Qing-ling1, 2
- 1Otorhinolaryngology Hospital, the First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China;
2Otorhinolaryngology Institute, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China
-
Online:2015-07-02Published:2015-07-02 -
Contact:Fu Qing-ling, M.D., Researcher, Otorhinolaryngology Hospital, the First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China; Otorhinolaryngology Institute, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Fu Qing-ling, M.D., Researcher, Otorhinolaryngology Hospital, the First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China; Otorhinolaryngology Institute, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程 -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81170896; the Science and Technology Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. 2012B031800045
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yao Yin, Guo Jie-bo, Deng Xue-quan, Sun Yue-qi, Fu Qing-ling. Intravenous versus intratracheal administration of mesenchymal stem cells in a mouse model of asthma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(28): 4478-4484.
share this article
| [1] Barnes PJ. Immunology of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(3):183-192. [2] Galli SJ, Tsai M, Piliponsky AM. The development of allergic inflammation. Nature. 2008;454(7203):445-454. [3] Di Nicola M, Carlo-Stella C, Magni M, et al. Human bone marrow stromal cells suppress T-lymphocyte proliferation induced by cellular or nonspecific mitogenic stimuli. Blood. 2002;99(10):3838-3843. [4] Corcione A, Benvenuto F, Ferretti E, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate B-cell functions. Blood. 2006;107(1):367-372. [5] Sotiropoulou PA, Perez SA, Gritzapis AD, et al. Interactions between human mesenchymal stem cells and natural killer cells. Stem Cells. 2006;24(1):74-85. [6] Sun YQ, Deng MX, He J, et al. Human pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells prevent allergic airway inflammation in mice. Stem Cells. 2012;30(12):2692-2699. [7] 李斌恺,赖克方,洪燕华,等.支气管哮喘小鼠气道反应性无创检测方法的建立[J].国际呼吸杂志,2009,29(1):5-8. [8] Baïz N, Annesi-Maesano I. Is the asthma epidemic still ascending? Clin Chest Med. 2012;33(3):419-429. [9] Eder W, Ege MJ, von Mutius E. The asthma epidemic. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(21):2226-2235. [10] Orihara K, Dil N, Anaparti V, et al. What's new in asthma pathophysiology and immunopathology? Expert Rev Respir Med. 2010;4(5):605-629. [11] Fahy JV. Type 2 inflammation in asthma--present in most, absent in many. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015;15(1):57-65. [12] Papaioannou AI, Kostikas K, Zervas E, et al. Control of asthma in real life: still a valuable goal? Eur Respir Rev. 2015; 24(136):361-369. [13] In 't Anker PS, Scherjon SA, Kleijburg-van der Keur C, et al. Isolation of mesenchymal stem cells of fetal or maternal origin from human placenta. Stem Cells. 2004;22(7):1338-1345. [14] Gronthos S, Mankani M, Brahim J, et al. Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(25):13625-13630. [15] Nadri S, Soleimani M. Comparative analysis of mesenchymal stromal cells from murine bone marrow and amniotic fluid. Cytotherapy. 2007;9(8):729-737. [16] Keating A. Mesenchymal stromal cells: new directions. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;10(6):709-716. [17] Kim N, Cho SG. New strategies for overcoming limitations of mesenchymal stem cell-based immune modulation. Int J Stem Cells. 2015;8(1):54-68. [18] Prockop DJ. Concise review: two negative feedback loops place mesenchymal stem/stromal cells at the center of early regulators of inflammation. Stem Cells. 2013;31(10): 2042- 2046. [19] Ahmad T, Mukherjee S, Pattnaik B, et al. Miro1 regulates intercellular mitochondrial transport & enhances mesenchymal stem cell rescue efficacy. EMBO J. 2014; 33(9):994-1010. [20] Nemeth K, Keane-Myers A, Brown JM, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells use TGF-beta to suppress allergic responses in a mouse model of ragweed-induced asthma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(12):5652-5657. [21] François M, Galipeau J. New insights on translational development of mesenchymal stromal cells for suppressor therapy. J Cell Physiol. 2012;227(11):3535-3538. [22] Weiss DJ. Stem cells, cell therapies, and bioengineering in lung biology and diseases. Comprehensive review of the recent literature 2010-2012. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2013;10(5): S45-97. [23] Bonfield TL, Koloze M, Lennon DP, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells suppress chronic airway inflammation in the murine ovalbumin asthma model. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010;299(6):L760-770. [24] 韩灵,孙悦奇,付清玲,等.呼吸道变应性炎性反应小鼠模型的建立[J].中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志,2013,48(3):224-228. [25] Abreu SC, Antunes MA, de Castro JC, et al. Bone marrow-derived mononuclear cells vs. mesenchymal stromal cells in experimental allergic asthma. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2013;187(2):190-198. [26] Lee RH, Pulin AA, Seo MJ, et al. Intravenous hMSCs improve myocardial infarction in mice because cells embolized in lung are activated to secrete the anti-inflammatory protein TSG-6. Cell Stem Cell. 2009;5(1):54-63. [27] Islam MN, Das SR, Emin MT, et al. Mitochondrial transfer from bone-marrow-derived stromal cells to pulmonary alveoli protects against acute lung injury. Nat Med. 2012;18(5): 759-765. [28] Galipeau J. The mesenchymal stromal cells dilemma--does a negative phase III trial of random donor mesenchymal stromal cells in steroid-resistant graft-versus-host disease represent a death knell or a bump in the road? Cytotherapy. 2013;15(1): 2-8. [29] Kretlow JD, Jin YQ, Liu W, et al. Donor age and cell passage affects differentiation potential of murine bone marrow-derived stem cells. BMC Cell Biol. 2008;9:60. [30] Weiss DJ, Bertoncello I, Borok Z, et al. Stem cells and cell therapies in lung biology and lung diseases. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2011;8(3):223-272. [31] Kips JC, Anderson GP, Fredberg JJ, et al. Murine models of asthma. Eur Respir J. 2003;22(2):374-382. [32] Gao P, Zhou Y, Xian L, et al. Functional effects of TGF-β1 on mesenchymal stem cell mobilization in cockroach allergen-induced asthma. J Immunol. 2014;192(10): 4560-4570. [33] Cho KS, Park HK, Park HY, et al. IFATS collection: Immunomodulatory effects of adipose tissue-derived stem cells in an allergic rhinitis mouse model. Stem Cells. 2009; 27(1):259-265. [34] Su WR, Zhang QZ, Shi SH, et al. Human gingiva-derived mesenchymal stromal cells attenuate contact hypersensitivity via prostaglandin E2-dependent mechanisms. Stem Cells. 2011;29(11):1849-1860. [35] Lewkowich IP, Herman NS, Schleifer KW, et al. CD4+CD25+ T cells protect against experimentally induced asthma and alter pulmonary dendritic cell phenotype and function. J Exp Med. 2005;202(11):1549-1561. [36] Pellerin L, Jenks JA, Bégin P, et al. Regulatory T cells and their roles in immune dysregulation and allergy. Immunol Res. 2014;58(2-3):358-368. [37] Cho KS, Park MK, Kang SA, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells ameliorate allergic airway inflammation by inducing regulatory T cells in a mouse model of asthma. Mediators Inflamm. 2014; 2014:436476. [38] 李建国,颛孙永勋,冉丕鑫,等.骨髓间充质干细胞对哮喘小鼠CD4+CD25+调节性T细胞及气道炎症的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(47):9302-9305. [39] Ge X, Bai C, Yang J, et al. Intratracheal transplantation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells reduced airway inflammation and up-regulated CD4?CD25? regulatory T cells in asthmatic mouse. Cell Biol Int. 2013; 37(7):675-686. [40] Ge X, Bai C, Yang J, et al. Effect of mesenchymal stem cells on inhibiting airway remodeling and airway inflammation in chronic asthma. J Cell Biochem. 2013;114(7):1595-1605. [41] Kapoor S, Patel SA, Kartan S, et al. Tolerance-like mediated suppression by mesenchymal stem cells in patients with dust mite allergy-induced asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 129(4):1094-1101.
|
| [1] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [2] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [3] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [4] | Gu Xia, Zhao Min, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Relationship between hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha and hypoxia signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1284-1289. |
| [5] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [6] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [7] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [8] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [9] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [10] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [11] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [12] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [13] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [14] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [15] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||